
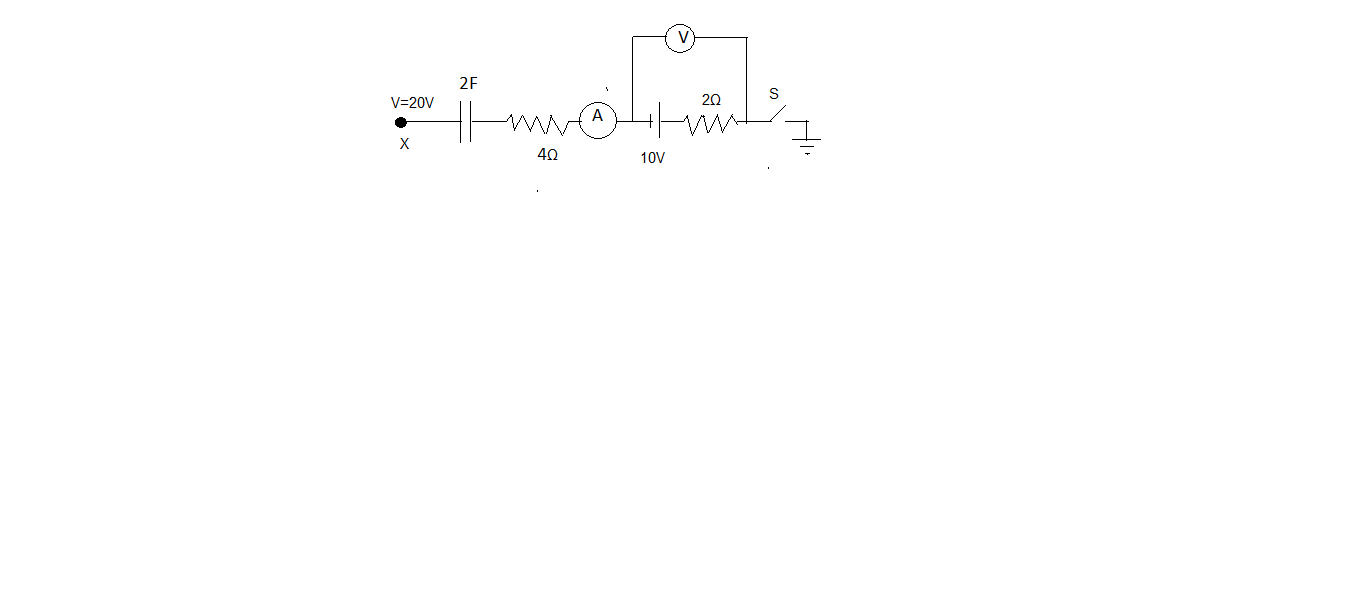
Initially the capacitor was uncharged and the switch was open. Switch is closed at $ t = 0 $ , Ammeter and voltmeter are ideal. [All units in S.I.]
List $ 1 $ List $ 2 $ Reading of voltmeter after long time 0 Just after closing the switch reading of ammeter 5 Just after closing the switch reading of voltmeter 10 Charge on capacitor after long time 60

| List $ 1 $ | List $ 2 $ |
| Reading of voltmeter after long time | 0 |
| Just after closing the switch reading of ammeter | 5 |
| Just after closing the switch reading of voltmeter | 10 |
| Charge on capacitor after long time | 60 |
Answer
541.5k+ views
Hint :In order to solve this question, we are going to see what changes occur in a circuit when a capacitor is charged. Just after closing the switch, the reading signifies the beginning stage of the charging of a capacitor and the ammeter and voltmeter readings are taken accordingly and also that for after the long time.
The current $ i $ for a series circuit having two resistors $ {r_1} $ and $ {r_2} $ , and voltages $ {V_1} $ and $ {V_2} $ is
$ i = \dfrac{{{V_1} + {V_2}}}{{{r_1} + {r_2}}} $
Complete Step By Step Answer:
After a long time, the current through the circuit since the capacitor will behave as an open circuit. Therefore, voltmeter will read $ 0V $
Just after closing the switch, the voltage will be zero, thus the reading of the ammeter that will be equal to the current will be $ i = \dfrac{{20 + 10}}{{4 + 2}} = 5A $
Reading of voltmeter just after closing the switch will be $ 20 - 2i = 10V $
After a long time, entire voltage will appear across the capacitor, hence, $ Q = CV = 2 \times 30 = 60C $
Note :
In this case, it is given that the ammeter and the voltmeter are the ideal ones. This means that in the case of an open circuit, the voltage is completely zero only, and there are no losses in the readings of the voltmeter and the ammeter. An ideal voltmeter has infinite resistance whereas an ideal ammeter has zero resistance.
The current $ i $ for a series circuit having two resistors $ {r_1} $ and $ {r_2} $ , and voltages $ {V_1} $ and $ {V_2} $ is
$ i = \dfrac{{{V_1} + {V_2}}}{{{r_1} + {r_2}}} $
Complete Step By Step Answer:
After a long time, the current through the circuit since the capacitor will behave as an open circuit. Therefore, voltmeter will read $ 0V $
Just after closing the switch, the voltage will be zero, thus the reading of the ammeter that will be equal to the current will be $ i = \dfrac{{20 + 10}}{{4 + 2}} = 5A $
Reading of voltmeter just after closing the switch will be $ 20 - 2i = 10V $
After a long time, entire voltage will appear across the capacitor, hence, $ Q = CV = 2 \times 30 = 60C $
Note :
In this case, it is given that the ammeter and the voltmeter are the ideal ones. This means that in the case of an open circuit, the voltage is completely zero only, and there are no losses in the readings of the voltmeter and the ammeter. An ideal voltmeter has infinite resistance whereas an ideal ammeter has zero resistance.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




