
Magnetic field at point O will be
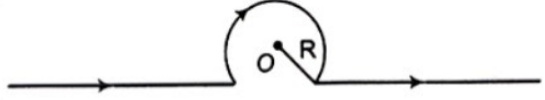
A.\[\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}l}{2R}\operatorname{int}erior\]
B.$\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}l}{2R}exterior$
C.$\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}l}{2R}\left( 1-\dfrac{1}{\pi } \right)\operatorname{int}erior$
D.$\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}l}{2R}\left( 1+\dfrac{1}{\pi } \right)exterior$

Answer
584.7k+ views
HintMagnetic field due to a straight wire and magnetic field due to a circular loop are opposite to each other.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Magnetic field:- The region near a magnet, where a magnetic needle experiences a torque and rests in a definite direction is called magnetic field.
When current flows in a conductor, then a magnetic field is produced around it. Magnetic field lines depend on the shape of the conductor.
For a straight wire
When the current is flow in a straight wire, then magnetic field lines in circular shape around it and the formula for magnetic field in a straight wire is
${{B}_{1}}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}}{2\pi }\dfrac{i}{R}$
Where ${{B}_{1}}=$ The magnetic field
$i=$ The current in the wire
$R=$ The distance of point O from the wire
Direction of the magnetic field is upward.
For circular loop
When current is flowing in a wire which is circular shape, then the magnetic field lines in circular loop but different way
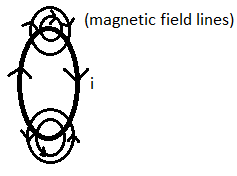
Formula of magnetic field for circle
${{B}_{2}}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i}{2R}$
Where $B=$ The magnetic field, $i=$ Current and $R=$ Radius of circle
Direction of the magnetic field is downward.
So the effective magnetic field due to both straight wire and circular loop is
$B={{B}_{1}}={{B}_{2}}$
$B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i}{2R}-\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i}{2\pi R}$
$B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i}{2R}\left( 1-\dfrac{1}{\pi } \right)$
Note:
When students find out the resultant magnetic field. Students added both, but the magnetic field is a vector quantity so the direction has an important role. Both magnetic fields ${{B}_{1}}$ and ${{B}_{2}}$ are opposite in direction. So subtract these magnetic fields from higher to lower.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Magnetic field:- The region near a magnet, where a magnetic needle experiences a torque and rests in a definite direction is called magnetic field.
When current flows in a conductor, then a magnetic field is produced around it. Magnetic field lines depend on the shape of the conductor.
For a straight wire
When the current is flow in a straight wire, then magnetic field lines in circular shape around it and the formula for magnetic field in a straight wire is
${{B}_{1}}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}}{2\pi }\dfrac{i}{R}$
Where ${{B}_{1}}=$ The magnetic field
$i=$ The current in the wire
$R=$ The distance of point O from the wire
Direction of the magnetic field is upward.
For circular loop
When current is flowing in a wire which is circular shape, then the magnetic field lines in circular loop but different way

Formula of magnetic field for circle
${{B}_{2}}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i}{2R}$
Where $B=$ The magnetic field, $i=$ Current and $R=$ Radius of circle
Direction of the magnetic field is downward.
So the effective magnetic field due to both straight wire and circular loop is
$B={{B}_{1}}={{B}_{2}}$
$B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i}{2R}-\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i}{2\pi R}$
$B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i}{2R}\left( 1-\dfrac{1}{\pi } \right)$
Note:
When students find out the resultant magnetic field. Students added both, but the magnetic field is a vector quantity so the direction has an important role. Both magnetic fields ${{B}_{1}}$ and ${{B}_{2}}$ are opposite in direction. So subtract these magnetic fields from higher to lower.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




