
Is pyrene an aromatic hydrocarbon?
Answer
489.9k+ views
Hint: As we know that aromatic hydrocarbons is a cyclic hydrocarbon with alternating double and single bonds. Aromatic hydrocarbons have $ \left( {4n + 2} \right)\pi $ electrons. The most common example of aromatic hydrocarbon is benzene.
Complete answer:
We know that aromatic hydrocarbons is a cyclic hydrocarbon with alternating double and single bonds. According to Huckel’s rule of aromaticity, aromatic hydrocarbon has $ \left( {4n + 2} \right)\pi $
electrons.
In the given question, we are asked to determine whether pyrene is an aromatic hydrocarbon or not. For this, first let’s see the structure of pyrene.
Structure of pyrene-
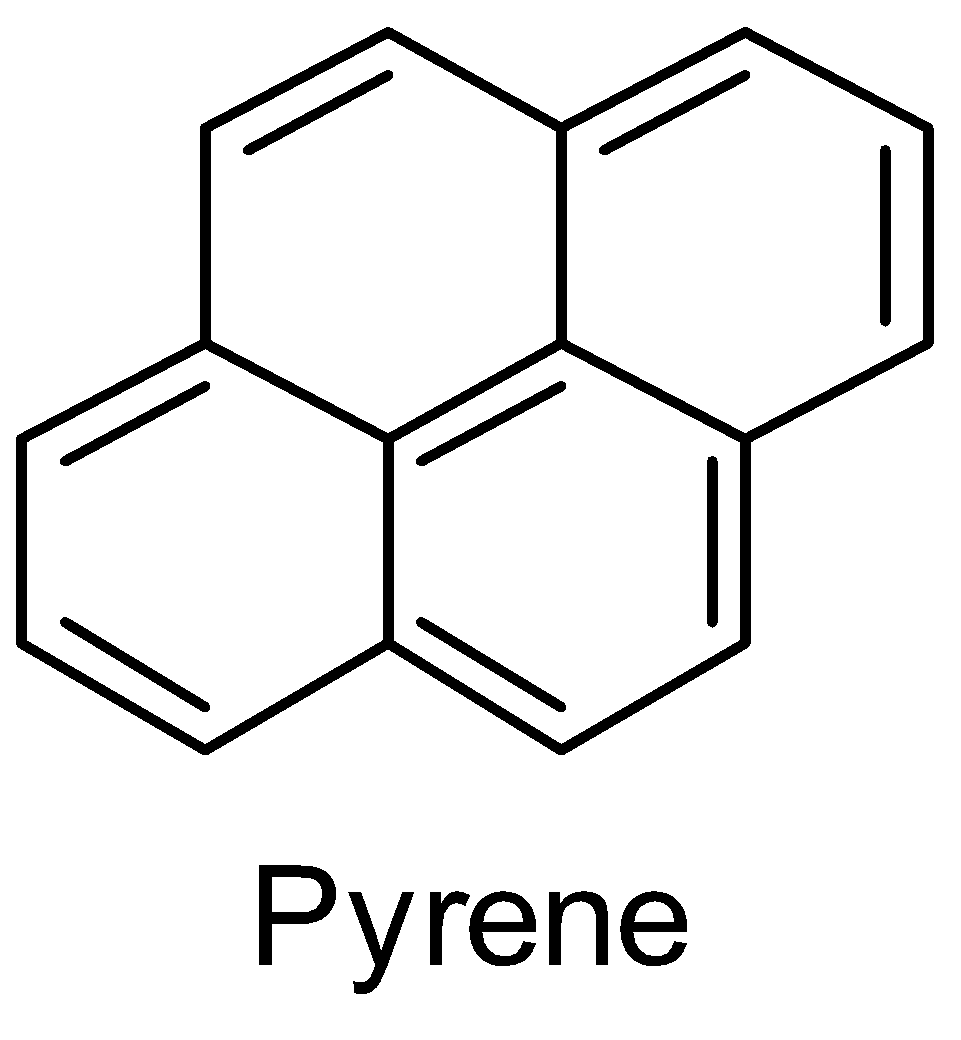
Pyrene belongs to the group of compounds called polycyclic aromatic compounds. The structure of pyrene shows three benzene rings. By drawing the resonance of the pyrene structure, the fourth ring is also a benzene ring. We can say that pyrene is a resonance hybrid with four benzene rings.
Pyrene also has $ \left( {4n + 2} \right)\pi $ electrons which satisfies the Huckel’s rule for aromaticity i.e. $ \left( {4n + 2} \right)\pi $ electrons where $ n = 3 $ .
Therefore, pyrene is an aromatic hydrocarbon.
Additional Information:
There are some other examples of aromatic hydrocarbons such as naphthalene that has $ 10\pi $ electrons and anthracene which has $ \left( {4n + 2} \right)\pi $ electrons. They both aromatic hydrocarbons satisfy Huckel’s rule of aromaticity.
Note:
Aromatic hydrocarbons are more stable than their non-cyclic counterparts. The carbon-carbon bonds in aromatic hydrocarbons are equivalent. The alternating double and single bonds with different lengths. They are all the same length and equivalent to each other. To show symmetry, we often use a circle in the formula of aromatic hydrocarbons to represent pi-electrons. Most of the aromatic compounds contain six carbon rings.
Complete answer:
We know that aromatic hydrocarbons is a cyclic hydrocarbon with alternating double and single bonds. According to Huckel’s rule of aromaticity, aromatic hydrocarbon has $ \left( {4n + 2} \right)\pi $
electrons.
In the given question, we are asked to determine whether pyrene is an aromatic hydrocarbon or not. For this, first let’s see the structure of pyrene.
Structure of pyrene-

Pyrene belongs to the group of compounds called polycyclic aromatic compounds. The structure of pyrene shows three benzene rings. By drawing the resonance of the pyrene structure, the fourth ring is also a benzene ring. We can say that pyrene is a resonance hybrid with four benzene rings.
Pyrene also has $ \left( {4n + 2} \right)\pi $ electrons which satisfies the Huckel’s rule for aromaticity i.e. $ \left( {4n + 2} \right)\pi $ electrons where $ n = 3 $ .
Therefore, pyrene is an aromatic hydrocarbon.
Additional Information:
There are some other examples of aromatic hydrocarbons such as naphthalene that has $ 10\pi $ electrons and anthracene which has $ \left( {4n + 2} \right)\pi $ electrons. They both aromatic hydrocarbons satisfy Huckel’s rule of aromaticity.
Note:
Aromatic hydrocarbons are more stable than their non-cyclic counterparts. The carbon-carbon bonds in aromatic hydrocarbons are equivalent. The alternating double and single bonds with different lengths. They are all the same length and equivalent to each other. To show symmetry, we often use a circle in the formula of aromatic hydrocarbons to represent pi-electrons. Most of the aromatic compounds contain six carbon rings.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




