
Mutual inductance M between two concentric coils of radii 1 m and 2 m is
$\begin{align}
& \text{A}\text{. }\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}\pi }{2} \\
& \text{B}\text{. }\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}\pi }{4} \\
& \text{C}\text{. }\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}\pi }{8} \\
& \text{D}\text{. }\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}\pi }{10} \\
\end{align}$
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: We are given the radii of two concentric coils. We need to find the mutual induction between these coils. We have an equation to find the mutual induction between two concentric coils. By substituting for the values in the equation we will get the solution.
Formula used:
$M=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}\pi {{r}^{2}}}{2R}$
Complete step-by-step answer:
In the question we are given two concentric coils and the radius of each coil is also given.
The figure below shows the two given concentric coils.
Let ‘${{r}_{1}}$’ the radius of the first coil. The n we are given,
${{r}_{1}}=1m$
Let ‘${{r}_{2}}$’ be the radius of the second coil. Then we have,
${{r}_{2}}=2m$
We are asked to find the mutual inductance between the two coils.
We know that the mutual induction between two concentric coils, one with radius ‘r’ and the other with radius ‘R’ is given by the formula,
$M=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}\pi {{r}^{2}}}{2R}$
Therefore, in the given situation the mutual induction between the two coils can be found using the above equation.
Thus we get the mutual induction as,
$\Rightarrow M=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}\pi {{r}_{1}}^{2}}{2{{r}_{2}}}$
By substituting the radii of the two coils, we get
$\Rightarrow M=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}\pi {{\left( 1 \right)}^{2}}}{2\times 2}$
By simplifying this we get,
$\Rightarrow M=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}\pi }{4}$
Therefore the mutual induction between the two concentric coils of radii 1 m and 2 m is given as, $M=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}\pi }{4}$
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Consider two concentric circles with radii ‘r’ and ‘R’ as given in the figure below.
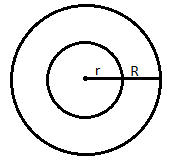
From the figure we can see that r < R.
Consider that a current ${{I}_{2}}$ flows through the outer coil.
Due to this current, there is a magnetic field at the centre of the coil given by,
${{B}_{2}}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}{{I}_{2}}}{2R}$
We can consider this magnetic field as a constant for a cross sectional area of the inner small circle.
Then we can calculate the magnetic flux through the inner coil as,
${{\phi }_{1}}={{B}_{2}}{{A}_{1}}$, were ‘${{\phi }_{1}}$’ is the magnetic flux of the inner coil and ‘${{A}_{1}}$’ is the area of the inner coil.
We know that magnetic flux in the inner coil can be written as,
${{\phi }_{1}}=M{{I}_{2}}$, where ‘M’ is mutual induction between the two coils.
We also know that area of a circle with radius ‘r’ is given by,
$A=\pi {{r}^{2}}$
Therefore the area of the inner circle will be,
${{A}_{1}}=\pi {{r}^{2}}$
By substituting all these known values we get,
$\Rightarrow M{{I}_{2}}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}{{I}_{2}}}{2R}\times \pi {{r}^{2}}$
By solving this we get,
$\Rightarrow M=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}}{2R}\times \pi {{r}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow M=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}\pi {{r}^{2}}}{2R}$
Therefore the equation for mutual induction between two coils is given by,
$M=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}\pi {{r}^{2}}}{2R}$
Formula used:
$M=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}\pi {{r}^{2}}}{2R}$
Complete step-by-step answer:
In the question we are given two concentric coils and the radius of each coil is also given.
The figure below shows the two given concentric coils.

Let ‘${{r}_{1}}$’ the radius of the first coil. The n we are given,
${{r}_{1}}=1m$
Let ‘${{r}_{2}}$’ be the radius of the second coil. Then we have,
${{r}_{2}}=2m$
We are asked to find the mutual inductance between the two coils.
We know that the mutual induction between two concentric coils, one with radius ‘r’ and the other with radius ‘R’ is given by the formula,
$M=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}\pi {{r}^{2}}}{2R}$
Therefore, in the given situation the mutual induction between the two coils can be found using the above equation.
Thus we get the mutual induction as,
$\Rightarrow M=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}\pi {{r}_{1}}^{2}}{2{{r}_{2}}}$
By substituting the radii of the two coils, we get
$\Rightarrow M=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}\pi {{\left( 1 \right)}^{2}}}{2\times 2}$
By simplifying this we get,
$\Rightarrow M=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}\pi }{4}$
Therefore the mutual induction between the two concentric coils of radii 1 m and 2 m is given as, $M=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}\pi }{4}$
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Consider two concentric circles with radii ‘r’ and ‘R’ as given in the figure below.

From the figure we can see that r < R.
Consider that a current ${{I}_{2}}$ flows through the outer coil.
Due to this current, there is a magnetic field at the centre of the coil given by,
${{B}_{2}}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}{{I}_{2}}}{2R}$
We can consider this magnetic field as a constant for a cross sectional area of the inner small circle.
Then we can calculate the magnetic flux through the inner coil as,
${{\phi }_{1}}={{B}_{2}}{{A}_{1}}$, were ‘${{\phi }_{1}}$’ is the magnetic flux of the inner coil and ‘${{A}_{1}}$’ is the area of the inner coil.
We know that magnetic flux in the inner coil can be written as,
${{\phi }_{1}}=M{{I}_{2}}$, where ‘M’ is mutual induction between the two coils.
We also know that area of a circle with radius ‘r’ is given by,
$A=\pi {{r}^{2}}$
Therefore the area of the inner circle will be,
${{A}_{1}}=\pi {{r}^{2}}$
By substituting all these known values we get,
$\Rightarrow M{{I}_{2}}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}{{I}_{2}}}{2R}\times \pi {{r}^{2}}$
By solving this we get,
$\Rightarrow M=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}}{2R}\times \pi {{r}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow M=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}\pi {{r}^{2}}}{2R}$
Therefore the equation for mutual induction between two coils is given by,
$M=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}\pi {{r}^{2}}}{2R}$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




