
Light enters at an angle of incidence in a transparent rod of refractive index $n$. For what value of the refractive index of the material of the rod the light once entered into it will not leave it through its lateral face whatsoever be the value of the angle of incidence.
A. $n > \sqrt 2 $
B. $n = 1$
C. $n = 1.1$
D. $n = 1.3$
Answer
495.9k+ views
Hint: The phenomenon in which the light is completely reflected under certain conditions is called Total Internal Reflection. To describe the relationship between the angle of incidence and refraction with the reference of the light or other wave that passes through two different isotropic media, Snell’s law is used. To solve the given problem, consider Snell’s law.
Complete step by step solution:
Given the light enters at the transparent rod at an incidence angle with the refractive index $n$.
To find the value of the refractive index of the rod material in which the light enters and will not leave through the lateral surface.
Consider the given image. Let ABCD be the rod of reference with the refractive index of $n$. It is where the light enters.
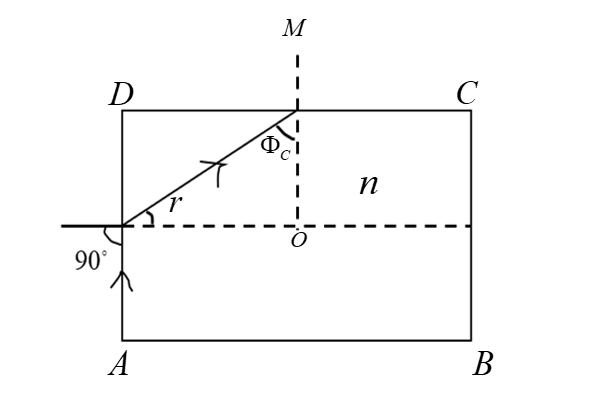
The light enters at the surface of the rod at the angle of ${90^ \circ }$. The light that comes in will not emerge out by the lateral surface.
At any value of the angle of incidence, the light will not emerge out by the lateral surface.
Apply Snell’s law at the surface of AD. Snell’s law is used to describe the relationship between the angle of incidence and refraction with the reference of the light or other wave that passes through two different isotropic media. Applying Snell’s law at AD surfaces,
$ \Rightarrow 1 \times \sin {90^ \circ } = n\sin r$
Where,
\[ \Rightarrow r = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{1}{n}\]
$ \Rightarrow \sin r = \dfrac{1}{n}$
Where, $n$ is the refractive index and $r$ is the angle of refraction.
Consider the total internal reflection at the lateral surface DC. The phenomenon in which the light is completely reflected under certain conditions is called Total Internal Reflection. For the total internal reflection at the lateral surface DC,
$ \Rightarrow {\Phi _C} > r$
The value of ${\Phi _C}$ is given as $\left( {90 - r} \right)$ in DMNO. Substitute,
$ \Rightarrow \left( {90 - r} \right) > r$
$ \Rightarrow 45 > r$
Taking $\sin $ on both sides,
$ \Rightarrow \sin 45 > \sin r$
The value of $\sin {45^ \circ }$ is $\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}$
and we know the value of $\sin r = \dfrac{1}{n}$. Substitute.
$ \Rightarrow \sin \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }} > \sin \dfrac{1}{n}$
$\therefore n > \sqrt 2 $
The value of the refractive index of the rod material in which the light enters and will not leave through the lateral surface is $n > \sqrt 2 $ .
Hence the correct option is $\left( A \right)$.
Note:
There is a wide range of applications in the branch of physics for Snell’s law especially for optics. The law is used in the making process of the apparatus like eyeglasses, cameras, lenses, etc. a refractometer is an instrument that is used to measure the refractive index of the liquids using Snell’s law. In the candy industry, this instrument plays an important role. This law is derived from Fermat’s principle.
Complete step by step solution:
Given the light enters at the transparent rod at an incidence angle with the refractive index $n$.
To find the value of the refractive index of the rod material in which the light enters and will not leave through the lateral surface.
Consider the given image. Let ABCD be the rod of reference with the refractive index of $n$. It is where the light enters.

The light enters at the surface of the rod at the angle of ${90^ \circ }$. The light that comes in will not emerge out by the lateral surface.
At any value of the angle of incidence, the light will not emerge out by the lateral surface.
Apply Snell’s law at the surface of AD. Snell’s law is used to describe the relationship between the angle of incidence and refraction with the reference of the light or other wave that passes through two different isotropic media. Applying Snell’s law at AD surfaces,
$ \Rightarrow 1 \times \sin {90^ \circ } = n\sin r$
Where,
\[ \Rightarrow r = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{1}{n}\]
$ \Rightarrow \sin r = \dfrac{1}{n}$
Where, $n$ is the refractive index and $r$ is the angle of refraction.
Consider the total internal reflection at the lateral surface DC. The phenomenon in which the light is completely reflected under certain conditions is called Total Internal Reflection. For the total internal reflection at the lateral surface DC,
$ \Rightarrow {\Phi _C} > r$
The value of ${\Phi _C}$ is given as $\left( {90 - r} \right)$ in DMNO. Substitute,
$ \Rightarrow \left( {90 - r} \right) > r$
$ \Rightarrow 45 > r$
Taking $\sin $ on both sides,
$ \Rightarrow \sin 45 > \sin r$
The value of $\sin {45^ \circ }$ is $\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}$
and we know the value of $\sin r = \dfrac{1}{n}$. Substitute.
$ \Rightarrow \sin \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }} > \sin \dfrac{1}{n}$
$\therefore n > \sqrt 2 $
The value of the refractive index of the rod material in which the light enters and will not leave through the lateral surface is $n > \sqrt 2 $ .
Hence the correct option is $\left( A \right)$.
Note:
There is a wide range of applications in the branch of physics for Snell’s law especially for optics. The law is used in the making process of the apparatus like eyeglasses, cameras, lenses, etc. a refractometer is an instrument that is used to measure the refractive index of the liquids using Snell’s law. In the candy industry, this instrument plays an important role. This law is derived from Fermat’s principle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




