
Let ABCD be a parallelogram, if F is the midpoint of AB and DF intersects AC at M, \[\overline a = \overline i + \overline j + 3\overline k \], $\overline c = \overline i + \overline j $ where $\overline a $ and $\overline c $ are position vectors of A and C respectively, which of the following is/are correct.
A. Position vector of M is $\overline i + \overline j + 2\overline k $
B. Position vector of M is $\overline i + \overline j + \overline k $
C. DM:MF = 2:1
D. DM:MF = 1:2
Answer
545.1k+ views
Hint: First we have to know about the position vector formula and apply it, then substitute the values in the formula to get the correct solution. Here in any parallelogram the opposite sides are equal and parallel. The diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other and divide the parallelogram into two similar triangles. The opposite angles are congruent.
Complete step by step answer:
Here we use the position vector formula which is given by:
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{m\overline b + n\overline a }}{{m + n}}$
Here to understand the problem we need to have a complete picture of the given parallelogram and the given steps.
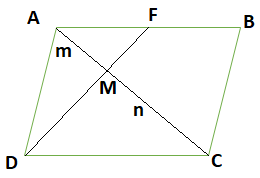
Here as given ABCD is a parallelogram, and F is the midpoint of AB, and DF intersects the diagonal AC at M.
As the diagonals bisect each other, hence the DF divides the diagonal AC at M in the ratio of 1:2, as F is the midpoint of AB.
Thus here MC = 2AM
$\therefore m = 1,n = 2$.
Now applying the position vector formula at the position vector M, as given below:
$ \Rightarrow \overline M = \dfrac{{m\overline a + n\overline c }}{{m + n}}$
Here \[\overline a = \overline i + \overline j + 3\overline k \] and $\overline c = \overline i + \overline j $, substituting in the position vector M:
$ \Rightarrow \overline M = \dfrac{{1(\overline i + \overline j + 3\overline k ) + 2(\overline i + \overline j )}}{{1 + 2}}$
$ \Rightarrow \overline M = \dfrac{{3\overline i + 3\overline j + 3\overline k }}{3}$
Here in the above expression taking 3 common and cancelling the 3 in numerator and the denominator:
$ \Rightarrow \overline M = \dfrac{{3(\overline i + \overline j + \overline k )}}{3}$
\[ \Rightarrow \overline M = \overline i + \overline j + \overline k \]
$\therefore $The position vector of M is \[\overline i + \overline j + \overline k \].
The position vector of M is \[\overline i + \overline j + \overline k \]
Note: It is important to remember when and how to apply the position vector, here when a line is internally divided then the position vector formula of $\overline r = \dfrac{{m\overline b + n\overline a }}{{m + n}}$ is applied, whereas if the line is divided externally then the position vector formula to be applied would be $\overline r = \dfrac{{m\overline b - n\overline a }}{{m - n}}$.
Complete step by step answer:
Here we use the position vector formula which is given by:
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{m\overline b + n\overline a }}{{m + n}}$
Here to understand the problem we need to have a complete picture of the given parallelogram and the given steps.

Here as given ABCD is a parallelogram, and F is the midpoint of AB, and DF intersects the diagonal AC at M.
As the diagonals bisect each other, hence the DF divides the diagonal AC at M in the ratio of 1:2, as F is the midpoint of AB.
Thus here MC = 2AM
$\therefore m = 1,n = 2$.
Now applying the position vector formula at the position vector M, as given below:
$ \Rightarrow \overline M = \dfrac{{m\overline a + n\overline c }}{{m + n}}$
Here \[\overline a = \overline i + \overline j + 3\overline k \] and $\overline c = \overline i + \overline j $, substituting in the position vector M:
$ \Rightarrow \overline M = \dfrac{{1(\overline i + \overline j + 3\overline k ) + 2(\overline i + \overline j )}}{{1 + 2}}$
$ \Rightarrow \overline M = \dfrac{{3\overline i + 3\overline j + 3\overline k }}{3}$
Here in the above expression taking 3 common and cancelling the 3 in numerator and the denominator:
$ \Rightarrow \overline M = \dfrac{{3(\overline i + \overline j + \overline k )}}{3}$
\[ \Rightarrow \overline M = \overline i + \overline j + \overline k \]
$\therefore $The position vector of M is \[\overline i + \overline j + \overline k \].
The position vector of M is \[\overline i + \overline j + \overline k \]
Note: It is important to remember when and how to apply the position vector, here when a line is internally divided then the position vector formula of $\overline r = \dfrac{{m\overline b + n\overline a }}{{m + n}}$ is applied, whereas if the line is divided externally then the position vector formula to be applied would be $\overline r = \dfrac{{m\overline b - n\overline a }}{{m - n}}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




