
Name the simplest ketones and write its molecular formula. What do we call the self-linking property of carbon?
Answer
503.4k+ views
Hint: Ketones are the organic functional groups, which contain a carbon having double bonds with one oxygen atom, and the other two bonds are with different groups. These two different groups may be the same, may be different, may be aryl or may be alkyl. However in case of ketones the different groups cannot be hydrogen.
Complete answer:
In organic chemistry, we have several functional groups. These functional groups are responsible for changes in the physical, chemical properties of the molecules.
Among all the functional groups few functional groups have carbon in them with oxygen, such functional groups are named carbonyl functional groups. Today we have three types of carbonyl functional groups namely, (i) aldehydes, (ii) ketones, (iii) carboxylic acids.
In ketones, the carbon forms a double bond with oxygen and two single bonds with different groups. These groups are any group other than hydrogen. As with both groups to be hydrogen we can identify them as aldehydes or ketones or alcohols.
The simplest ketone is acetone or named by I.U.P.A.C as Propan $2$ one. The structure of acetone is as follows,
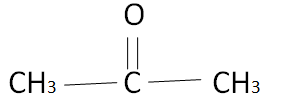
The self-linking property of carbon is known as catenation. Due to this phenomenon, carbon atoms link together and form a series called a homologous series. In the series iff the number of carbon is one then it is termed as meth, two carbons eth, three carbons prop, and so on.
Note:
The carbonyl groups are almost the same in structural representation but differ in other physical and chemical properties. In aldehydes, the group is $ - CHO$ like $R - CHO$ . The ketones are represented as $R - CO - {R'}$ whereas carboxylic acid is represented as $R - COOH$ . It is to remember that alcohol also forms a direct bond with carbon.
Complete answer:
In organic chemistry, we have several functional groups. These functional groups are responsible for changes in the physical, chemical properties of the molecules.
Among all the functional groups few functional groups have carbon in them with oxygen, such functional groups are named carbonyl functional groups. Today we have three types of carbonyl functional groups namely, (i) aldehydes, (ii) ketones, (iii) carboxylic acids.
In ketones, the carbon forms a double bond with oxygen and two single bonds with different groups. These groups are any group other than hydrogen. As with both groups to be hydrogen we can identify them as aldehydes or ketones or alcohols.
The simplest ketone is acetone or named by I.U.P.A.C as Propan $2$ one. The structure of acetone is as follows,

The self-linking property of carbon is known as catenation. Due to this phenomenon, carbon atoms link together and form a series called a homologous series. In the series iff the number of carbon is one then it is termed as meth, two carbons eth, three carbons prop, and so on.
Note:
The carbonyl groups are almost the same in structural representation but differ in other physical and chemical properties. In aldehydes, the group is $ - CHO$ like $R - CHO$ . The ketones are represented as $R - CO - {R'}$ whereas carboxylic acid is represented as $R - COOH$ . It is to remember that alcohol also forms a direct bond with carbon.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




