
\[\left( + \right)\text{ }-\] sucrose is made up of:
a.D-glucose and L-fructose.
b.D-glucose and D-fructose.
c.L-glucose and D-fructose.
d.L-glucose and L-fructose.
Answer
526.8k+ views
Hint: We know that sucrose is a disaccharide that is formed by the addition of a glucose molecule and a fructose molecule by the formation of a glycoside bond between them, with the release of a water molecule from it. Thus, sucrose formation is a result of the dehydration process.
Complete step by step solution:
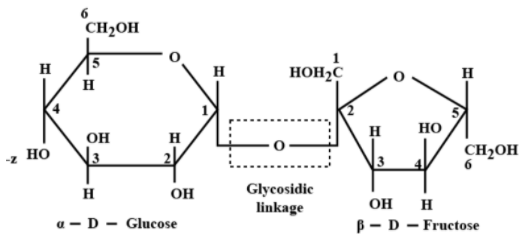
Sucrose is a natural polysaccharide with the molecular formula On \[{{C}_{12}}{{H}_{22}}{{O}_{11}}\] hydrolysis in acidic medium sucrose gives to two different monosaccharide’s which are Glucose and fructose
\[\underset{Sucrose}{\mathop{\left[ {{C}_{12}}{{H}_{22}}{{O}_{11}} \right]}}\,+\underset{Water}{\mathop{\left[ {{H}_{2}}O \right]}}\,\xrightarrow{{}}\underset{D-(+)-Glucose}{\mathop{\left[ {{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}} \right]}}\,+\underset{D-(-)Fructose}{\mathop{\left[ {{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}} \right]}}\,.\]
Predominantly glucose forms pyranose rings as it contains aldehyde \[\left( CHO \right)\] group at the end of the chain. The pyranose ring is a six-membered ring with five predominantly glucose forms pyranose rings as it contains aldehyde \[\left( CHO \right)\] group at the end of the chain. The pyranose ring is a six-membered ring with five carbon atoms and one oxygen atom in it. So, the glucose exists as a pyranose form in sucrose.
As the hemiacetal group and the hydroxyl \[~\left( -OH \right)\] group lie on opposite sides to each other in a glucopyranose ring, this pyranose form of glucose is named alpha pyranose. Hence the glucose unit in sucrose is -D-glucopyranose. But mostly fructose forms furanose rings as it contains ketone groups at the second carbon of the chain.
Therefore, the correct answer is option B.
Note:
Remember that for human consumption, sucrose is extracted and refined from either sugarcane or sugar beet. The sugar mills that are present in the tropical regions near where sugarcane is grown, the cane is crushed there and raw sugar is produced which is shipped to other factories for refining into pure sucrose and for the removal of toxic substances and impurities.
Complete step by step solution:
Sucrose is a natural polysaccharide with the molecular formula On \[{{C}_{12}}{{H}_{22}}{{O}_{11}}\] hydrolysis in acidic medium sucrose gives to two different monosaccharide’s which are Glucose and fructose
\[\underset{Sucrose}{\mathop{\left[ {{C}_{12}}{{H}_{22}}{{O}_{11}} \right]}}\,+\underset{Water}{\mathop{\left[ {{H}_{2}}O \right]}}\,\xrightarrow{{}}\underset{D-(+)-Glucose}{\mathop{\left[ {{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}} \right]}}\,+\underset{D-(-)Fructose}{\mathop{\left[ {{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}} \right]}}\,.\]
Predominantly glucose forms pyranose rings as it contains aldehyde \[\left( CHO \right)\] group at the end of the chain. The pyranose ring is a six-membered ring with five predominantly glucose forms pyranose rings as it contains aldehyde \[\left( CHO \right)\] group at the end of the chain. The pyranose ring is a six-membered ring with five carbon atoms and one oxygen atom in it. So, the glucose exists as a pyranose form in sucrose.
As the hemiacetal group and the hydroxyl \[~\left( -OH \right)\] group lie on opposite sides to each other in a glucopyranose ring, this pyranose form of glucose is named alpha pyranose. Hence the glucose unit in sucrose is -D-glucopyranose. But mostly fructose forms furanose rings as it contains ketone groups at the second carbon of the chain.

Therefore, the correct answer is option B.
Note:
Remember that for human consumption, sucrose is extracted and refined from either sugarcane or sugar beet. The sugar mills that are present in the tropical regions near where sugarcane is grown, the cane is crushed there and raw sugar is produced which is shipped to other factories for refining into pure sucrose and for the removal of toxic substances and impurities.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




