
Is light converging or diverging when reflected off a concave mirror?
Answer
493.2k+ views
Hint: This question is based on the concept of reflection of light. Reflection of light is the phenomenon of bouncing back of light in the same medium on striking the surface of any object. It can also be said that reflection occurs when light travelling through one material bounces off a different material.
Complete step by step answer:
To understand the reflection of light, we need to understand the laws of reflection. There are two laws of reflection:
(1) The first law of reflection states that the incident ray, reflected ray and the normal, all lie in the same plane.
(2) The second law of reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
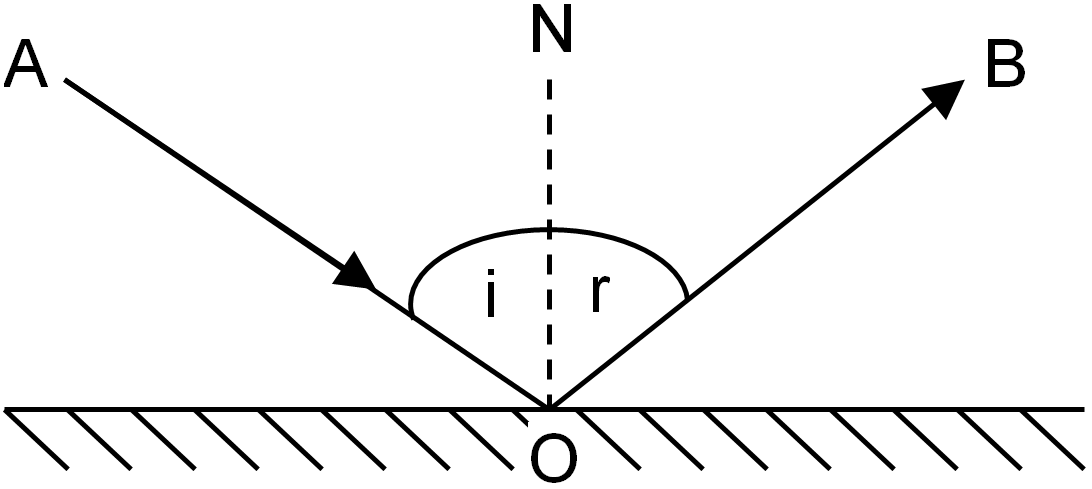
There are basically two types of mirror on the basis of reflection of light, namely, concave mirror and convex mirror.
A concave mirror has a reflective surface that is curved inward and away from the light source. The concave mirror is also known as a converging mirror as it converges the ray of light. A convex mirror has a reflective surface that is curved inward and towards the light source. The concave mirror is also known as a diverging mirror as it diverges the ray of light.
So, we can say that a concave mirror is a converging mirror as it converges the incoming ray of light as it passes through a mirror.
Additional information:
There are two types of reflection on the basis of the angle of reflection of incident light after it gets reflected:
Specular reflection is a type of reflection in which the incident ray is reflected at one single angle. In specular reflection, the incident light is reflected into a single outgoing direction. Diffuse reflection is a type of reflection of light from a surface in which an incident ray is reflected at many angles, rather than at just one angle as in the case of specular reflection.
Note: As we know that a concave mirror is known as a converging mirror, similarly a concave mirror is known as a diverging mirror as it diverges the incident ray of light on passing through the mirror. In convex mirrors also, both specular and diffused reflection takes place.
Complete step by step answer:
To understand the reflection of light, we need to understand the laws of reflection. There are two laws of reflection:
(1) The first law of reflection states that the incident ray, reflected ray and the normal, all lie in the same plane.
(2) The second law of reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.

There are basically two types of mirror on the basis of reflection of light, namely, concave mirror and convex mirror.
A concave mirror has a reflective surface that is curved inward and away from the light source. The concave mirror is also known as a converging mirror as it converges the ray of light. A convex mirror has a reflective surface that is curved inward and towards the light source. The concave mirror is also known as a diverging mirror as it diverges the ray of light.
So, we can say that a concave mirror is a converging mirror as it converges the incoming ray of light as it passes through a mirror.
Additional information:
There are two types of reflection on the basis of the angle of reflection of incident light after it gets reflected:
Specular reflection is a type of reflection in which the incident ray is reflected at one single angle. In specular reflection, the incident light is reflected into a single outgoing direction. Diffuse reflection is a type of reflection of light from a surface in which an incident ray is reflected at many angles, rather than at just one angle as in the case of specular reflection.
Note: As we know that a concave mirror is known as a converging mirror, similarly a concave mirror is known as a diverging mirror as it diverges the incident ray of light on passing through the mirror. In convex mirrors also, both specular and diffused reflection takes place.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




