
Length of the intercept of the normal at the point \[P\left( a{{t}^{2}},2at \right)\] of the parabola \[{{y}^{2}}=4ax\] made by the circle described on the focal distance of the point \[P\] as diameter is:
(A) \[a\sqrt{2+{{t}^{2}}}\]
(B) \[\dfrac{a}{2}\sqrt{1+{{t}^{2}}}\]
(C) \[2a\sqrt{1+{{t}^{2}}}\]
(D) \[a\sqrt{1+{{t}^{2}}}\]
Answer
595.5k+ views
Hint: First of all, we have to make a proper diagram for the given data. We have to draw the parabola \[{{y}^{2}}=4ax\] and draw a circle such that it passes through the point \[P\left( a{{t}^{2}},2at \right)\] on the parabola and the focus S of the parabola. Then, we can form a right-angled triangle and apply Pythagoras theorem to obtain the length of the intercept. We will also need formulas like distance formula, $\sqrt{{{({{x}_{1}}-{{x}_{2}})}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{1}}-{{y}_{2}} \right)}^{2}}}$ and distance between point and line, \[d=\left| \dfrac{Am+Bn+C}{\sqrt{{{A}^{2}}+{{B}^{2}}}} \right|\] .
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given, parabola is \[{{y}^{2}}=4ax\], whose focus S is \[\left( a,0 \right)\].
The normal equation of \[{{y}^{2}}=4ax\] at point \[P\left( a{{t}^{2}},2at \right)\] is given as: \[y=tx+2at+{{t}^{3}}\].
Now let this normal meet the described circle at the point N.
Then, \[\angle SNP={{90}^{\circ }}\].
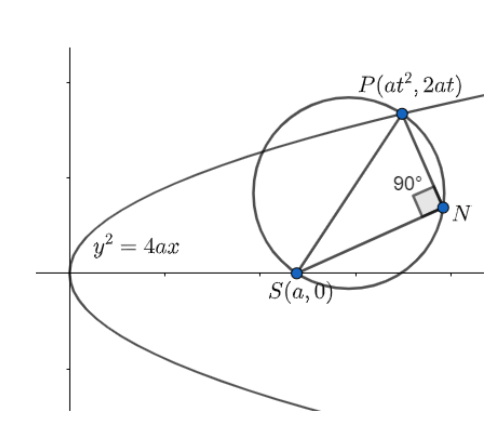
Now as per the Pythagoras theorem, we know the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the square of sum of the other two sides.
So, by applying Pythagorean theorem in \[\Delta SNP\], we have
\[P{{N}^{2}}=S{{P}^{2}}-S{{N}^{2}}\],
Now distance between two points $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right),\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)$ is given by the formula,
$\sqrt{{{({{x}_{1}}-{{x}_{2}})}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{1}}-{{y}_{2}} \right)}^{2}}}$
Now using the distance formula, the distance between \[P\left( a{{t}^{2}},2at \right)\] and \[S(a,0)\] is:
\[SP=\sqrt{{{\left( a-a{{t}^{2}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -2at \right)}^{2}}}\]
\[SP=\sqrt{{{\left( a-a{{t}^{2}} \right)}^{2}}+4a{{t}^{2}}}\]
\[SP=\sqrt{{{\left( a+a{{t}^{2}} \right)}^{2}}}\]
\[SP=a+a{{t}^{2}}\]
Now the distance from a point (m, n) to a line, Ax + By + C = 0, is given by the formula, we get
\[d=\left| \dfrac{Am+Bn+C}{\sqrt{{{A}^{2}}+{{B}^{2}}}} \right|\]
Now the distance between \[S\left( a,0 \right)\] and \[y=tx+2at+{{t}^{3}}\] is found to be;
\[SN=\left| \dfrac{at-2at-a{{t}^{3}}}{\sqrt{1+{{t}^{2}}}} \right|\]
\[SN=\dfrac{at+a{{t}^{3}}}{\sqrt{1+{{t}^{2}}}}\]
\[SN=\dfrac{at+\left( 1+{{t}^{2}} \right)}{\sqrt{1+{{t}^{2}}}}\]
\[SN=at\left( \sqrt{1+{{t}^{2}}} \right)\]
As we know, \[P{{N}^{2}}=S{{P}^{2}}-S{{N}^{2}}\], substituting we get:
\[P{{N}^{2}}={{\left( a+a{{t}^{2}} \right)}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}{{t}^{2}}\left( 1+{{t}^{2}} \right)\]
\[={{a}^{2}}\left[ 1+{{t}^{4}}+2{{t}^{2}}-{{t}^{2}}-{{t}^{4}} \right]\]
\[={{a}^{2}}\left[ 1+{{t}^{2}} \right]\]
\[PN=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}\left( 1+{{t}^{2}} \right)}\] = \[a\sqrt{1+{{t}^{2}}}\].
So, the length of intercept is \[a\sqrt{1+{{t}^{2}}}\].
Note: Remember that lines drawn from each end of the diameter to any point on the semicircle, makes an angle 90 degrees at the intersection of these lines. Most students are not able to solve the question completely because they get stuck while finding SN, so to avoid this it is necessary that students must learn the formula of normal to parabola \[y=tx+2at+{{t}^{3}}\] for completing the question. Any sort of silly mistakes or calculations errors while finding the distances must be taken care of.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given, parabola is \[{{y}^{2}}=4ax\], whose focus S is \[\left( a,0 \right)\].
The normal equation of \[{{y}^{2}}=4ax\] at point \[P\left( a{{t}^{2}},2at \right)\] is given as: \[y=tx+2at+{{t}^{3}}\].
Now let this normal meet the described circle at the point N.
Then, \[\angle SNP={{90}^{\circ }}\].

Now as per the Pythagoras theorem, we know the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the square of sum of the other two sides.
So, by applying Pythagorean theorem in \[\Delta SNP\], we have
\[P{{N}^{2}}=S{{P}^{2}}-S{{N}^{2}}\],
Now distance between two points $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right),\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)$ is given by the formula,
$\sqrt{{{({{x}_{1}}-{{x}_{2}})}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{1}}-{{y}_{2}} \right)}^{2}}}$
Now using the distance formula, the distance between \[P\left( a{{t}^{2}},2at \right)\] and \[S(a,0)\] is:
\[SP=\sqrt{{{\left( a-a{{t}^{2}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -2at \right)}^{2}}}\]
\[SP=\sqrt{{{\left( a-a{{t}^{2}} \right)}^{2}}+4a{{t}^{2}}}\]
\[SP=\sqrt{{{\left( a+a{{t}^{2}} \right)}^{2}}}\]
\[SP=a+a{{t}^{2}}\]
Now the distance from a point (m, n) to a line, Ax + By + C = 0, is given by the formula, we get
\[d=\left| \dfrac{Am+Bn+C}{\sqrt{{{A}^{2}}+{{B}^{2}}}} \right|\]
Now the distance between \[S\left( a,0 \right)\] and \[y=tx+2at+{{t}^{3}}\] is found to be;
\[SN=\left| \dfrac{at-2at-a{{t}^{3}}}{\sqrt{1+{{t}^{2}}}} \right|\]
\[SN=\dfrac{at+a{{t}^{3}}}{\sqrt{1+{{t}^{2}}}}\]
\[SN=\dfrac{at+\left( 1+{{t}^{2}} \right)}{\sqrt{1+{{t}^{2}}}}\]
\[SN=at\left( \sqrt{1+{{t}^{2}}} \right)\]
As we know, \[P{{N}^{2}}=S{{P}^{2}}-S{{N}^{2}}\], substituting we get:
\[P{{N}^{2}}={{\left( a+a{{t}^{2}} \right)}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}{{t}^{2}}\left( 1+{{t}^{2}} \right)\]
\[={{a}^{2}}\left[ 1+{{t}^{4}}+2{{t}^{2}}-{{t}^{2}}-{{t}^{4}} \right]\]
\[={{a}^{2}}\left[ 1+{{t}^{2}} \right]\]
\[PN=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}\left( 1+{{t}^{2}} \right)}\] = \[a\sqrt{1+{{t}^{2}}}\].
So, the length of intercept is \[a\sqrt{1+{{t}^{2}}}\].
Note: Remember that lines drawn from each end of the diameter to any point on the semicircle, makes an angle 90 degrees at the intersection of these lines. Most students are not able to solve the question completely because they get stuck while finding SN, so to avoid this it is necessary that students must learn the formula of normal to parabola \[y=tx+2at+{{t}^{3}}\] for completing the question. Any sort of silly mistakes or calculations errors while finding the distances must be taken care of.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




