
Lindlar’s catalyst is:
A. $Pt$ in ethanol
B. $Pd+CaC{{O}_{3}}$
C. $Ni$ in ethanol
D. $Na$ in liquid $N{{H}_{3}}$
Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: Try to recall that Lindlar’s catalyst is a heterogeneous catalyst which is used for the partial hydrogenation of alkynes. It gives cis-alkenes on reaction with alkynes. Now, by using this you can easily answer the given question.
Complete step by step answer:
- It is known to you that $Pd+CaC{{O}_{3}}$ is known as Lindlar catalyst and is named after its inventor Herbert Lindlar Wilson.
- It is a heterogeneous catalyst which consists of palladium deposited on calcium carbonate with traces of lead and quinoline.
- Since, palladium is a good absorber of hydrogen and has very high catalytic properties. Therefore, it is poisoned with various forms of lead or sulphur or quinoline in order to reduce its activity of reducing double bonds.
- So, $Pd+CaC{{O}_{3}}$ is used for the partial hydrogenation of alkynes to alkenes and does not have the ability to reduce double bonds.
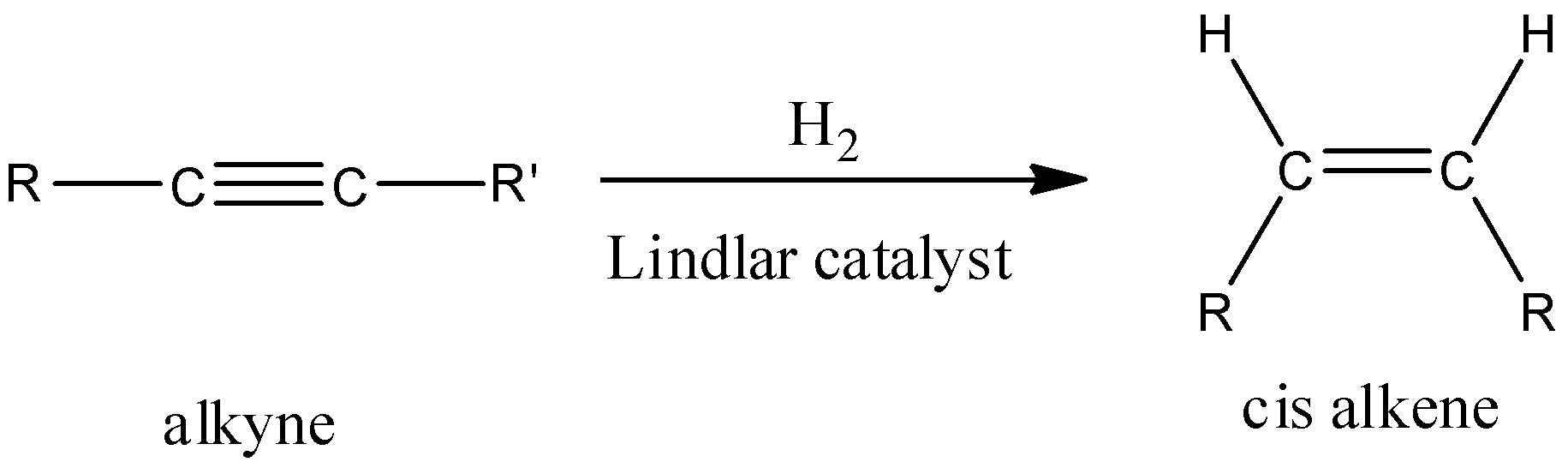
- Also, the product formed by using Lindlar’s catalyst i.e. $Pd+CaC{{O}_{3}}$ is a cis-alkene.
- In the hydrogenation reaction of alkynes in presence of $Pd+CaC{{O}_{3}}$, hydrogen atoms get added to the same side (cis) of alkyne and form cis-alkenes through syn addition (addition of two substituents on the same side of alkyne or alkene).
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Note that Hydrogenation of alkynes in presence of Lindlar’s catalyst is stereoselective and happens through syn addition. Also, it should be remembered that if $Pd+CaC{{O}_{3}}$ is directly used without being poisoned then it will hydrogenate alkynes directly to alkanes. That’s why quinoline is used as a catalytic poison to stop the reaction at alkene.
Complete step by step answer:
- It is known to you that $Pd+CaC{{O}_{3}}$ is known as Lindlar catalyst and is named after its inventor Herbert Lindlar Wilson.
- It is a heterogeneous catalyst which consists of palladium deposited on calcium carbonate with traces of lead and quinoline.
- Since, palladium is a good absorber of hydrogen and has very high catalytic properties. Therefore, it is poisoned with various forms of lead or sulphur or quinoline in order to reduce its activity of reducing double bonds.
- So, $Pd+CaC{{O}_{3}}$ is used for the partial hydrogenation of alkynes to alkenes and does not have the ability to reduce double bonds.

- Also, the product formed by using Lindlar’s catalyst i.e. $Pd+CaC{{O}_{3}}$ is a cis-alkene.
- In the hydrogenation reaction of alkynes in presence of $Pd+CaC{{O}_{3}}$, hydrogen atoms get added to the same side (cis) of alkyne and form cis-alkenes through syn addition (addition of two substituents on the same side of alkyne or alkene).
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Note that Hydrogenation of alkynes in presence of Lindlar’s catalyst is stereoselective and happens through syn addition. Also, it should be remembered that if $Pd+CaC{{O}_{3}}$ is directly used without being poisoned then it will hydrogenate alkynes directly to alkanes. That’s why quinoline is used as a catalytic poison to stop the reaction at alkene.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




