
What is the main reactant for glycolysis?
Answer
521.1k+ views
Hint: Glycolysis is a metabolic process that involves breaking down glucose into pyruvate molecules and hydrogen ions and energy. This energy is released in the form of ATP molecules, the ultimate energy currencies of the body.
Complete answer:
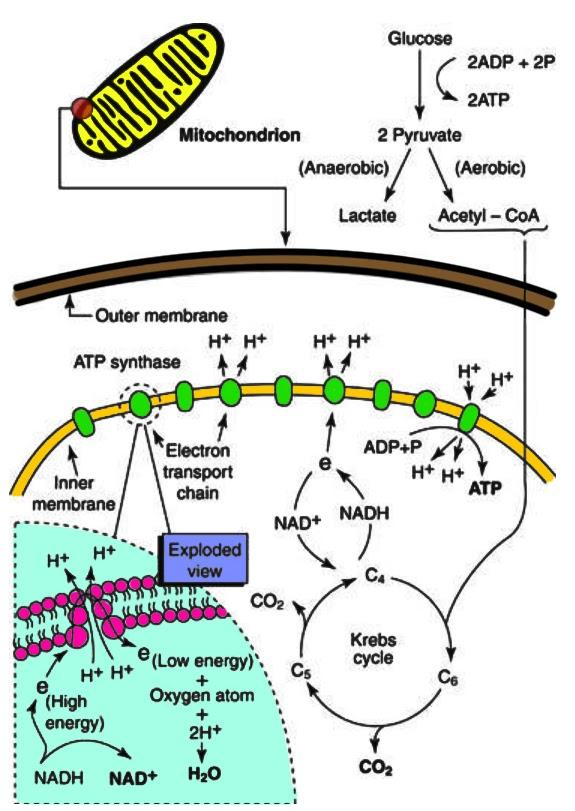
The main reaction of the glycolysis is given below which involves Glucose as the main reactant that leads to formation of two pyruvate molecules as products. In this reaction $NAD^+$ stands for Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and ADP stands for Adenosine Diphosphate. P is obviously phosphorous. All these components along with a glucose molecule undergo oxidation reaction that leads to formation pyruvate molecules, 2 ATPs ( Adenosine Triphosphate), 2 NADH ions that is, Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Hydrogen(Hydride) and independent hydrogen atoms. These ATPs are ultimately used by the body as energy currencies.
$C_6H_{12}O_6$ + 2 $NAD^+$ + 2 ADP + 2 P → 2 pyruvic acid, (CH3(C=O)COOH + 2 ATP + 2 NADH + 2 $H^+$
The process of glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm or mitochondria of cells of both plants and animals. The ATP molecule released from this reaction stores the chemical energy of this reaction and eventually burns itself to fuel up any given task such as food digestion or cognition, etc. whereas the $NAD^+$ takes one hydrogen ion from glucose to form NADH. However, this NADH and Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide ($FADH_2$) transport their electrons to mitochondria to utilize their energy for further processing.
Note:
The process mentioned above is common to aerobic respirations only whereas for anaerobic process of respiration these NADH ions get dissolved to form $NAD^+$ ions in order to compensate the absence of oxygen and maintain the continuous flow of energy.
Complete answer:
The main reaction of the glycolysis is given below which involves Glucose as the main reactant that leads to formation of two pyruvate molecules as products. In this reaction $NAD^+$ stands for Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and ADP stands for Adenosine Diphosphate. P is obviously phosphorous. All these components along with a glucose molecule undergo oxidation reaction that leads to formation pyruvate molecules, 2 ATPs ( Adenosine Triphosphate), 2 NADH ions that is, Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Hydrogen(Hydride) and independent hydrogen atoms. These ATPs are ultimately used by the body as energy currencies.
$C_6H_{12}O_6$ + 2 $NAD^+$ + 2 ADP + 2 P → 2 pyruvic acid, (CH3(C=O)COOH + 2 ATP + 2 NADH + 2 $H^+$
The process of glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm or mitochondria of cells of both plants and animals. The ATP molecule released from this reaction stores the chemical energy of this reaction and eventually burns itself to fuel up any given task such as food digestion or cognition, etc. whereas the $NAD^+$ takes one hydrogen ion from glucose to form NADH. However, this NADH and Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide ($FADH_2$) transport their electrons to mitochondria to utilize their energy for further processing.

Note:
The process mentioned above is common to aerobic respirations only whereas for anaerobic process of respiration these NADH ions get dissolved to form $NAD^+$ ions in order to compensate the absence of oxygen and maintain the continuous flow of energy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




