
What do you mean by covalent bond?
Write the electron dot structure of methane and ethane
Explain the following with examples.
(i) Addition Reaction
(ii) Displacement Reaction
Answer
568.5k+ views
Hint:
A chemical bond is a force of attraction between two or more elements, molecules or ions that keeps them together and leads to the formation of new chemical compound with similar or different properties compare to the constituent species of the bond
Complete step by step answer:
a) Covalent bond: A covalent bond also known as molecular bond is formed by mutual sharing of pairs of electrons between two similar atoms or different atoms. These are generally formed by nonmetals and some special type of metals that show anomalous behavior among their group like lithium.
As shown in the following example both $Cl$require one electron to complete their octet and that is furnished by mutual sharing of an electron pair thus forming a covalent bond
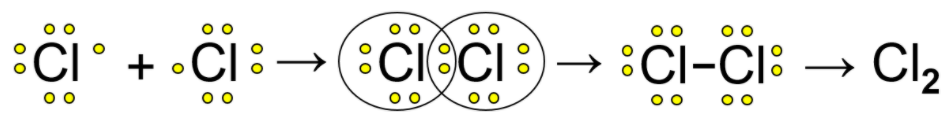
Covalent bonds are the basis of organic chemistry and are the major reason behind creation of various compounds of carbon like ethane \[\left( {{C_2}{H_6}} \right)\] ,methane $(C{H_4})$, glucose $\left( {{C_6}{H_{12}}{O_6}} \right)$ that are very much viable and necessary for both industrial and human needs.
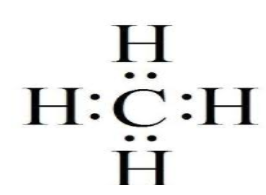
b) Electron dot structure of methane $\left( {C{H_4}} \right)$
As carbon atom requires four electrons to complete its octet it makes covalent bond with four hydrogen atom which have one electron each and themselves require a total of four electron so that each of them can achieve a duplet
Electron dot Structure of Ethane \[\left( {{C_2}{H_6}} \right)\]
As shown below for ethane the sharing is between two carbon atom and six hydrogen atom such that both carbon achieve octet and all six hydrogen achieve duplet
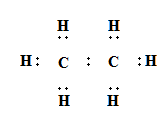
c)
i) Additions Reaction: These are the reaction in which molecules combined with each other to form a large molecules without formation of any by-product
Example: Hydrogenation of ethane to form ethane is a type of addition reaction
${C_2}{H_4} \oplus {H_2} \to {C_2}{H_6}$
ii) Displacement Reaction: It is a type of reaction in which one type of atom or ion is displaced by another atom or ion
Example: Displacement of Hydrogen from hydrogen chloride by zinc
$Zn \oplus 2HCl \to ZnC{l_2} \oplus {H_2} \uparrow $
Note: In Covalent bond mutual sharing of electrons takes place else if both electrons are shared only by one atom then the bond comes into a special category of covalent bond called co-ordinate bond or dative bond.
A chemical bond is a force of attraction between two or more elements, molecules or ions that keeps them together and leads to the formation of new chemical compound with similar or different properties compare to the constituent species of the bond
Complete step by step answer:
a) Covalent bond: A covalent bond also known as molecular bond is formed by mutual sharing of pairs of electrons between two similar atoms or different atoms. These are generally formed by nonmetals and some special type of metals that show anomalous behavior among their group like lithium.
As shown in the following example both $Cl$require one electron to complete their octet and that is furnished by mutual sharing of an electron pair thus forming a covalent bond

Covalent bonds are the basis of organic chemistry and are the major reason behind creation of various compounds of carbon like ethane \[\left( {{C_2}{H_6}} \right)\] ,methane $(C{H_4})$, glucose $\left( {{C_6}{H_{12}}{O_6}} \right)$ that are very much viable and necessary for both industrial and human needs.
b) Electron dot structure of methane $\left( {C{H_4}} \right)$
As carbon atom requires four electrons to complete its octet it makes covalent bond with four hydrogen atom which have one electron each and themselves require a total of four electron so that each of them can achieve a duplet

Electron dot Structure of Ethane \[\left( {{C_2}{H_6}} \right)\]
As shown below for ethane the sharing is between two carbon atom and six hydrogen atom such that both carbon achieve octet and all six hydrogen achieve duplet
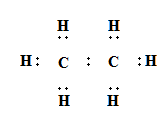
c)
i) Additions Reaction: These are the reaction in which molecules combined with each other to form a large molecules without formation of any by-product
Example: Hydrogenation of ethane to form ethane is a type of addition reaction
${C_2}{H_4} \oplus {H_2} \to {C_2}{H_6}$
ii) Displacement Reaction: It is a type of reaction in which one type of atom or ion is displaced by another atom or ion
Example: Displacement of Hydrogen from hydrogen chloride by zinc
$Zn \oplus 2HCl \to ZnC{l_2} \oplus {H_2} \uparrow $
Note: In Covalent bond mutual sharing of electrons takes place else if both electrons are shared only by one atom then the bond comes into a special category of covalent bond called co-ordinate bond or dative bond.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




