
Name a reagent which can distinguish between ethene and ethane.
Answer
564.9k+ views
Hint:The reagent reaction is a type of additional reaction.
Type of hydrocarbon does not undergo addition reactions.
Bromine water is a coloured solution which gets decolourized on reaction with the particular type of hydrocarbons.
Complete step by step answer:
Bromine test:
Bromine water used as a reagent.
Bromine water is known as bromide, bromine solution with the chemical formula $B{r_2}$. Bromine water is prepared by dissolving diatomic bromine and has high oxidizing properties and is obtained as a yellow mixture. ($B{r_2}$) in water (${H_2}O$).
This test is a type of addition reaction. The only non-metal which is in the liquid state is bromine. Bromine is said to have very good oxidizing property.
Bromine water can also be prepared in a chemical laboratory by mixing fumes of bromine with water.
The bromine water test is qualitative, used to identify the alkane or alkene functional groups present in the compound.
Alkane does not react with the bromine water solution and the dark yellow colour of bromine solution remains the same. Example: Ethane
${H_3}C - C{H_3} \to Noreaction$
Alkene undergoes an addition reaction. For example, ethene reacts with bromine water to give 1,2-dibromoethane.
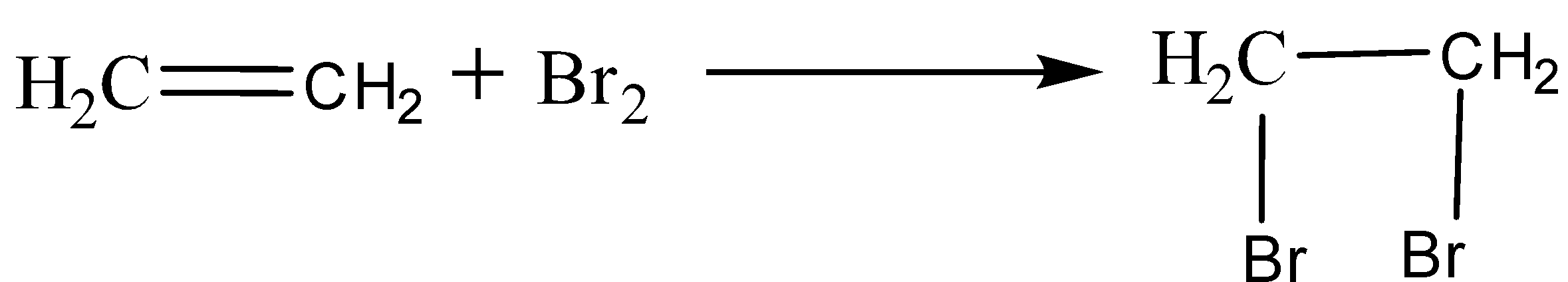
Alternative solution:
$KMn{O_4}$ solution:
Ethane does not react with alkaline $KMn{O_4}$, the purple colour of $KMn{O_4}$ and remains the same.
Ethene reacts with alkaline $KMn{O_4}$, it oxidizes ethene to give ethane 1,2-diol (ethylene glycol).
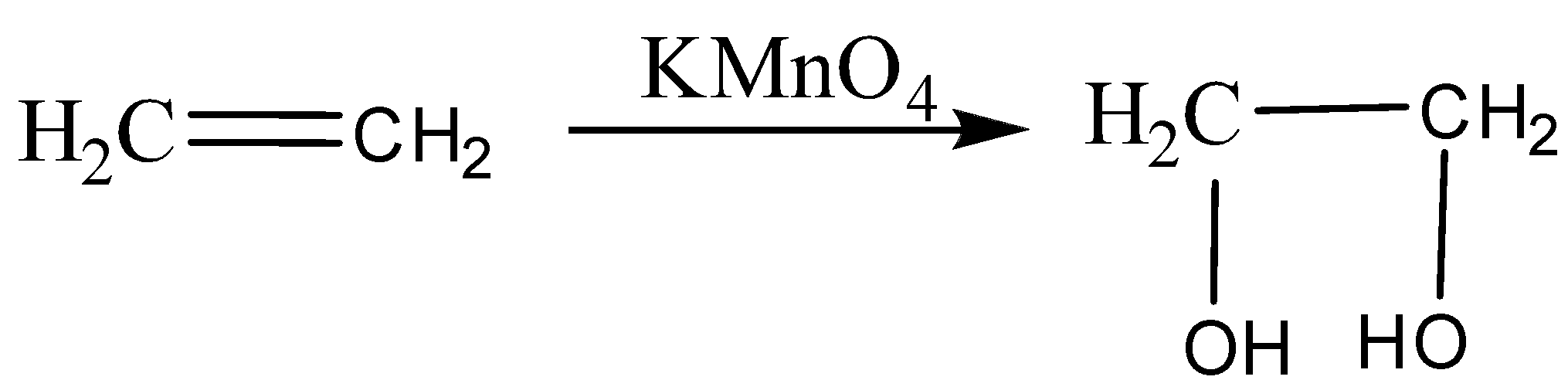
The purple colour of $KMn{O_4}$ changes into colourless after oxidation.
Note:
Bromine water test works by halogenation mechanism.
Bromine water test takes place at room temperature in case of gaseous alkene but in case of liquid alkenes, the reaction will take place in presence of $CC{l_4}$.
Type of hydrocarbon does not undergo addition reactions.
Bromine water is a coloured solution which gets decolourized on reaction with the particular type of hydrocarbons.
Complete step by step answer:
Bromine test:
Bromine water used as a reagent.
Bromine water is known as bromide, bromine solution with the chemical formula $B{r_2}$. Bromine water is prepared by dissolving diatomic bromine and has high oxidizing properties and is obtained as a yellow mixture. ($B{r_2}$) in water (${H_2}O$).
This test is a type of addition reaction. The only non-metal which is in the liquid state is bromine. Bromine is said to have very good oxidizing property.
Bromine water can also be prepared in a chemical laboratory by mixing fumes of bromine with water.
The bromine water test is qualitative, used to identify the alkane or alkene functional groups present in the compound.
Alkane does not react with the bromine water solution and the dark yellow colour of bromine solution remains the same. Example: Ethane
${H_3}C - C{H_3} \to Noreaction$
Alkene undergoes an addition reaction. For example, ethene reacts with bromine water to give 1,2-dibromoethane.
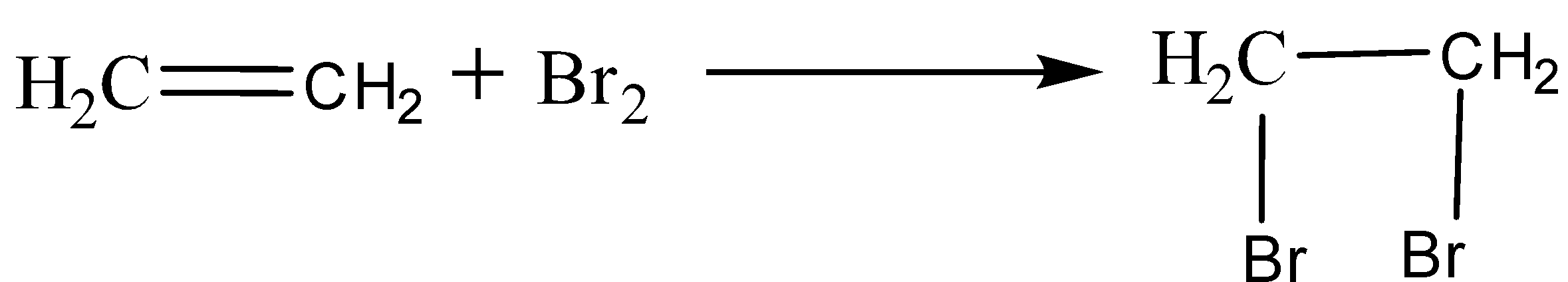
Alternative solution:
$KMn{O_4}$ solution:
Ethane does not react with alkaline $KMn{O_4}$, the purple colour of $KMn{O_4}$ and remains the same.
Ethene reacts with alkaline $KMn{O_4}$, it oxidizes ethene to give ethane 1,2-diol (ethylene glycol).

The purple colour of $KMn{O_4}$ changes into colourless after oxidation.
Note:
Bromine water test works by halogenation mechanism.
Bromine water test takes place at room temperature in case of gaseous alkene but in case of liquid alkenes, the reaction will take place in presence of $CC{l_4}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




