
Mention two applications of polaroids.
Answer
599.1k+ views
Hint: When a plane-polarized light ray is passed through a Polaroid, the intensity of the light ray is affected as some parts of the electric vector of light are removed by the Polaroid. The polaroids can be used where we need to control the intensity of light.
Complete step by step answer:
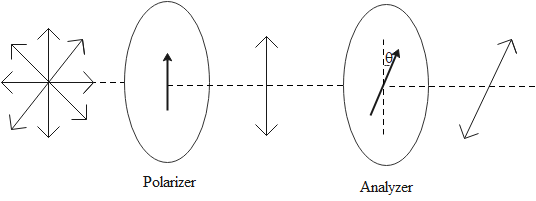
The light waves are electromagnetic waves. Such waves are transverse and have an electric field vector and magnetic field vector which are perpendicular to each other.
An unpolarized wave is one that has its vectors vibrating in all directions. A source of light like the sun or an electric bulb emits unpolarized light waves. We can convert an unpolarized and polarized light by passing the unpolarized light through a polarizer. The polarizer allows only certain components of the field vector to pass through while other components are removed. The result is that we get light which is polarized in a certain direction. This process is called polarization.
The intensity of light depends on its vibrations. When light is passed through a polarizer, its intensity is decreased due to the removal of some vibrations. Malus’ law gives a mathematical relation between the intensity of the light incident on the polaroid and the intensity of light obtained after passing it through the polaroid.
Applications of polaroids are as follows:
They can be used as an analyser and polarizer to study polarization of light
They can be used as a light filter in some photographic plates
They are used in LCD displays like in televisions, computer screens, phone screens, calculators, etc.
Note: An analyzer is also a polarizer that is placed after a polarizer and rotating the analyzer affects the intensity of the polarized light. It is used to further reduce the intensity of light and also adjust it by adjusting the angle of the analyser with respect to the polarizer.
Complete step by step answer:
The light waves are electromagnetic waves. Such waves are transverse and have an electric field vector and magnetic field vector which are perpendicular to each other.
An unpolarized wave is one that has its vectors vibrating in all directions. A source of light like the sun or an electric bulb emits unpolarized light waves. We can convert an unpolarized and polarized light by passing the unpolarized light through a polarizer. The polarizer allows only certain components of the field vector to pass through while other components are removed. The result is that we get light which is polarized in a certain direction. This process is called polarization.
The intensity of light depends on its vibrations. When light is passed through a polarizer, its intensity is decreased due to the removal of some vibrations. Malus’ law gives a mathematical relation between the intensity of the light incident on the polaroid and the intensity of light obtained after passing it through the polaroid.

Applications of polaroids are as follows:
They can be used as an analyser and polarizer to study polarization of light
They can be used as a light filter in some photographic plates
They are used in LCD displays like in televisions, computer screens, phone screens, calculators, etc.
Note: An analyzer is also a polarizer that is placed after a polarizer and rotating the analyzer affects the intensity of the polarized light. It is used to further reduce the intensity of light and also adjust it by adjusting the angle of the analyser with respect to the polarizer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




