
What is meant by vegetative propagation? Name the vegetative parts through which potato and bryophyllum reproduce.
Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: Vegetative propagation also known as cloning is a technique that helps in the cultivation of only a high yielding variety of plants. It induces the plants to reach their maturation stage early. On the other hand, it also discourages evolution and leads to the accumulation of harmful mutations.
Complete answer:
Vegetative propagation is a type of asexual reproduction in which a fragment of the plant or any special reproductive structure can give rise to a new plant. The vegetative part in potato is known as the ‘node’ or ‘eye’ while in bryophyllum it is through ‘leaves’.
Vegetative propagation allows the production of exact copies or clones of the parent plant. It can occur naturally or artificially. In natural vegetative propagation, an axillary bud grows naturally into the lateral shoot and the base of the shoot gives rise to adventurous roots. Plants growing by natural vegetative propagation are-
-Rhizome- They are root-like stems growing horizontally beneath the soil. The nodes of the stem give rise to new roots and shoot (transforms into new plantlets). Example- iris, ginger, etc.
-Bulb- They grow as lateral buds from the parent plant body and give rise to new plants. Example- daffodil, etc.
-Tuber- It is the swollen, fleshy, underground part of the root. It gives rise to axillary buds from nodes or ‘eyes’ that grow into new plants. Example- the potato.
-Stolon- Stolon or Runner grows horizontally above the ground and touches the ground to give rise to new roots and shoot. Example- strawberry.
The methods of artificial vegetative propagation include-
-Cutting- It is the process of cutting a stem or bud from the parent plant which upon planting gives new root and stem. Example- garden geraniums, snake plants, etc.
-Grafting and Budding- It refers to ligating a cut piece of the stem (in Grafting) or a bud (in budding) to a mature plant stem having roots. Example- rose, avocado, etc.
Note: The application of vegetative propagation to produce new plants under sterile conditions in artificial media is known as Tissue culture. It is also known as Micropropagation. The nutrient media used here consists of hormones like auxin, cytokinin, and gibberellic acid; elements like potassium, calcium, sodium, magnesium; and carbohydrates. The hormones stimulate the growth of callus which finally develops into a new plant.
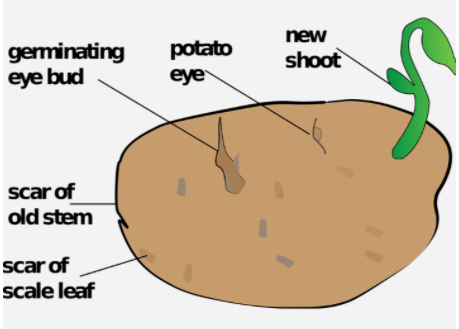
Eye bud in potato
Complete answer:
Vegetative propagation is a type of asexual reproduction in which a fragment of the plant or any special reproductive structure can give rise to a new plant. The vegetative part in potato is known as the ‘node’ or ‘eye’ while in bryophyllum it is through ‘leaves’.
Vegetative propagation allows the production of exact copies or clones of the parent plant. It can occur naturally or artificially. In natural vegetative propagation, an axillary bud grows naturally into the lateral shoot and the base of the shoot gives rise to adventurous roots. Plants growing by natural vegetative propagation are-
-Rhizome- They are root-like stems growing horizontally beneath the soil. The nodes of the stem give rise to new roots and shoot (transforms into new plantlets). Example- iris, ginger, etc.
-Bulb- They grow as lateral buds from the parent plant body and give rise to new plants. Example- daffodil, etc.
-Tuber- It is the swollen, fleshy, underground part of the root. It gives rise to axillary buds from nodes or ‘eyes’ that grow into new plants. Example- the potato.
-Stolon- Stolon or Runner grows horizontally above the ground and touches the ground to give rise to new roots and shoot. Example- strawberry.
The methods of artificial vegetative propagation include-
-Cutting- It is the process of cutting a stem or bud from the parent plant which upon planting gives new root and stem. Example- garden geraniums, snake plants, etc.
-Grafting and Budding- It refers to ligating a cut piece of the stem (in Grafting) or a bud (in budding) to a mature plant stem having roots. Example- rose, avocado, etc.
Note: The application of vegetative propagation to produce new plants under sterile conditions in artificial media is known as Tissue culture. It is also known as Micropropagation. The nutrient media used here consists of hormones like auxin, cytokinin, and gibberellic acid; elements like potassium, calcium, sodium, magnesium; and carbohydrates. The hormones stimulate the growth of callus which finally develops into a new plant.

Eye bud in potato
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




