
How do I multiply a vector by a scalar?
Answer
546.3k+ views
Hint: To multiply a vector by a scalar, just multiply the same or comparable parts, that is, the vector's size(magnitude) by the scalar's size. This will bring out another vector which is the product of the two given magnitudes, and which is heading in the same direction.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The terms vectors and scalars represent different types of physical quantities.
Vector, in mathematics and physics, is a quantity that has both a magnitude and a direction.
Whereas a scalar is a quantity that solely has only magnitude and has no direction.
Hence when it is necessary for them to interact, the only possible method is multiplication because adding a scalar to a vector is impossible due to their various measurements in space.
Moreover, it is possible to multiply a vector by a scalar. A scalar, be that as it may, cannot be multiplied by a vector.
To multiply a vector by a scalar, just multiply the similar components, that is, the vector’s magnitude by the scalar’s magnitude.
This will now result in a new vector that has the same direction as the vector and is the product of the two magnitudes of the quantities.
For example,
Let us consider the vector $\vec{a}$ and the scalar quantity k,
When we multiply them, we denote them as $k\vec{a}$
Pictorially, if we consider various values of k as 1,2,3, -1, -2
We get,
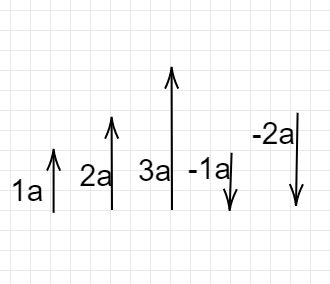
From the above-given set of vectors, we can see that the direction of the vector $\vec{a}$ ,
when the value of the scalar is positive, it remains the same whereas,
when the value of the scalar is negative, the direction becomes exactly opposite.
Note: If we have a vector of type, $\vec{a}=2\hat{i}+\hat{j}+5\hat{k}$ and the scalar quantity which we have to multiply is $3$ then,
$\Rightarrow 3\vec{a}=3\left( 2\hat{i}+\hat{j}+5\hat{k} \right)$
On opening the brackets and multiplying the contents in them we get,
$\Rightarrow 3\vec{a}=6\hat{i}+3\hat{j}+15\hat{k}$
Just multiply the coefficients or the magnitudes.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The terms vectors and scalars represent different types of physical quantities.
Vector, in mathematics and physics, is a quantity that has both a magnitude and a direction.
Whereas a scalar is a quantity that solely has only magnitude and has no direction.
Hence when it is necessary for them to interact, the only possible method is multiplication because adding a scalar to a vector is impossible due to their various measurements in space.
Moreover, it is possible to multiply a vector by a scalar. A scalar, be that as it may, cannot be multiplied by a vector.
To multiply a vector by a scalar, just multiply the similar components, that is, the vector’s magnitude by the scalar’s magnitude.
This will now result in a new vector that has the same direction as the vector and is the product of the two magnitudes of the quantities.
For example,
Let us consider the vector $\vec{a}$ and the scalar quantity k,
When we multiply them, we denote them as $k\vec{a}$
Pictorially, if we consider various values of k as 1,2,3, -1, -2
We get,

From the above-given set of vectors, we can see that the direction of the vector $\vec{a}$ ,
when the value of the scalar is positive, it remains the same whereas,
when the value of the scalar is negative, the direction becomes exactly opposite.
Note: If we have a vector of type, $\vec{a}=2\hat{i}+\hat{j}+5\hat{k}$ and the scalar quantity which we have to multiply is $3$ then,
$\Rightarrow 3\vec{a}=3\left( 2\hat{i}+\hat{j}+5\hat{k} \right)$
On opening the brackets and multiplying the contents in them we get,
$\Rightarrow 3\vec{a}=6\hat{i}+3\hat{j}+15\hat{k}$
Just multiply the coefficients or the magnitudes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




