
What isomerism is exhibited by the following pairs of compounds?
$C{H_3}C{H_2}CH = C{H_2}$ And $C{H_3}CH = CHC{H_3}$
$(A)$ Functional
$(B)$ Positional
$(C)$ Chain
$(D)$ Tautomerism
Answer
504k+ views
Hint: Isomers are molecule or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formulas that are the same number of atoms of each element but distinct arrangements of atoms in space and having different chemical and physical properties. There are two main forms of isomerism which are structural or constitutional isomerism and stereoisomerism.
Complete answer:
The following pair is positional isomerism. Positional isomerism are constitutional isomers that have the same carbon skeleton and the same functional groups but differ from each other in the location of the functional groups on or in the carbon chain.
\[1\]-Butene and \[2\]-Butene are constitutional isomerism.
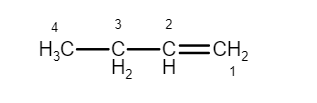
(\[1\]-Butene)
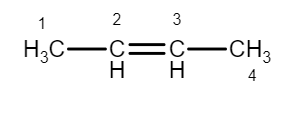
(\[2\]-Butene)
They have the same carbon skeleton, they have the same functional group, an alkene group. The difference between the \[1\]-Butene and \[2\]-Butene is in the location of the alkene group in the carbon chain. In \[1\]-Butene, the alkene group is terminal; in \[2\]-Butene it is internal.The number of possible constitutional isomers increases greatly with the number of available atoms. There are only two butanes, but there are three pentanes, \[18\] octanes.
Thus the correct option for the given question is option (B).
Note:
The simplest hydrocarbon methane\[(C{H_4})\] and propane\[(C{H_3}C{H_3})\] have no constitutional isomers, as there is no other way to connect the carbons and hydrogens of these molecules consistent with the tetravalency of carbon and the univalency of hydrogen. Timing and energy are also factors of isomerism.
Complete answer:
The following pair is positional isomerism. Positional isomerism are constitutional isomers that have the same carbon skeleton and the same functional groups but differ from each other in the location of the functional groups on or in the carbon chain.
\[1\]-Butene and \[2\]-Butene are constitutional isomerism.

(\[1\]-Butene)

(\[2\]-Butene)
They have the same carbon skeleton, they have the same functional group, an alkene group. The difference between the \[1\]-Butene and \[2\]-Butene is in the location of the alkene group in the carbon chain. In \[1\]-Butene, the alkene group is terminal; in \[2\]-Butene it is internal.The number of possible constitutional isomers increases greatly with the number of available atoms. There are only two butanes, but there are three pentanes, \[18\] octanes.
Thus the correct option for the given question is option (B).
Note:
The simplest hydrocarbon methane\[(C{H_4})\] and propane\[(C{H_3}C{H_3})\] have no constitutional isomers, as there is no other way to connect the carbons and hydrogens of these molecules consistent with the tetravalency of carbon and the univalency of hydrogen. Timing and energy are also factors of isomerism.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




