
What is the molecular formula of the most common disaccharide?
Answer
508.2k+ views
Hint: Saccharides are carbohydrates. Monosaccharide is the simplest carbohydrate which cannot hydrolyze further to give a smaller compound. Disaccharide are those which upon hydrolysis give two molecules of monosaccharides.
Complete answer:
Carbohydrates are the hydrates of carbon. Monosaccharides are simplest carbohydrates which cannot hydrolyze further to give a smaller compound. Disaccharides are those which upon hydrolysis give two molecules of monosaccharides. The most common disaccharide Is sucrose which is mainly derived from plants. The molecular formula for sucrose is \[{{C}_{12}}{{H}_{22}}{{O}_{11}}\]. Sucrose on acid hydrolysis gives an equimolar mixture of two monosaccharides which is glucose and fructose. This is illustrated in the following diagram:
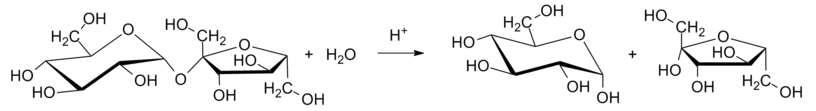
During this hydrolysis, the optical rotation of the solution changes from dextrorotatory to levorotatory. Thus, the above process is called inversion of sugar and the resulting solution is called invert sugar.
Additional information: In biological processes, the hydrolysis of sugar takes place in the presence of sucrase enzymes. Both monosaccharide units are joined to each other through their reducing centre i.e. carbonyl groups that’s why sucrose is non-reducing sugar. Non-reducing sugars are those which don't give Tollen’s reagent and Fehling solution test. As, sucrose is synthesized from the sugarcane and thus it is also called cane-sugar.
Note:
It is important to note that the most common disaccharide is sucrose which is also called table sugar. The molecular formula for sucrose is \[{{C}_{12}}{{H}_{22}}{{O}_{11}}\] . It is an example of non- reducing sugar i.e. doesn’t give the Fehling and Tollens test.
Complete answer:
Carbohydrates are the hydrates of carbon. Monosaccharides are simplest carbohydrates which cannot hydrolyze further to give a smaller compound. Disaccharides are those which upon hydrolysis give two molecules of monosaccharides. The most common disaccharide Is sucrose which is mainly derived from plants. The molecular formula for sucrose is \[{{C}_{12}}{{H}_{22}}{{O}_{11}}\]. Sucrose on acid hydrolysis gives an equimolar mixture of two monosaccharides which is glucose and fructose. This is illustrated in the following diagram:

During this hydrolysis, the optical rotation of the solution changes from dextrorotatory to levorotatory. Thus, the above process is called inversion of sugar and the resulting solution is called invert sugar.
Additional information: In biological processes, the hydrolysis of sugar takes place in the presence of sucrase enzymes. Both monosaccharide units are joined to each other through their reducing centre i.e. carbonyl groups that’s why sucrose is non-reducing sugar. Non-reducing sugars are those which don't give Tollen’s reagent and Fehling solution test. As, sucrose is synthesized from the sugarcane and thus it is also called cane-sugar.
Note:
It is important to note that the most common disaccharide is sucrose which is also called table sugar. The molecular formula for sucrose is \[{{C}_{12}}{{H}_{22}}{{O}_{11}}\] . It is an example of non- reducing sugar i.e. doesn’t give the Fehling and Tollens test.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




