
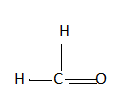
How would you name the following compound?

Answer
548.7k+ views
Hint:Naming a compound in organic is said to be nomenclature which we study in general organic chemistry. Identify the compound then look for the functional group. Identify if it has any double bonds or any triple bonds. Use the rules that are given to name a compound.
Complete step by step answer:
It is important for us to name a compound to put it into a certain category for a better study and characterisation of the compound. In organic chemistry nomenclature has certain rules which must be followed while naming a compound. Let’s take the example given above understand the rules and solve the question
RULE: 1
Identify the longest chain in the given compound. The longest chain is also known as ‘parent chain’.
RULE: 2
After identifying the parent chain, identify the groups present in the chain also known as substituent.
RULE: 3
Start numbering the carbons from where the substituent or group can get the lowest number. If a carbon has two different groups then write them in letter in alphabetical order.
RULE: 4
If the same group for example ‘$C{H_3}$ ‘ exists twice in the parent chain the location of that point is given where they are located. Also the number of how many times the group is present is indicated by a prefix (di, tri, and tetra).
RULE: 5
When the compound has more than one group the groups are named alphabetically. The prefixes used while naming the group are iso, for example isobutyl.
RULE: 6
If the parent chain has the same number of carbon, then the chain which has more side chains, lowest number of substituents, or the chain that has lowest branches are preferred.
RULE: 7
A ring hydrocarbon is denoted with cyclo which is written before the name of the compound.
RULE: 8
In case of unsaturated hydrocarbons, like alkene or alkynes the base name should end with –ene or –ane. Triple bonds are also named in this way, they have –yne added at the end of base name.
RULE: 9
The parent chain with multiple bonds is numbered in a way that the multiple bond gets the first number. Double or triple bonds have priority over other substituent groups. Always remember if there is a double and single bond present the lowest numbering is given to a double bond.
Now let’s name the compound given above, look for the parent chain. It has one carbon so for one carbon we say ‘meth’. It also has a double bond and a substituent as $'OH'$ . So the compound would be called ‘methanol’. We use $'Ol'$ as a suffix for alcohol.
Additional Information:
The base name refers to the number in the parent chain. The suffix decides the functional group of the compound. As mentioned above other groups are known as substituents.
Note:
In chemistry, nomenclature is assigned by the international union of pure and applied chemistry (IUPAC). Which is published in the blue book of organic chemistry. For simple molecules we use more common names rather than the name provided by the IUPAC. We use certain prefixes, suffixes and infixes to describe the name of the compound. Let’s revisit all the rules in one or two lines. First we identify then we give highest precedence, then identify the functional group, put the prefix and suffix.
Complete step by step answer:
It is important for us to name a compound to put it into a certain category for a better study and characterisation of the compound. In organic chemistry nomenclature has certain rules which must be followed while naming a compound. Let’s take the example given above understand the rules and solve the question
RULE: 1
Identify the longest chain in the given compound. The longest chain is also known as ‘parent chain’.
RULE: 2
After identifying the parent chain, identify the groups present in the chain also known as substituent.
RULE: 3
Start numbering the carbons from where the substituent or group can get the lowest number. If a carbon has two different groups then write them in letter in alphabetical order.
RULE: 4
If the same group for example ‘$C{H_3}$ ‘ exists twice in the parent chain the location of that point is given where they are located. Also the number of how many times the group is present is indicated by a prefix (di, tri, and tetra).
RULE: 5
When the compound has more than one group the groups are named alphabetically. The prefixes used while naming the group are iso, for example isobutyl.
RULE: 6
If the parent chain has the same number of carbon, then the chain which has more side chains, lowest number of substituents, or the chain that has lowest branches are preferred.
RULE: 7
A ring hydrocarbon is denoted with cyclo which is written before the name of the compound.
RULE: 8
In case of unsaturated hydrocarbons, like alkene or alkynes the base name should end with –ene or –ane. Triple bonds are also named in this way, they have –yne added at the end of base name.
RULE: 9
The parent chain with multiple bonds is numbered in a way that the multiple bond gets the first number. Double or triple bonds have priority over other substituent groups. Always remember if there is a double and single bond present the lowest numbering is given to a double bond.
Now let’s name the compound given above, look for the parent chain. It has one carbon so for one carbon we say ‘meth’. It also has a double bond and a substituent as $'OH'$ . So the compound would be called ‘methanol’. We use $'Ol'$ as a suffix for alcohol.
Additional Information:
The base name refers to the number in the parent chain. The suffix decides the functional group of the compound. As mentioned above other groups are known as substituents.
| NUMBER OF CARBONS | NAME |
| 1 | Meth |
| 2 | Eth |
| 3 | Prop |
| 4 | But |
| 5 | Pent |
| 6 | Hex |
| 7 | Hep |
| 8 | Oct |
| 9 | Non |
| 10 | Dec |
Note:
In chemistry, nomenclature is assigned by the international union of pure and applied chemistry (IUPAC). Which is published in the blue book of organic chemistry. For simple molecules we use more common names rather than the name provided by the IUPAC. We use certain prefixes, suffixes and infixes to describe the name of the compound. Let’s revisit all the rules in one or two lines. First we identify then we give highest precedence, then identify the functional group, put the prefix and suffix.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




