
$\left( {}_{32}G{{e}^{76}},{}_{34}S{{e}^{76}} \right) and \left( {}_{14}S{{i}^{30}},{}_{16}{{S}^{32}} \right)$ and are examples of:
A. isotopes and isobars
B. isobars and isotones
C. isotones and isotopes
D. isobars and isotopes
Answer
592.8k+ views
Hint: In nuclear chemistry, the nuclides are classified based on the number of protons and neutrons of the nuclei as isotopes, isotones and isobars. We represent nuclide by:
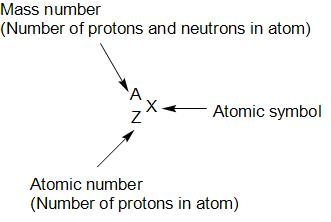
Complete step by step answer:
- Let’s discuss about $\left( {}_{32}G{{e}^{76}},{}_{34}S{{e}^{76}} \right)$ first:
In the above example we can see that Ge and Se are having the same mass number that is A = 76. And these differ in atomic number or we can say proton number, that are: 32 and 34.
Ge will have total neutron = mass number - atomic number. That is 76 - 32 = 44 neutrons.
So will have total neutron = mass number - atomic number. That is 76 - 34 = 42 neutrons.
- These are examples of isobars. As, isobars are the nuclei of neighbouring elements having the same mass number. They however differ, in atomic numbers and therefore in the number of neutrons also.
- Let’s discuss about $\left( {}_{14}S{{i}^{30}},{}_{16}{{S}^{32}} \right)$:
In this example we can see that the atomic masses of both are different: Si is having atomic mass 30 and S is having atomic mass 32. These are atomic numbers 14 and 16.
Silicon will have total neutron = mass number - atomic number. That is 30 - 14 = 16 neutrons.
Sulphur will have total neutron = mass number - atomic number. That is 32 - 16 = 16 neutrons.
- This is an example of isotones, as isotones are the nuclei that contain the same number of neutrons. The nuclei however differ in number of protons and also in mass number.
So, the answer is “(B) isobars and isotones”.
Note: We should not get confused in the terms isotone, isotope and isobars. Isobars have the same mass number and differ in atomic number and hence in number of neutrons also. Isotones have the same number of neutrons and differ in the number of protons and also in mass number. Isotopes are nuclei that belong to the same element and hence contain the same number of protons. These differ in the number of neutrons and hence in mass number.

Complete step by step answer:
- Let’s discuss about $\left( {}_{32}G{{e}^{76}},{}_{34}S{{e}^{76}} \right)$ first:
In the above example we can see that Ge and Se are having the same mass number that is A = 76. And these differ in atomic number or we can say proton number, that are: 32 and 34.
Ge will have total neutron = mass number - atomic number. That is 76 - 32 = 44 neutrons.
So will have total neutron = mass number - atomic number. That is 76 - 34 = 42 neutrons.
- These are examples of isobars. As, isobars are the nuclei of neighbouring elements having the same mass number. They however differ, in atomic numbers and therefore in the number of neutrons also.
- Let’s discuss about $\left( {}_{14}S{{i}^{30}},{}_{16}{{S}^{32}} \right)$:
In this example we can see that the atomic masses of both are different: Si is having atomic mass 30 and S is having atomic mass 32. These are atomic numbers 14 and 16.
Silicon will have total neutron = mass number - atomic number. That is 30 - 14 = 16 neutrons.
Sulphur will have total neutron = mass number - atomic number. That is 32 - 16 = 16 neutrons.
- This is an example of isotones, as isotones are the nuclei that contain the same number of neutrons. The nuclei however differ in number of protons and also in mass number.
So, the answer is “(B) isobars and isotones”.
Note: We should not get confused in the terms isotone, isotope and isobars. Isobars have the same mass number and differ in atomic number and hence in number of neutrons also. Isotones have the same number of neutrons and differ in the number of protons and also in mass number. Isotopes are nuclei that belong to the same element and hence contain the same number of protons. These differ in the number of neutrons and hence in mass number.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




