
List the applications of Photoelectric effect.
Answer
521k+ views
Hint: When electromagnetic radiation, such as light, hits a material, electrons are emitted from the material and this process is referred to as Photoelectric effect. The escaping electrons are called photoelectrons. The photons present in a light beam have energy, and this energy is called photon energy.
Complete step by step answer:
Photoelectric effect is a phenomenon in which the electromagnetic radiation is made of a series of particles called photons. This phenomenon is a part of electronic physics, and is studied under quantum physics.
When a photon hits an electron on a metal surface, the electron can be emitted. The emitted electrons are called photoelectrons.
In the photoemission process, if an electron within some material absorbs the energy of one photon and acquires more energy than the work function (the electron binding energy) of the material, then the electron is ejected from the material. The electrons will not escape the material when the photon energy is low.
(i) On increasing the frequency the saturation current remains the same.
(ii) On increasing the Intensity the saturation current also increases.
Applications of Photoelectric effect are as follows:
(i)Photo - cell is the most important application. It is most commonly found in solar panels. It works on the basic principle of the light striking the cathode which causes the emission of electrons, which in turn produces current.
(ii)Photomultiplier tubes make use of photoelectric effect to convert light intensity into electrical currents.
(iii)Photoelectric effect also finds application in photocopies, light meter, photodiodes, and phototransistors.
(iv)Scintillators: A scintillator is a device that emits light when it attracts radiation from either source in the lab or cosmic sources.
Additional Information:
Photoelectric effect means when light hits a material, i.e., in general when electromagnetic radiation hits any material, then photoelectrons are released or emitted from the surface. This happens because the material absorbs the energy from the EM rays and the electrons in the material fly’s off, gaining the extra energy.
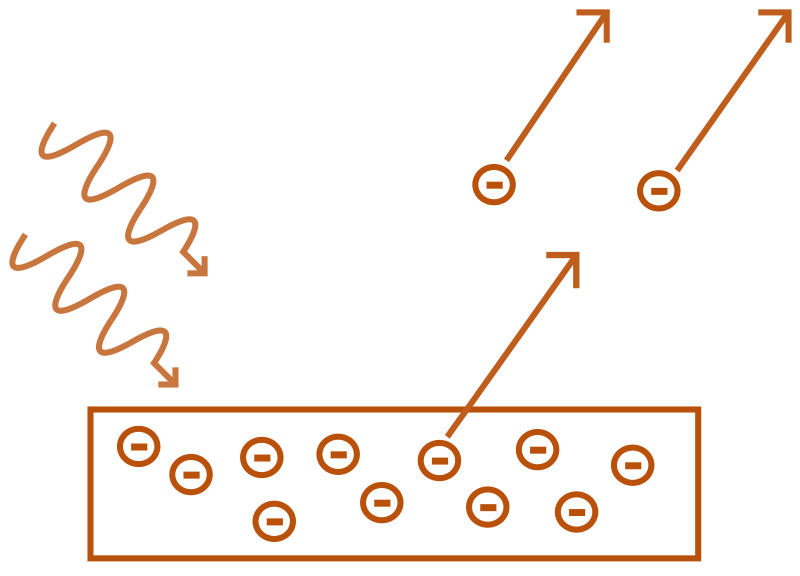
The number of photoelectrons emitted depends on the intensity of the electromagnetic radiation.
Note:
It must be remembered that: The energy of incident photons must be equal to or greater than the sum of metal's work function and photoelectron kinetic energy for photoelectric emission to take place.
Complete step by step answer:
Photoelectric effect is a phenomenon in which the electromagnetic radiation is made of a series of particles called photons. This phenomenon is a part of electronic physics, and is studied under quantum physics.
When a photon hits an electron on a metal surface, the electron can be emitted. The emitted electrons are called photoelectrons.
In the photoemission process, if an electron within some material absorbs the energy of one photon and acquires more energy than the work function (the electron binding energy) of the material, then the electron is ejected from the material. The electrons will not escape the material when the photon energy is low.
(i) On increasing the frequency the saturation current remains the same.
(ii) On increasing the Intensity the saturation current also increases.
Applications of Photoelectric effect are as follows:
(i)Photo - cell is the most important application. It is most commonly found in solar panels. It works on the basic principle of the light striking the cathode which causes the emission of electrons, which in turn produces current.
(ii)Photomultiplier tubes make use of photoelectric effect to convert light intensity into electrical currents.
(iii)Photoelectric effect also finds application in photocopies, light meter, photodiodes, and phototransistors.
(iv)Scintillators: A scintillator is a device that emits light when it attracts radiation from either source in the lab or cosmic sources.
Additional Information:
Photoelectric effect means when light hits a material, i.e., in general when electromagnetic radiation hits any material, then photoelectrons are released or emitted from the surface. This happens because the material absorbs the energy from the EM rays and the electrons in the material fly’s off, gaining the extra energy.

The number of photoelectrons emitted depends on the intensity of the electromagnetic radiation.
Note:
It must be remembered that: The energy of incident photons must be equal to or greater than the sum of metal's work function and photoelectron kinetic energy for photoelectric emission to take place.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




