
ln a flowering plant, archesporium gives rise to
(a)Only the wall of the sporangium
(b)Both wall and the sporogenous cells
(c)Only tapetum and sporogenous cells
(d)None of the above
Answer
592.2k+ views
Hint: They are the cells that produce male gametes and are enclosed in a protective layer which later helps in the pollination in plants and produce seeds resulting in the production of new offsprings.
Complete answer:
During the alternate generation in angiosperms, the archesporium divides. These archesporial cells are the structure present in a sporophyte that produces spores after division. The division in archesporium will lead to the formation of the anther wall and sporogenous cells.
Additional Information:
-Archesporium is a large single cell that originates from the nucellus of an ovule.
-They are hydrodermal in origin and undergo periclinal division.
-Hypodermal origin comes from the hypodermis layer which is the lowermost layer of the integumentary system in the vertebrates.
-After division it forms two cells, one is the parietal cell which forms an anther wall while the other is the primary sporogenous cells.
-The parietal cell layers will divide in various directions to give rise to several concentric layers of anther wall.
-The primary sporogenous cells will form the microspore mother cell.
-The sporogenous layer formed will be around two to four cells thick.
-The microspore mother cell after division will give rise to microspores or male gametes.
-The microspore or the male gamete is called the pollen grains which later help in the process of pollination.
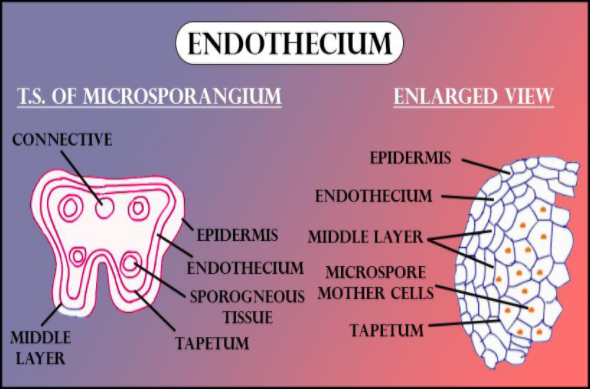
So, the correct answer is ‘Both wall and the sporogenous cells’.
Note: The microspore or the male gametophyte formed will have several layers: Epidermis (outer single layer, degenerates at maturity), endothecium (single layer below the epidermis, have fibrous thickening), many middle layers (cells degenerates in the mature anther), and tapetum (single layer having dense cytoplasm and provide nutrition to the developing microspore).
Complete answer:
During the alternate generation in angiosperms, the archesporium divides. These archesporial cells are the structure present in a sporophyte that produces spores after division. The division in archesporium will lead to the formation of the anther wall and sporogenous cells.
Additional Information:
-Archesporium is a large single cell that originates from the nucellus of an ovule.
-They are hydrodermal in origin and undergo periclinal division.
-Hypodermal origin comes from the hypodermis layer which is the lowermost layer of the integumentary system in the vertebrates.
-After division it forms two cells, one is the parietal cell which forms an anther wall while the other is the primary sporogenous cells.
-The parietal cell layers will divide in various directions to give rise to several concentric layers of anther wall.
-The primary sporogenous cells will form the microspore mother cell.
-The sporogenous layer formed will be around two to four cells thick.
-The microspore mother cell after division will give rise to microspores or male gametes.
-The microspore or the male gamete is called the pollen grains which later help in the process of pollination.

So, the correct answer is ‘Both wall and the sporogenous cells’.
Note: The microspore or the male gametophyte formed will have several layers: Epidermis (outer single layer, degenerates at maturity), endothecium (single layer below the epidermis, have fibrous thickening), many middle layers (cells degenerates in the mature anther), and tapetum (single layer having dense cytoplasm and provide nutrition to the developing microspore).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




