
Methoxymethane and ethanol are:
a.) Position isomers
b.) Chain isomers
c.) Functional isomers
d.) Optical isomers.
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: We can find the type of isomerism by the difference in the structural arrangement. First we can check the bonding of atoms and if the bonding is the same then we can go for orientation of the atoms.
Complete step by step answer:
Isomers are compounds which have the same chemical formula but different structural arrangement. Difference in structural arrangement refers to the difference in bonding or difference in the alignment of atoms in the molecule or compound.
There are two types of Isomerism
Structural isomerism
Stereoisomerism
Structural isomerism: In this type of isomerism, there is a difference in the attachment of the atoms in the molecules or compounds. Different structural formulas are given specific IUPAC names. Structural isomerism is further classified into following types:
Chain Isomerism: In this type of structural isomerism, though the molecular formula is identical, the carbon skeleton of two or more compounds will be different. In other words there will be a difference in branching of carbon.
Position Isomerism: In this type of structural isomerism, though the molecular formula is identical, the position of the functional group will be different.
Functional Isomerism: In this type of structural isomerism, though the molecular formula is identical but functional groups attached to them will be different.
Metamerism: In this type of structural isomerism, though the molecular formula is identical but the alkyl groups attached on each side of the functional group will be different.
Tautomerism: In this type of structural isomerism, though the molecular formula is identical, the position of protons and electrons will be different.
Stereoisomerism: this type of isomerism can only be observed in three dimensional space. In this type the orientations of the atoms will be different. Stereoisomerism can be further divided into two types:
Geometric isomerism: in this type, the atoms have different spatial arrangements. It is also known as cis-trans isomerism.
Optical isomerism: Here the compounds have similar bonds and have different spatial arrangement forming non superimposable mirror images.
Structure of Methoxymethane:
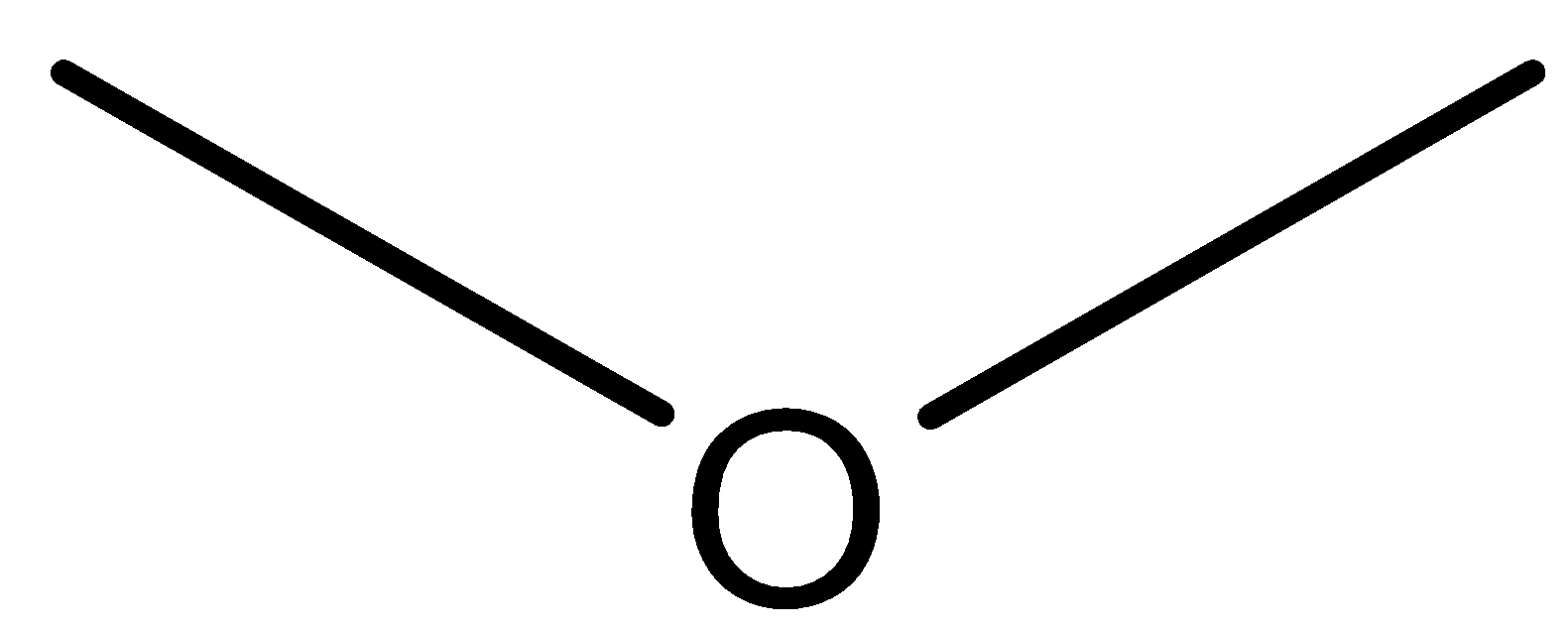
Structure of Ethanol:
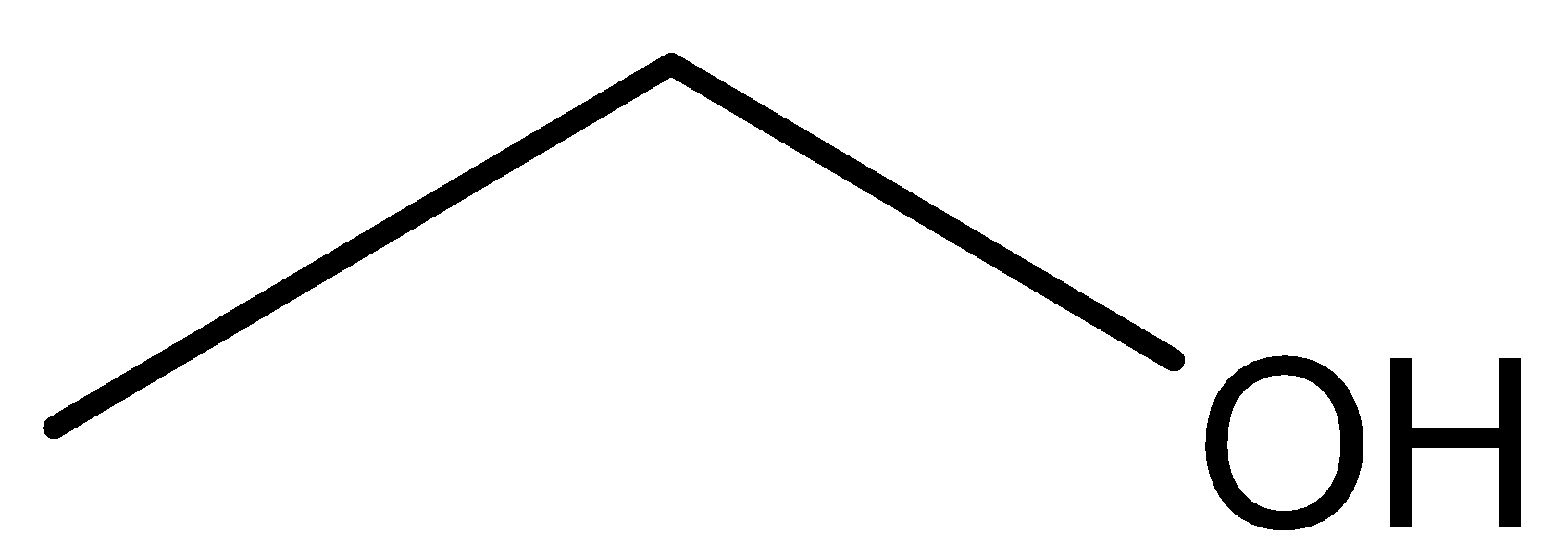
We can observe from both the structure that both the compounds has same molecular formula that is${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{O}}$. Further methoxymethane has ether as the functional group while ethanol has alcohol as the functional group. So both these compounds are functional isomers.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Two compounds which have different IUPAC names will for sure have different structural arrangements. Further as isomers differ in the structure of the compounds that is the difference in arrangement of atoms attached will show different chemical properties.
Complete step by step answer:
Isomers are compounds which have the same chemical formula but different structural arrangement. Difference in structural arrangement refers to the difference in bonding or difference in the alignment of atoms in the molecule or compound.
There are two types of Isomerism
Structural isomerism
Stereoisomerism
Structural isomerism: In this type of isomerism, there is a difference in the attachment of the atoms in the molecules or compounds. Different structural formulas are given specific IUPAC names. Structural isomerism is further classified into following types:
Chain Isomerism: In this type of structural isomerism, though the molecular formula is identical, the carbon skeleton of two or more compounds will be different. In other words there will be a difference in branching of carbon.
Position Isomerism: In this type of structural isomerism, though the molecular formula is identical, the position of the functional group will be different.
Functional Isomerism: In this type of structural isomerism, though the molecular formula is identical but functional groups attached to them will be different.
Metamerism: In this type of structural isomerism, though the molecular formula is identical but the alkyl groups attached on each side of the functional group will be different.
Tautomerism: In this type of structural isomerism, though the molecular formula is identical, the position of protons and electrons will be different.
Stereoisomerism: this type of isomerism can only be observed in three dimensional space. In this type the orientations of the atoms will be different. Stereoisomerism can be further divided into two types:
Geometric isomerism: in this type, the atoms have different spatial arrangements. It is also known as cis-trans isomerism.
Optical isomerism: Here the compounds have similar bonds and have different spatial arrangement forming non superimposable mirror images.
Structure of Methoxymethane:

Structure of Ethanol:

We can observe from both the structure that both the compounds has same molecular formula that is${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{O}}$. Further methoxymethane has ether as the functional group while ethanol has alcohol as the functional group. So both these compounds are functional isomers.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Two compounds which have different IUPAC names will for sure have different structural arrangements. Further as isomers differ in the structure of the compounds that is the difference in arrangement of atoms attached will show different chemical properties.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




