
Light enters from air to glass having refractive index 1.50. What is the speed of light in the glass? The speed of light in vacuum is $3\times {{10}^{8}}m{{s}^{-1}}$
Answer
588.6k+ views
Hint: The given refractive index of glass is with respect to air. The refractive index of glass is given as the ratio of speed of light in vacuum to the speed of light in the medium. We can replace the speed of light in vacuum with the speed of light in air as they are approximately the same. Hence we can determine the speed of light in glass from the definition of refractive index.
Complete solution:
Let us first define the refractive index of a medium in general.
Refractive index of a medium is the ratio of the speed of the light in vacuum to its speed of light in the medium. This can be mathematically represented as,
$\eta =\dfrac{\text{Speed of light in (vacuum/air)}}{\text{Speed of light in medium}}...(1)$
The refractive index of glass is given as 1.5 and speed of light in air is given as $3\times {{10}^{8}}m{{s}^{-1}}$.Hence we can use the equation 1 to determine the speed of light in the glass.
$\begin{align}
& \eta =\dfrac{\text{Speed of light in (vacuum/air)}}{\text{Speed of light in medium}} \\
& 1.5=\dfrac{3\times {{10}^{8}}}{\text{Speed of light in medium}} \\
& \text{Speed of light in medium}=\dfrac{3\times {{10}^{8}}}{1.5}=2\times {{10}^{8}}m{{s}^{-1}}. \\
\end{align}$
Hence the speed of light in glass is $2\times {{10}^{8}}m{{s}^{-1}}$.
Note:
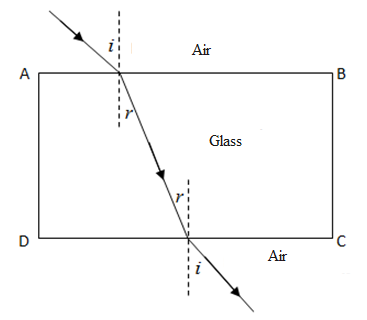
According to Snell’s law, the refractive index of a medium is also given by,
$\eta =\dfrac{\operatorname{Sin}i}{\operatorname{Sin}r}$ where i is the angle of incidence and r is the angle of refraction. Refractive index for glass is greater than one. Hence from this we can imply that angle of incidence is greater than the angle of refraction i.e. light bends as it moves from air to glass. One more key point to be kept in mind is that the frequency of light does not change when a monochromatic light enters from a rarer to denser medium, but its wavelength does.
Complete solution:
Let us first define the refractive index of a medium in general.
Refractive index of a medium is the ratio of the speed of the light in vacuum to its speed of light in the medium. This can be mathematically represented as,
$\eta =\dfrac{\text{Speed of light in (vacuum/air)}}{\text{Speed of light in medium}}...(1)$
The refractive index of glass is given as 1.5 and speed of light in air is given as $3\times {{10}^{8}}m{{s}^{-1}}$.Hence we can use the equation 1 to determine the speed of light in the glass.
$\begin{align}
& \eta =\dfrac{\text{Speed of light in (vacuum/air)}}{\text{Speed of light in medium}} \\
& 1.5=\dfrac{3\times {{10}^{8}}}{\text{Speed of light in medium}} \\
& \text{Speed of light in medium}=\dfrac{3\times {{10}^{8}}}{1.5}=2\times {{10}^{8}}m{{s}^{-1}}. \\
\end{align}$
Hence the speed of light in glass is $2\times {{10}^{8}}m{{s}^{-1}}$.
Note:

According to Snell’s law, the refractive index of a medium is also given by,
$\eta =\dfrac{\operatorname{Sin}i}{\operatorname{Sin}r}$ where i is the angle of incidence and r is the angle of refraction. Refractive index for glass is greater than one. Hence from this we can imply that angle of incidence is greater than the angle of refraction i.e. light bends as it moves from air to glass. One more key point to be kept in mind is that the frequency of light does not change when a monochromatic light enters from a rarer to denser medium, but its wavelength does.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




