
Let $ABC$ is an equilateral triangle of side \[10m\] and $D$ is the midpoint of $BC$ . Charges of $ + 100, - 100{\text{ and }} + 75\mu C$ bs are placed at $B,C,D$ respectively. Find the force on a $ + 1\mu C$ charge placed at$A$ . (Give your answer in S.I. unit).
Answer
497.4k+ views
Hint:To solve this question firstly we will draw the figure and simplify the forces on $ + 1\mu C$ . We will calculate the net electric field along the x-axis and then net field of point $A$ , after net force acting on the point charger of $ + 1\mu C$ .
Formula used:
$E = \dfrac{{kq}}{{{r^2}}}$
$\Rightarrow F = qE$
Where, $E$ is the electric field strength,$k = 9 \times {10^9}$ is the electrostatic constant,$q$ is the charge, $r$ is the distance to the charge creating the field and $F$ is the force.
Complete step by step answer:
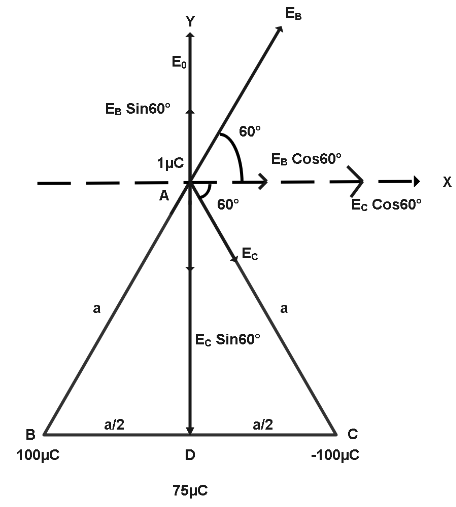
Now, we will calculate net field along -axis at point $A$
$E(x) = E(B)\operatorname{Cos} {60^ \circ } + E(C)\operatorname{Cos} {60^ \circ } \\
\Rightarrow E(y) = E(D) + E(B)\operatorname{Sin} {60^ \circ } - E(C)\operatorname{Sin} {60^ \circ } $
Given that,
$a = 10m$
$\Rightarrow Q(A) = 1\mu C$
$\Rightarrow Q(B) = 100\mu C$
$\Rightarrow Q(C) = - 100\mu C$
$\Rightarrow Q(D) = 75\mu C$
$\Rightarrow k = 9 \times {10^9}N{M^2}{\text{ }}{C^{ - 2}}$
Now electric field at $A$
$\because {E_A} = k\dfrac{{{Q_A}}}{{{a^2}}} \\
\Rightarrow {E_A} = 9 \times {10^9} \times \dfrac{{100 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}}}{{{{10}^2}}} \\
\Rightarrow {E_A} = 9000N{\text{ }}{C^{ - 1}} \\ $
Now, electric field at $B$ is $E(B)$
$\because {E_B} = k\dfrac{{{Q_B}}}{{{a^2}}} \\
\Rightarrow {E_B} = 9 \times {10^9} \times \dfrac{{100 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}}}{{{{10}^2}}} \\
\Rightarrow {E_B} = 9000N{\text{ }}{C^{ - 1}} \\ $
Now,electric field at $D$ is $E(D)$
$\because {E_D} = k\dfrac{{{Q_D}}}{{{a^2}}} \\
\Rightarrow {E_D} = 9 \times {10^9} \times \dfrac{{75 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}}}{{\dfrac{{3 \times {{10}^2}}}{4}}} \\
\Rightarrow {E_D} = 900 \times {10^{(9 - 6 - 2)}} \\
\Rightarrow {E_D} = 9000N{\text{ }}{C^{ - 1}} \\ $
So,
$E(x) = 9000\cos {60^ \circ } + 9000\cos {60^ \circ } \\
\Rightarrow E(x) = \left( {9000 \times \dfrac{1}{2}} \right) \times 2 \\
\Rightarrow E(x) = 9000N{\text{ }}{C^{ - 1}} \\ $
Now,
$E(y) = 9000 + 9000\cos {60^ \circ } + 9000\cos {60^ \circ } \\
\Rightarrow E(y) = 9000N{\text{ }}{C^{ - 1}} \\ $
So, net electric field at $A$
${E_n} = \sqrt {E_x^2 + E_y^2} \\
\Rightarrow {E_n} = \sqrt {{{(9000)}^2} + {{(9000)}^2}} \\
\Rightarrow {E_n} = 9000\sqrt 2 \\
\Rightarrow {E_n} = 12727.9N{\text{ }}{C^{ - 1}} \\ $
So, net force acting on point charge of $ + 1\mu C$ is Given By
$F = qE \\
\Rightarrow F = 1 \times {10^{ - 6}} \times 12727.9 \\
\therefore F = 12.73 \times {10^{ - 2}}N \\ $
Hence, the net force acting on $ + 1\mu C$ is $12.73 \times {10^{ - 2}}N$.
Note:While simplifying the forces don’t make mistakes in angles go step by step calculation to avoid mistakes. The repulsive or attractive interaction between any two charged bodies is called an electric force. Similar to any force, its impact and effects on the given body are described by Newton's laws of motion.
Formula used:
$E = \dfrac{{kq}}{{{r^2}}}$
$\Rightarrow F = qE$
Where, $E$ is the electric field strength,$k = 9 \times {10^9}$ is the electrostatic constant,$q$ is the charge, $r$ is the distance to the charge creating the field and $F$ is the force.
Complete step by step answer:

Now, we will calculate net field along -axis at point $A$
$E(x) = E(B)\operatorname{Cos} {60^ \circ } + E(C)\operatorname{Cos} {60^ \circ } \\
\Rightarrow E(y) = E(D) + E(B)\operatorname{Sin} {60^ \circ } - E(C)\operatorname{Sin} {60^ \circ } $
Given that,
$a = 10m$
$\Rightarrow Q(A) = 1\mu C$
$\Rightarrow Q(B) = 100\mu C$
$\Rightarrow Q(C) = - 100\mu C$
$\Rightarrow Q(D) = 75\mu C$
$\Rightarrow k = 9 \times {10^9}N{M^2}{\text{ }}{C^{ - 2}}$
Now electric field at $A$
$\because {E_A} = k\dfrac{{{Q_A}}}{{{a^2}}} \\
\Rightarrow {E_A} = 9 \times {10^9} \times \dfrac{{100 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}}}{{{{10}^2}}} \\
\Rightarrow {E_A} = 9000N{\text{ }}{C^{ - 1}} \\ $
Now, electric field at $B$ is $E(B)$
$\because {E_B} = k\dfrac{{{Q_B}}}{{{a^2}}} \\
\Rightarrow {E_B} = 9 \times {10^9} \times \dfrac{{100 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}}}{{{{10}^2}}} \\
\Rightarrow {E_B} = 9000N{\text{ }}{C^{ - 1}} \\ $
Now,electric field at $D$ is $E(D)$
$\because {E_D} = k\dfrac{{{Q_D}}}{{{a^2}}} \\
\Rightarrow {E_D} = 9 \times {10^9} \times \dfrac{{75 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}}}{{\dfrac{{3 \times {{10}^2}}}{4}}} \\
\Rightarrow {E_D} = 900 \times {10^{(9 - 6 - 2)}} \\
\Rightarrow {E_D} = 9000N{\text{ }}{C^{ - 1}} \\ $
So,
$E(x) = 9000\cos {60^ \circ } + 9000\cos {60^ \circ } \\
\Rightarrow E(x) = \left( {9000 \times \dfrac{1}{2}} \right) \times 2 \\
\Rightarrow E(x) = 9000N{\text{ }}{C^{ - 1}} \\ $
Now,
$E(y) = 9000 + 9000\cos {60^ \circ } + 9000\cos {60^ \circ } \\
\Rightarrow E(y) = 9000N{\text{ }}{C^{ - 1}} \\ $
So, net electric field at $A$
${E_n} = \sqrt {E_x^2 + E_y^2} \\
\Rightarrow {E_n} = \sqrt {{{(9000)}^2} + {{(9000)}^2}} \\
\Rightarrow {E_n} = 9000\sqrt 2 \\
\Rightarrow {E_n} = 12727.9N{\text{ }}{C^{ - 1}} \\ $
So, net force acting on point charge of $ + 1\mu C$ is Given By
$F = qE \\
\Rightarrow F = 1 \times {10^{ - 6}} \times 12727.9 \\
\therefore F = 12.73 \times {10^{ - 2}}N \\ $
Hence, the net force acting on $ + 1\mu C$ is $12.73 \times {10^{ - 2}}N$.
Note:While simplifying the forces don’t make mistakes in angles go step by step calculation to avoid mistakes. The repulsive or attractive interaction between any two charged bodies is called an electric force. Similar to any force, its impact and effects on the given body are described by Newton's laws of motion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




