
M-nitro ethylbenzene on \[B{r_2}\] and UV light, what is the product?
Answer
522.6k+ views
Hint: The reaction taking place here is known as halogenation or side chain free radical halogenation. The reaction takes place in the presence of UV light. The application of this reaction is in industries where the synthesis of chloroform, dichloromethane, and hexachlorobutadiene takes place.
Complete answer: Free radical halogenation is a reaction of alkenes where the H atom of an alkene gets substituted with chlorine or bromine. The reaction is typical of alkanes and alkyl-substituted aromatics. There are three steps in the mechanism of free radical halogenation, which are as follows:
Step 1: initiation-there is splitting or hemolysis of \[B{r_2}/C{l_2}\] molecules taking place, and these will act as free radicals. This step is initiated by UV radiation.
Step 2: propagation-part a. The free radical will abstract hydrogen from the alkyl molecule to form HX and a methyl radical.
Part b. the methyl radical form will abstract a Br or Cl from another molecule of \[B{r_2}/C{l_2}\] and will form the methyl halide product with another halogen (\[Br/Cl\]) as free radical.
Step 3: termination-various reactions between the possible pairs of radicals take place to form alkyl molecules, \[B{r_2}/C{l_2}\]or the product alkyl halide. These reactions remove the radical and do not interfere with the cycle.
Now let us look into our question. It says m-nitro ethyl benzene reacts with \[B{r_2}\]in presence of UV light. This reaction will take place as follows:
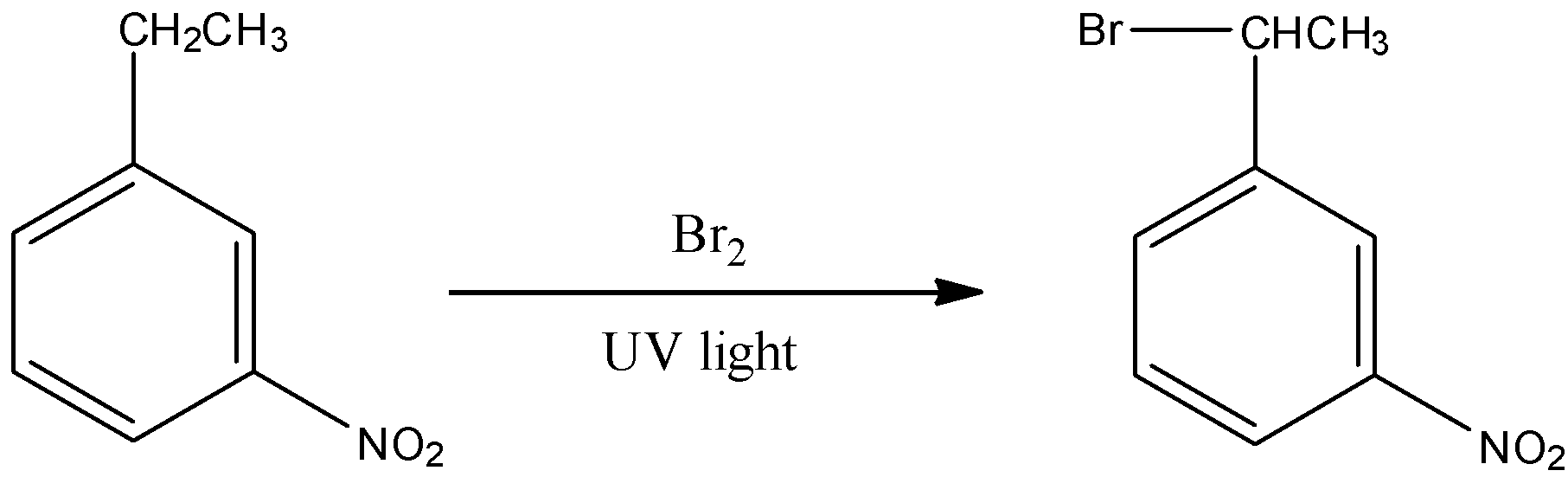
Therefore the product formed is 1-(1-Bromoethyl)-m-nitrobenzene.
Note:
UV light is used in the reaction as a source of energy for the homolytic cleavage (splitting of bond in which the bonding electron pair is distributed evenly between the products.) of \[B{r_2}/C{l_2}\] atom. The reaction can also take place in the presence of heat if UV light is not present. But most commonly UV light is used because it is the most convenient energy source in labs.
Complete answer: Free radical halogenation is a reaction of alkenes where the H atom of an alkene gets substituted with chlorine or bromine. The reaction is typical of alkanes and alkyl-substituted aromatics. There are three steps in the mechanism of free radical halogenation, which are as follows:
Step 1: initiation-there is splitting or hemolysis of \[B{r_2}/C{l_2}\] molecules taking place, and these will act as free radicals. This step is initiated by UV radiation.
Step 2: propagation-part a. The free radical will abstract hydrogen from the alkyl molecule to form HX and a methyl radical.
Part b. the methyl radical form will abstract a Br or Cl from another molecule of \[B{r_2}/C{l_2}\] and will form the methyl halide product with another halogen (\[Br/Cl\]) as free radical.
Step 3: termination-various reactions between the possible pairs of radicals take place to form alkyl molecules, \[B{r_2}/C{l_2}\]or the product alkyl halide. These reactions remove the radical and do not interfere with the cycle.
Now let us look into our question. It says m-nitro ethyl benzene reacts with \[B{r_2}\]in presence of UV light. This reaction will take place as follows:

Therefore the product formed is 1-(1-Bromoethyl)-m-nitrobenzene.
Note:
UV light is used in the reaction as a source of energy for the homolytic cleavage (splitting of bond in which the bonding electron pair is distributed evenly between the products.) of \[B{r_2}/C{l_2}\] atom. The reaction can also take place in the presence of heat if UV light is not present. But most commonly UV light is used because it is the most convenient energy source in labs.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




