
Let \[z = x + iy\] be a complex number where \[x\] and \[y\] are integers. Then the area of the rectangle whose vertices are the roots of the equation \[\bar z{z^3} + z{\bar z^3} = 350\] is
A. 48
B. 32
C. 40
D. 80
Answer
591.3k+ views
Hint: Try to take the common terms and apply the formula \[\bar zz = z\bar z = {\left| z \right|^2}\] to reduce the given equation. Then substitute the value of \[z\& \bar z\] to find the equations in terms of \[x\& y\]. Solve those obtained equations to get the vertices of the rectangle and then find its equation to get the final answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given that \[z = x + iy\] be a complex number where \[x\] and \[y\] are integers. So, we have \[\bar z = x - iy\].
Also given that \[\bar z{z^3} + z{\bar z^3} = 350\].
We know that for a complex number \[\bar zz = z\bar z = {\left| z \right|^2}\]. By using this formula, we have
\[
\Rightarrow \left( {\bar zz} \right){z^2} + \left( {z\bar z} \right){z^2} = 350 \\
\Rightarrow \left( {\bar zz} \right){z^2} + \left( {z\bar z} \right){{\bar z}^2} = 350 \\
\Rightarrow {\left| z \right|^2}{z^2} + {\left| z \right|^2}{{\bar z}^2} = 350 \\
\Rightarrow {\left| z \right|^2}\left( {{z^2} + {{\bar z}^2}} \right) = 350 \\
\]
Substituting \[z = x + iy\] and \[\bar z = x - iy\] we have
\[
\Rightarrow {\left| {x + iy} \right|^2}\left[ {{{\left( {x + iy} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {x - iy} \right)}^2}} \right] = 350 \\
\Rightarrow {\left( {\sqrt {{x^2} + {y^2}} } \right)^2}\left[ {{{\left( {x + iy} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {x - iy} \right)}^2}} \right] = 350\,{\text{ }}\left[ {\because \left| z \right| = \left| {a + ib} \right| = \sqrt {{a^2} + {b^2}} } \right] \\
\Rightarrow \left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right)\left[ {\left( {{x^2} + 2xiy + {i^2}{y^2}} \right) + \left( {x - 2xiy + {i^2}{y^2}} \right)} \right] = 350 \\
\Rightarrow \left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right)\left( {{x^2} + {x^2} + 2xiy - 2xiy - {y^2} - {y^2}} \right) = 350{\text{ }}\left[ {\because {i^2} = - 1} \right] \\
\Rightarrow \left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right)\left( {2{x^2} - 2{y^2}} \right) = 350 \\
\Rightarrow \left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right)\left( {{x^2} - {y^2}} \right)2 = 350 \\
\Rightarrow \left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right)\left( {{x^2} - {y^2}} \right) = \dfrac{{350}}{2} = 175 \\
\]
Since, \[x\] and \[y\] are integers we can have two possible ways.
\[\left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right) = 25\& \left( {{x^2} - {y^2}} \right) = 7\] or \[\left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right) = 35\& \left( {{x^2} - {y^2}} \right) = 5\]
Now consider, \[\left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right) = 25\& \left( {{x^2} - {y^2}} \right) = 7\]. Adding both the equations, we have
\[
\Rightarrow \left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right) + \left( {{x^2} - {y^2}} \right) = 25 + 7 \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} + {x^2} + {y^2} - {y^2} = 32 \\
\Rightarrow 2{x^2} = 32 \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} = \dfrac{{32}}{2} = 16 \\
\therefore x = \sqrt {16} = \pm 4...............\left( 1 \right) \\
\]
Subtracting the equation \[{x^2} - {y^2} = 7\] from \[{x^2} + {y^2} = 25\], we get
\[
\Rightarrow \left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right) - \left( {{x^2} - {y^2}} \right) = 25 - 7 \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} - {x^2} + {y^2} + {y^2} = 16 \\
\Rightarrow 2{y^2} = 18 \\
\Rightarrow {y^2} = \dfrac{{18}}{2} = 9 \\
\therefore y = \sqrt 9 = \pm 3 \\
\]
Now, \[\left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right) = 35\& \left( {{x^2} - {y^2}} \right) = 5\]. Adding both the equations, we have
\[
\Rightarrow \left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right) + \left( {{x^2} - {y^2}} \right) = 35 + 5 \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} + {x^2} + {y^2} - {y^2} = 40 \\
\Rightarrow 2{x^2} = 40 \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} = \dfrac{{40}}{2} = 20 \\
\therefore x = \sqrt {20} \\
\]
So, for the equations \[\left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right) = 35\& \left( {{x^2} - {y^2}} \right) = 5\] we are not getting the values of \[x\] and \[y\] as integers.
Therefore, the vertices of the rectangle are \[\left( {x,y} \right) = \left( {4,3} \right),\left( { - 4,3} \right),\left( { - 4, - 3} \right),\left( {4, - 3} \right)\]. Let \[l\] be the length and \[b\] be the width of the rectangle as shown in the figure.
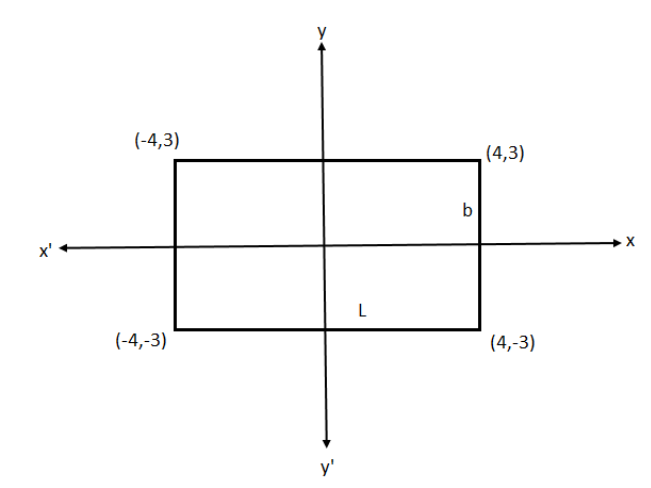
So, \[l\] is the distance between the points \[\left( {4,3} \right),\left( { - 4,3} \right)\].
Hence \[l = \sqrt {{{\left( { - 4 - 4} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {3 - 3} \right)}^2}} = \sqrt {{{\left( { - 8} \right)}^2} + {{\left( 0 \right)}^2}} = 8\]
And \[b\] is the distance between the points \[\left( {4,3} \right),\left( {4, - 3} \right)\]
Hence \[b = \sqrt {{{\left( {4 - 4} \right)}^2} + {{\left( { - 3 - 3} \right)}^2}} = \sqrt {{{\left( 0 \right)}^2} + {{\left( { - 6} \right)}^2}} = \sqrt {{6^2}} = 6\]
We know that if \[l\& b\] are length and breadth of rectangle respectively then its area is given by \[l \times b\]
So, the area of the rectangle formed is equal to \[8 \times 6 = 48\].
Thus, the area of the rectangle formed with the vertices is 48 square units.
Note: The distance between the two points \[\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)\] and \[\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)\] is given by \[\sqrt {{{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2}} \]. If \[l\& b\] are the length and breadth of the rectangle respectively then its area is given by \[l \times b\] square units. Always write the units after the area of the rectangle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given that \[z = x + iy\] be a complex number where \[x\] and \[y\] are integers. So, we have \[\bar z = x - iy\].
Also given that \[\bar z{z^3} + z{\bar z^3} = 350\].
We know that for a complex number \[\bar zz = z\bar z = {\left| z \right|^2}\]. By using this formula, we have
\[
\Rightarrow \left( {\bar zz} \right){z^2} + \left( {z\bar z} \right){z^2} = 350 \\
\Rightarrow \left( {\bar zz} \right){z^2} + \left( {z\bar z} \right){{\bar z}^2} = 350 \\
\Rightarrow {\left| z \right|^2}{z^2} + {\left| z \right|^2}{{\bar z}^2} = 350 \\
\Rightarrow {\left| z \right|^2}\left( {{z^2} + {{\bar z}^2}} \right) = 350 \\
\]
Substituting \[z = x + iy\] and \[\bar z = x - iy\] we have
\[
\Rightarrow {\left| {x + iy} \right|^2}\left[ {{{\left( {x + iy} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {x - iy} \right)}^2}} \right] = 350 \\
\Rightarrow {\left( {\sqrt {{x^2} + {y^2}} } \right)^2}\left[ {{{\left( {x + iy} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {x - iy} \right)}^2}} \right] = 350\,{\text{ }}\left[ {\because \left| z \right| = \left| {a + ib} \right| = \sqrt {{a^2} + {b^2}} } \right] \\
\Rightarrow \left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right)\left[ {\left( {{x^2} + 2xiy + {i^2}{y^2}} \right) + \left( {x - 2xiy + {i^2}{y^2}} \right)} \right] = 350 \\
\Rightarrow \left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right)\left( {{x^2} + {x^2} + 2xiy - 2xiy - {y^2} - {y^2}} \right) = 350{\text{ }}\left[ {\because {i^2} = - 1} \right] \\
\Rightarrow \left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right)\left( {2{x^2} - 2{y^2}} \right) = 350 \\
\Rightarrow \left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right)\left( {{x^2} - {y^2}} \right)2 = 350 \\
\Rightarrow \left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right)\left( {{x^2} - {y^2}} \right) = \dfrac{{350}}{2} = 175 \\
\]
Since, \[x\] and \[y\] are integers we can have two possible ways.
\[\left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right) = 25\& \left( {{x^2} - {y^2}} \right) = 7\] or \[\left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right) = 35\& \left( {{x^2} - {y^2}} \right) = 5\]
Now consider, \[\left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right) = 25\& \left( {{x^2} - {y^2}} \right) = 7\]. Adding both the equations, we have
\[
\Rightarrow \left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right) + \left( {{x^2} - {y^2}} \right) = 25 + 7 \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} + {x^2} + {y^2} - {y^2} = 32 \\
\Rightarrow 2{x^2} = 32 \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} = \dfrac{{32}}{2} = 16 \\
\therefore x = \sqrt {16} = \pm 4...............\left( 1 \right) \\
\]
Subtracting the equation \[{x^2} - {y^2} = 7\] from \[{x^2} + {y^2} = 25\], we get
\[
\Rightarrow \left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right) - \left( {{x^2} - {y^2}} \right) = 25 - 7 \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} - {x^2} + {y^2} + {y^2} = 16 \\
\Rightarrow 2{y^2} = 18 \\
\Rightarrow {y^2} = \dfrac{{18}}{2} = 9 \\
\therefore y = \sqrt 9 = \pm 3 \\
\]
Now, \[\left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right) = 35\& \left( {{x^2} - {y^2}} \right) = 5\]. Adding both the equations, we have
\[
\Rightarrow \left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right) + \left( {{x^2} - {y^2}} \right) = 35 + 5 \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} + {x^2} + {y^2} - {y^2} = 40 \\
\Rightarrow 2{x^2} = 40 \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} = \dfrac{{40}}{2} = 20 \\
\therefore x = \sqrt {20} \\
\]
So, for the equations \[\left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right) = 35\& \left( {{x^2} - {y^2}} \right) = 5\] we are not getting the values of \[x\] and \[y\] as integers.
Therefore, the vertices of the rectangle are \[\left( {x,y} \right) = \left( {4,3} \right),\left( { - 4,3} \right),\left( { - 4, - 3} \right),\left( {4, - 3} \right)\]. Let \[l\] be the length and \[b\] be the width of the rectangle as shown in the figure.

So, \[l\] is the distance between the points \[\left( {4,3} \right),\left( { - 4,3} \right)\].
Hence \[l = \sqrt {{{\left( { - 4 - 4} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {3 - 3} \right)}^2}} = \sqrt {{{\left( { - 8} \right)}^2} + {{\left( 0 \right)}^2}} = 8\]
And \[b\] is the distance between the points \[\left( {4,3} \right),\left( {4, - 3} \right)\]
Hence \[b = \sqrt {{{\left( {4 - 4} \right)}^2} + {{\left( { - 3 - 3} \right)}^2}} = \sqrt {{{\left( 0 \right)}^2} + {{\left( { - 6} \right)}^2}} = \sqrt {{6^2}} = 6\]
We know that if \[l\& b\] are length and breadth of rectangle respectively then its area is given by \[l \times b\]
So, the area of the rectangle formed is equal to \[8 \times 6 = 48\].
Thus, the area of the rectangle formed with the vertices is 48 square units.
Note: The distance between the two points \[\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)\] and \[\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)\] is given by \[\sqrt {{{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2}} \]. If \[l\& b\] are the length and breadth of the rectangle respectively then its area is given by \[l \times b\] square units. Always write the units after the area of the rectangle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




