
mcPBA $\to$ meta-chloro perbenzoic acid.

Stereochemistry of the product of the above reaction is:
(a) Meso
(b) Racemic
(c) Diastereomers
(d) Optically inactive due to absence of chiral center.

Answer
545.7k+ views
Hint: \[mcPBA\] is useful reagent which is used in organic chemistry for the synthesis of epoxides from alkenes. The addition of oxygen takes place to the double bond of alkene.
Complete step by step answer:
The reaction between an alkene and \[mcPBA\] is called an epoxidation reaction. The epoxidation reaction is also termed as oxygen insertion reaction.
\[mcPBA\] is known as meta-chloro perbenzoic acid or meta-chloroperoxybenzoic acid. It contains a peroxide linkage. It is a stable peracid and the oxygen attached to the carboxylic group is electron deficient oxygen or electrophilic. It attacks the electron rich alkene and the reaction proceeds through a concerted transition state.
The mechanism for the reaction is shown as
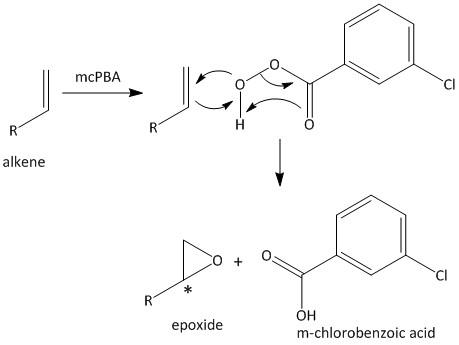
The addition of oxygen atom to the alkene results in the generation of chiral center marked as (*). Thus the compound is optically inactive due to formation of a racemic compound.
Before going into the answer of the question let us understand the given options one by one. Meso compounds are achiral compounds which contain two or more stereogenic centers. The compounds are superimposable mirror images of each other.
Racemic compounds are the compounds which contain equal amounts of both the enantiomers. Diastereomers are pairs of isomers which are not mirror images of one another.
The given alkene is a mono substituted alkene. The addition of an alkene will generate a chiral center. As a result the reaction gives an equal mixture of enantiomers which is called a racemic mixture. The product of the reaction is shown as
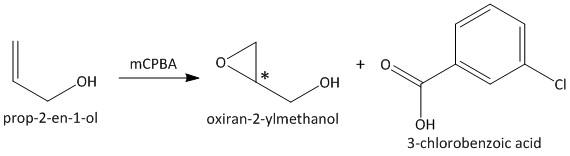
Hence the stereochemistry of the product of the given reaction is racemic.
option (b) is the correct answer.
Note: The epoxidation reaction is a useful reaction in organic chemistry for the generation of chiral centers. Reaction of unsymmetrical polysubstituted alkenes leads to generation of both pair of enantiomers and diastereomers.
Complete step by step answer:
The reaction between an alkene and \[mcPBA\] is called an epoxidation reaction. The epoxidation reaction is also termed as oxygen insertion reaction.
\[mcPBA\] is known as meta-chloro perbenzoic acid or meta-chloroperoxybenzoic acid. It contains a peroxide linkage. It is a stable peracid and the oxygen attached to the carboxylic group is electron deficient oxygen or electrophilic. It attacks the electron rich alkene and the reaction proceeds through a concerted transition state.
The mechanism for the reaction is shown as

The addition of oxygen atom to the alkene results in the generation of chiral center marked as (*). Thus the compound is optically inactive due to formation of a racemic compound.
Before going into the answer of the question let us understand the given options one by one. Meso compounds are achiral compounds which contain two or more stereogenic centers. The compounds are superimposable mirror images of each other.
Racemic compounds are the compounds which contain equal amounts of both the enantiomers. Diastereomers are pairs of isomers which are not mirror images of one another.
The given alkene is a mono substituted alkene. The addition of an alkene will generate a chiral center. As a result the reaction gives an equal mixture of enantiomers which is called a racemic mixture. The product of the reaction is shown as

Hence the stereochemistry of the product of the given reaction is racemic.
option (b) is the correct answer.
Note: The epoxidation reaction is a useful reaction in organic chemistry for the generation of chiral centers. Reaction of unsymmetrical polysubstituted alkenes leads to generation of both pair of enantiomers and diastereomers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




