
Name the lens which produces a virtual, magnified image. Draw ray diagrams to the image formation.
Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: Recall the properties of concave lens and convex lens. The magnification of the lens is the ratio of image height to the object height. The lens produces virtual images when the image is formed on the same side of the object.
Complete step by step answer:We know that the virtual image is the opposite of the real image, that is it cannot be seen on the screen. The image formed by the concave lens is always virtual, because the image is formed on the same side of the object from the lens. The convex lens produces a virtual image when the object is placed between the pole of the lens and first principle focus.
The image formed by a concave lens is never magnified. The convex lens produces magnified images when the object is placed between the first principal focus and pole of the lens.
Therefore, the image formed by the convex lens is virtual and magnified if it satisfies the above condition.
The following figure shows image formation by the convex lens.
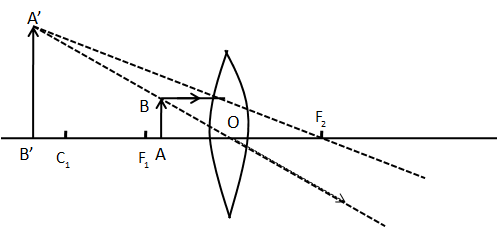
In the above ray diagram, AB is the height of object and A’B’ is the height of image, \[{F_1}\] is the first principal focus, \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{1}}}\] is the curvature of the lens and \[{{\text{F}}_2}\] is the second principal focus.
From the above ray diagram, we can say that the image is magnified and since it is formed on the same side of the object, we can say the image is virtual.
Note:Students should remember that the convex lens produces a real image if the object is placed beyond the first principle focus on the opposite side of the lens. It produces a virtual image if the object is at the right of the principal focus. The magnification of the lens is the ratio of image height to the object height. Since the image height is greater than the object height, the image will be magnified.
Complete step by step answer:We know that the virtual image is the opposite of the real image, that is it cannot be seen on the screen. The image formed by the concave lens is always virtual, because the image is formed on the same side of the object from the lens. The convex lens produces a virtual image when the object is placed between the pole of the lens and first principle focus.
The image formed by a concave lens is never magnified. The convex lens produces magnified images when the object is placed between the first principal focus and pole of the lens.
Therefore, the image formed by the convex lens is virtual and magnified if it satisfies the above condition.
The following figure shows image formation by the convex lens.

In the above ray diagram, AB is the height of object and A’B’ is the height of image, \[{F_1}\] is the first principal focus, \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{1}}}\] is the curvature of the lens and \[{{\text{F}}_2}\] is the second principal focus.
From the above ray diagram, we can say that the image is magnified and since it is formed on the same side of the object, we can say the image is virtual.
Note:Students should remember that the convex lens produces a real image if the object is placed beyond the first principle focus on the opposite side of the lens. It produces a virtual image if the object is at the right of the principal focus. The magnification of the lens is the ratio of image height to the object height. Since the image height is greater than the object height, the image will be magnified.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




