
What is meant by dispersive power of a transparent material?
Answer
597.3k+ views
Hint: Dispersion is known as the phenomenon of splitting of white light into its constituent colours. The band of colours is called a spectrum. Dispersive power of a transparent medium is the separation of different colours of light by refraction.
Complete step by step answer:
The dispersion was initially observed through a glass prism. It takes place because the refractive index of the material of the medium is different for different colours. By the word colours, it means the wavelengths. The dispersive power for any transparent medium is measured by the ratio of difference in refractive index of two different wavelengths to the refractive index at some specified intermediate wavelength.
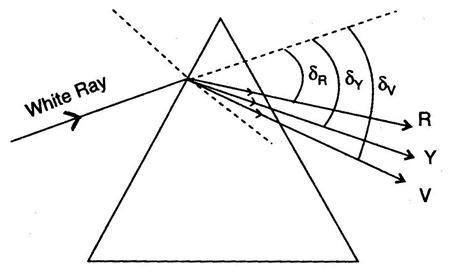
Let us consider a glass prism as an example, the refractive index of a prism is given by the relation
$\mu =\dfrac { \sin { \dfrac { A+D }{ 2 } } }{ \sin { \dfrac { A }{ 2 } } }$
Where, A is the angle of prism and
D is the angle of minimum deviation
If A is the refracting angle of a small angled prism and δ is the angle of deviation. The prism formula becomes,
$\mu =\dfrac { \sin { \dfrac { A+\delta }{ 2 } } }{ \sin { \dfrac { A }{ 2 } } }$
As we are considering small angled prism, $\sin { \dfrac { A+\delta }{ 2 } } =\dfrac { A+\delta }{ 2 }$ and $\sin { \dfrac { A }{ 2 } } =\dfrac { A }{ 2 }$
$\mu =\dfrac { \dfrac { A+\delta }{ 2 } }{ \dfrac { A }{ 2 } }$
$\mu A=A+\delta$
Therefore, $\delta =\left( \mu -1 \right) A$
If δv and δr are the deviations of violet and red rays, the corresponding wavelengths are given as μv and μr . So, the angular dispersion is given as
${ \delta }_{ v }-{ \delta }_{ r }=\left( { \mu }_{ v }-{ \mu }_{ r } \right) A$
The angular dispersion is known as the difference in deviation between extreme colours.
If δy and μy are the deviation and refractive index of an intermediate wavelength yellow,
${ \delta }_{ y }=\left( { \mu }_{ y }-1 \right) A$
On dividing both equations, we get
$\dfrac { { \delta }_{ v }-{ \delta }_{ r } }{ { \delta }_{ y } } =\dfrac { { \mu }_{ v }-{ \mu }_{ r } }{ { \mu }_{ y } }$
The expression $\dfrac { { \delta }_{ v }-{ \delta }_{ r } }{ { \delta }_{ y } }$ is known as dispersive power of the material of the prism and is denoted by ω
$\omega =\dfrac{{{\mu }_{v}}-{{\mu }_{r}}}{{{\mu }_{y}}}$
The dispersive power of the material of a prism is defined as the ratio of angular dispersion for any two wavelengths to the deviation of mean wavelength.
Note: The deviation and the refractive index is more for violet rays than red rays. Therefore, the violet rays travel with a smaller velocity in glass medium than red rays. The refractive index and deviation of yellow rays are taken as mean values.
Complete step by step answer:
The dispersion was initially observed through a glass prism. It takes place because the refractive index of the material of the medium is different for different colours. By the word colours, it means the wavelengths. The dispersive power for any transparent medium is measured by the ratio of difference in refractive index of two different wavelengths to the refractive index at some specified intermediate wavelength.

Let us consider a glass prism as an example, the refractive index of a prism is given by the relation
$\mu =\dfrac { \sin { \dfrac { A+D }{ 2 } } }{ \sin { \dfrac { A }{ 2 } } }$
Where, A is the angle of prism and
D is the angle of minimum deviation
If A is the refracting angle of a small angled prism and δ is the angle of deviation. The prism formula becomes,
$\mu =\dfrac { \sin { \dfrac { A+\delta }{ 2 } } }{ \sin { \dfrac { A }{ 2 } } }$
As we are considering small angled prism, $\sin { \dfrac { A+\delta }{ 2 } } =\dfrac { A+\delta }{ 2 }$ and $\sin { \dfrac { A }{ 2 } } =\dfrac { A }{ 2 }$
$\mu =\dfrac { \dfrac { A+\delta }{ 2 } }{ \dfrac { A }{ 2 } }$
$\mu A=A+\delta$
Therefore, $\delta =\left( \mu -1 \right) A$
If δv and δr are the deviations of violet and red rays, the corresponding wavelengths are given as μv and μr . So, the angular dispersion is given as
${ \delta }_{ v }-{ \delta }_{ r }=\left( { \mu }_{ v }-{ \mu }_{ r } \right) A$
The angular dispersion is known as the difference in deviation between extreme colours.
If δy and μy are the deviation and refractive index of an intermediate wavelength yellow,
${ \delta }_{ y }=\left( { \mu }_{ y }-1 \right) A$
On dividing both equations, we get
$\dfrac { { \delta }_{ v }-{ \delta }_{ r } }{ { \delta }_{ y } } =\dfrac { { \mu }_{ v }-{ \mu }_{ r } }{ { \mu }_{ y } }$
The expression $\dfrac { { \delta }_{ v }-{ \delta }_{ r } }{ { \delta }_{ y } }$ is known as dispersive power of the material of the prism and is denoted by ω
$\omega =\dfrac{{{\mu }_{v}}-{{\mu }_{r}}}{{{\mu }_{y}}}$
The dispersive power of the material of a prism is defined as the ratio of angular dispersion for any two wavelengths to the deviation of mean wavelength.
Note: The deviation and the refractive index is more for violet rays than red rays. Therefore, the violet rays travel with a smaller velocity in glass medium than red rays. The refractive index and deviation of yellow rays are taken as mean values.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




