
What is the mechanism of halogenations of alkanes?
Answer
594.9k+ views
Hint: Halogenation of alkanes means the substitution of a halogen atom(s) by the removal of one or more hydrogen atoms in the alkane. The mechanism of halogenations occurs in three steps: chain initiation, chain propagation, and chain termination.
Complete step by step answer:
When alkane is treated with a suitable halogen in the presence of ultraviolet light or by heating the reaction mixture to 520-670 K, haloalkane is produced.
For example, chlorination of methane. The reaction is given below:
$\underset{methane}{\mathop C{{H}_{4}}}\,+C{{l}_{2}}\xrightarrow{hv}\underset{chloromethane}{\mathop C{{H}_{3}}Cl}\,+HCl$
$\underset{chloromethane}{\mathop C{{H}_{3}}Cl}\,+C{{l}_{2}}\xrightarrow{hv}\underset{dichloromethane}{\mathop C{{H}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}}\,+HCl$
$\underset{dichloromethane}{\mathop C{{H}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}}\,+C{{l}_{2}}\xrightarrow{hv}\underset{trichloromethane}{\mathop CHC{{l}_{3}}}\,+HCl$
$\underset{trichloromethane}{\mathop CHC{{l}_{3}}}\,+C{{l}_{2}}\xrightarrow{hv}\underset{tetrachloromethane}{\mathop CC{{l}_{4}}}\,+HCl$
Mechanism of halogenations: The halogenations occur in three steps and it follows a free-radical mechanism.
(a)- Chain initiation: When a mixture of $C{{H}_{4}}$and $C{{l}_{2}}$ is heated at 520-670 K in dark or is subjected to UV light at room temperature, $C{{l}_{2}}$ absorbs energy and undergoes homolytic fission which produces chlorine-free radicals.

(b)- Chain propagation: There are two steps in propagation. In the first reaction, the $\bullet Cl$ attacks the $C{{H}_{4}}$ molecule and abstracts a hydrogen atom forming $\bullet C{{H}_{3}}$ and a molecule of $HCl$as shown in reaction. In the second reaction, $\bullet C{{H}_{3}}$ thus produced reacts further with a molecule of $C{{l}_{2}}$ forming a molecule of methyl chloride and another $\bullet Cl$. These reactions continue until the formation of $CC{{l}_{4}}$.
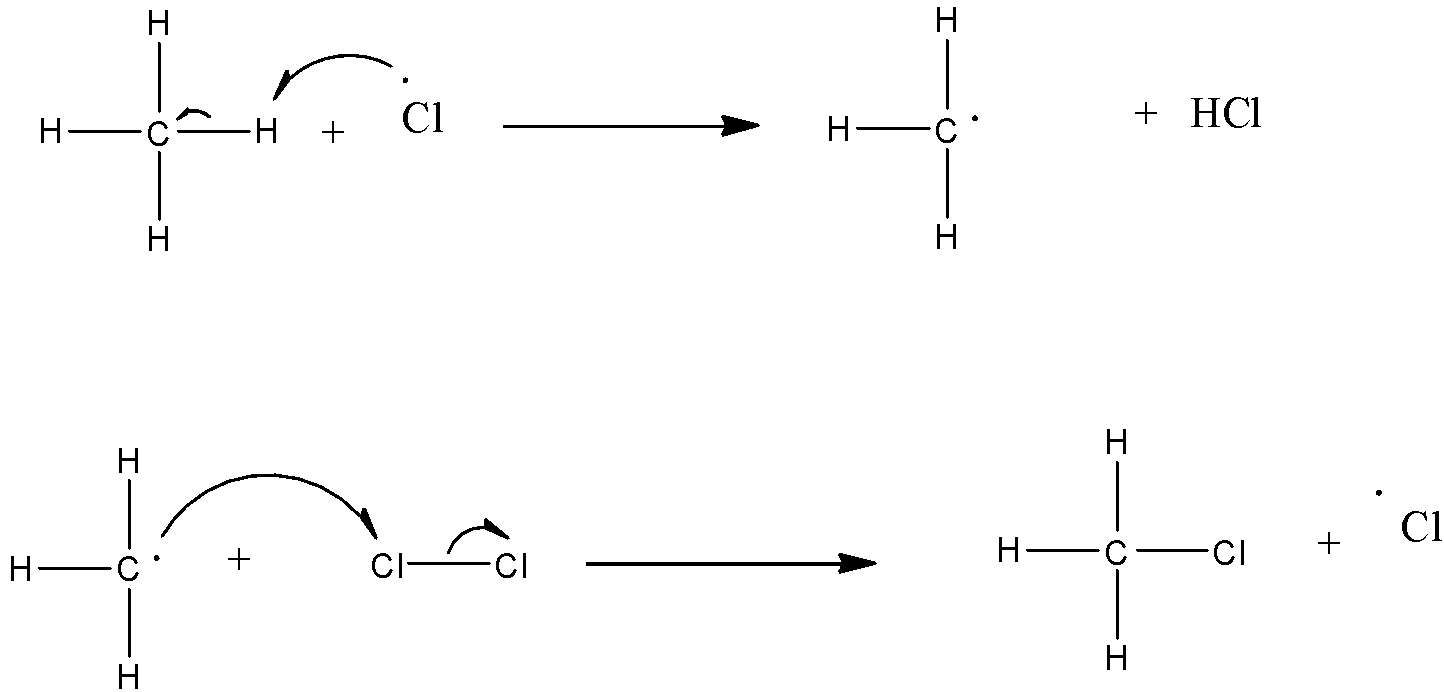
$C{{H}_{3}}Cl+\bullet Cl\to \bullet C{{H}_{2}}Cl+HCl$
$\bullet C{{H}_{2}}Cl+C{{l}_{2}}\to C{{H}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}+\bullet Cl$
$C{{H}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}+\bullet Cl\to \bullet CHC{{l}_{2}}+HCl$
$\bullet CHC{{l}_{2}}+C{{l}_{2}}\to CHC{{l}_{3}}+\bullet Cl$
$CHC{{l}_{3}}+\bullet Cl\to \bullet CC{{l}_{3}}+HCl$
$\bullet CC{{l}_{3}}+C{{l}_{2}}\to CC{{l}_{4}}+\bullet Cl$
(c)- Chain termination: The chain reactions till now formed to have two types of free radicals combine to form molecules. The reaction is given below:
$\bullet Cl+\bullet Cl\to Cl-Cl$
$\bullet C{{H}_{3}}+\bullet C{{H}_{3}}\to C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{3}}$
$\bullet C{{H}_{3}}+\bullet Cl\to C{{H}_{3}}-Cl$
So, by following these steps the halogenations of an alkane are done.
Note: The order of reactivity of the halogens towards the halogenations reaction of alkanes as follows: ${{F}_{2}}$ > $C{{l}_{2}}$ > $B{{r}_{2}}$ > ${{I}_{2}}$.The iodination reaction is reversible as follows:
$C{{H}_{4}}+{{I}_{2}}\rightleftharpoons C{{H}_{3}}-I+HI$.
Complete step by step answer:
When alkane is treated with a suitable halogen in the presence of ultraviolet light or by heating the reaction mixture to 520-670 K, haloalkane is produced.
For example, chlorination of methane. The reaction is given below:
$\underset{methane}{\mathop C{{H}_{4}}}\,+C{{l}_{2}}\xrightarrow{hv}\underset{chloromethane}{\mathop C{{H}_{3}}Cl}\,+HCl$
$\underset{chloromethane}{\mathop C{{H}_{3}}Cl}\,+C{{l}_{2}}\xrightarrow{hv}\underset{dichloromethane}{\mathop C{{H}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}}\,+HCl$
$\underset{dichloromethane}{\mathop C{{H}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}}\,+C{{l}_{2}}\xrightarrow{hv}\underset{trichloromethane}{\mathop CHC{{l}_{3}}}\,+HCl$
$\underset{trichloromethane}{\mathop CHC{{l}_{3}}}\,+C{{l}_{2}}\xrightarrow{hv}\underset{tetrachloromethane}{\mathop CC{{l}_{4}}}\,+HCl$
Mechanism of halogenations: The halogenations occur in three steps and it follows a free-radical mechanism.
(a)- Chain initiation: When a mixture of $C{{H}_{4}}$and $C{{l}_{2}}$ is heated at 520-670 K in dark or is subjected to UV light at room temperature, $C{{l}_{2}}$ absorbs energy and undergoes homolytic fission which produces chlorine-free radicals.

(b)- Chain propagation: There are two steps in propagation. In the first reaction, the $\bullet Cl$ attacks the $C{{H}_{4}}$ molecule and abstracts a hydrogen atom forming $\bullet C{{H}_{3}}$ and a molecule of $HCl$as shown in reaction. In the second reaction, $\bullet C{{H}_{3}}$ thus produced reacts further with a molecule of $C{{l}_{2}}$ forming a molecule of methyl chloride and another $\bullet Cl$. These reactions continue until the formation of $CC{{l}_{4}}$.

$C{{H}_{3}}Cl+\bullet Cl\to \bullet C{{H}_{2}}Cl+HCl$
$\bullet C{{H}_{2}}Cl+C{{l}_{2}}\to C{{H}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}+\bullet Cl$
$C{{H}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}+\bullet Cl\to \bullet CHC{{l}_{2}}+HCl$
$\bullet CHC{{l}_{2}}+C{{l}_{2}}\to CHC{{l}_{3}}+\bullet Cl$
$CHC{{l}_{3}}+\bullet Cl\to \bullet CC{{l}_{3}}+HCl$
$\bullet CC{{l}_{3}}+C{{l}_{2}}\to CC{{l}_{4}}+\bullet Cl$
(c)- Chain termination: The chain reactions till now formed to have two types of free radicals combine to form molecules. The reaction is given below:
$\bullet Cl+\bullet Cl\to Cl-Cl$
$\bullet C{{H}_{3}}+\bullet C{{H}_{3}}\to C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{3}}$
$\bullet C{{H}_{3}}+\bullet Cl\to C{{H}_{3}}-Cl$
So, by following these steps the halogenations of an alkane are done.
Note: The order of reactivity of the halogens towards the halogenations reaction of alkanes as follows: ${{F}_{2}}$ > $C{{l}_{2}}$ > $B{{r}_{2}}$ > ${{I}_{2}}$.The iodination reaction is reversible as follows:
$C{{H}_{4}}+{{I}_{2}}\rightleftharpoons C{{H}_{3}}-I+HI$.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




