
What law of thermodynamics explains why only a fraction of the energy ingested by organism A is used in making new cells or growing?
 A. The first law of thermodynamics, which states that matter is never created or destroyed.
A. The first law of thermodynamics, which states that matter is never created or destroyed.
B. The first law of thermodynamics which deals with the conservation of energy.
C. The second law of thermodynamics, which explains that all systems seek entropy.
D. The second law of thermodynamics which deals with the conservation of momentum in a physical system.

Answer
580.2k+ views
Hint: The first law of thermodynamics, one form of energy is converted into another form of energy. The second law states that the total entropy of the system can never decrease.
Step by step answer:The first law of thermodynamics defines the law of conservation of energy. According to the law of conservation of energy, the total energy of an isolated system remains constant. It also means energy can neither be created nor can be destroyed but can only be transformed or transferred from one form of energy to another form of energy. For example, when a stick of dynamite explodes, chemical energy is converted into kinetic energy.
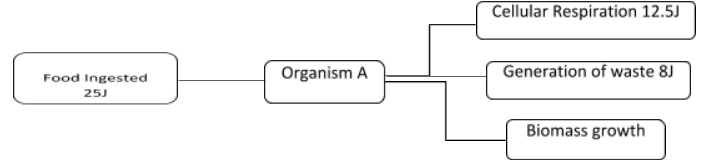
The food ingested by an organism is used for various cellular level activities like cellular respiration, ATP generation, waste generation, and also lost as heat. So, here the energy is distributed for all the purposes and not utilized only for cell growth and development.
Therefore, from all the options provided above, option B: the first law of thermodynamics which deals with the conservation of energy is the appropriate and correct answer.
Note:Conservation of energy for some systems which do not have time translation symmetry. A mathematical transformation in physics that moves the times of events through a common interval is called time translation symmetry. The Law of conservation of energy is not only applicable for living organisms but it is used in chemistry, physics, mathematics, quantum theory, and mechanics. However, conservation of mass is different from the conservation of energy.
Step by step answer:The first law of thermodynamics defines the law of conservation of energy. According to the law of conservation of energy, the total energy of an isolated system remains constant. It also means energy can neither be created nor can be destroyed but can only be transformed or transferred from one form of energy to another form of energy. For example, when a stick of dynamite explodes, chemical energy is converted into kinetic energy.
The food ingested by an organism is used for various cellular level activities like cellular respiration, ATP generation, waste generation, and also lost as heat. So, here the energy is distributed for all the purposes and not utilized only for cell growth and development.
Therefore, from all the options provided above, option B: the first law of thermodynamics which deals with the conservation of energy is the appropriate and correct answer.
Note:Conservation of energy for some systems which do not have time translation symmetry. A mathematical transformation in physics that moves the times of events through a common interval is called time translation symmetry. The Law of conservation of energy is not only applicable for living organisms but it is used in chemistry, physics, mathematics, quantum theory, and mechanics. However, conservation of mass is different from the conservation of energy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




