
Indicate whether the following complex is low spin or high spin complex:
\[{K_4}[Cr{(CN)_6}]\] .
Answer
501.9k+ views
Hint: When there is a question on spin of the coordination compounds first think about what crystal field theory states and what is that which makes the complex low or high spin and the electrons distribution in the complex and the role of the ligands and how they cause a complex to be low or high spin complex.
Complete answer:
The field of ligands plays an important role in deciding the spin of the complex. If there is a weak field ligand then the energy that is required for the pairing of two electrons is greater than the energy required to place an electron in the higher energy level which results in more number of unpaired electrons in its d orbital forming a high spin complex. If there is a strong field ligand then the energy that is required for the pairing of two electrons is lesser than the energy required to place an electron in the higher energy level which results in less number of unpaired electrons or more number of paired electrons in its d orbital forming a low spin complex.
The following steps can help in determination of high spin or low spin for any complex:
1.Determine the shape of the complex (i.e., octahedral, tetrahedral, square planar).
2.Determine the oxidation state of the metal centre.
3.Determine the d electron configuration of the metal centre.
4.Draw the crystal field diagram of the complex with regards to its geometry.
5.Determine whether the splitting energy is greater than the pairing energy.
6.Determine the strength of the ligand(from the spectrochemical series).
So, let’s go with our complex:
\[{K_4}[Cr{(CN)_6}]\] - Potassium Hexacyano Chromium(II) complex.
There are 6 ligands in the complex, which suggests that the shape of the complex is octahedral.
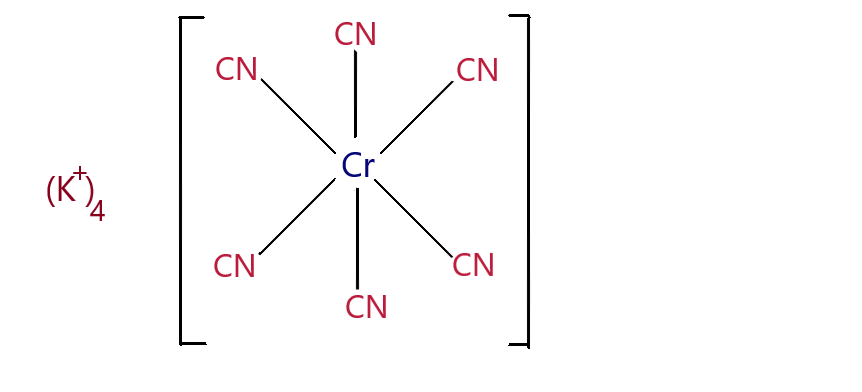
To find the oxidation state of the metal centre:
The charge on the whole complex is -4 since there are \[4{K^ + }\] . Cyanide is an anionic ligand and has -1 charge.
So the oxidation state of chromium is
\[x + ( - 6) = - 4\]
\[x = - 4 + 6\]
\[x = + 2\]
So, chromium is in +2 oxidation state.
The atomic number of Cr is 24.
The electronic configuration of Cr is \[[Ar]3{d^5}4{s^1}\] .
So \[C{r^{2 + }}\] is \[[Ar]3{d^4}\] .
This complex is \[{d^2}s{p^3}\] hybridised.
Cyanide is a strong field ligand and hence the pairing energy is lesser than the energy required to add an electron in the higher energy orbital.
The splitting of \[C{r^{2 + }}\] will be as follows;
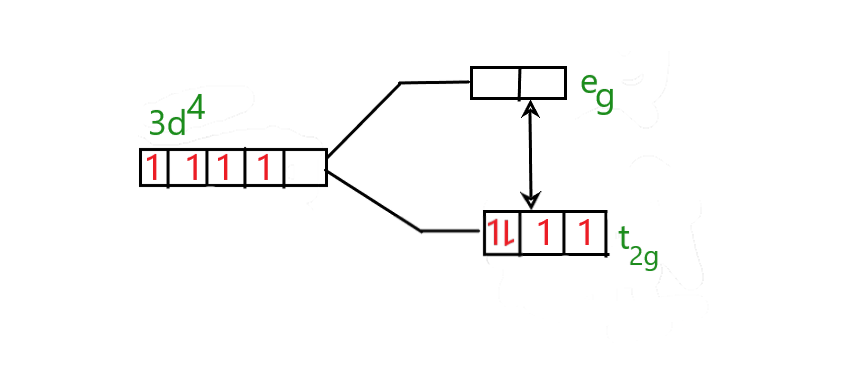
Hence the electrons are paired and occupied only in the lower energy level.
Hence with all this evidence shows that the \[{K_4}[Cr{(CN)_6}]\] complex is a low spin complex.
Note:
\[C{r^{2 + }}\] acts as a reducing agent. It is unstable with 4 electrons in the complex hence it tends to donate 1 electron and become a half filled orbital which is more stable.
Complete answer:
The field of ligands plays an important role in deciding the spin of the complex. If there is a weak field ligand then the energy that is required for the pairing of two electrons is greater than the energy required to place an electron in the higher energy level which results in more number of unpaired electrons in its d orbital forming a high spin complex. If there is a strong field ligand then the energy that is required for the pairing of two electrons is lesser than the energy required to place an electron in the higher energy level which results in less number of unpaired electrons or more number of paired electrons in its d orbital forming a low spin complex.
The following steps can help in determination of high spin or low spin for any complex:
1.Determine the shape of the complex (i.e., octahedral, tetrahedral, square planar).
2.Determine the oxidation state of the metal centre.
3.Determine the d electron configuration of the metal centre.
4.Draw the crystal field diagram of the complex with regards to its geometry.
5.Determine whether the splitting energy is greater than the pairing energy.
6.Determine the strength of the ligand(from the spectrochemical series).
So, let’s go with our complex:
\[{K_4}[Cr{(CN)_6}]\] - Potassium Hexacyano Chromium(II) complex.
There are 6 ligands in the complex, which suggests that the shape of the complex is octahedral.

To find the oxidation state of the metal centre:
The charge on the whole complex is -4 since there are \[4{K^ + }\] . Cyanide is an anionic ligand and has -1 charge.
So the oxidation state of chromium is
\[x + ( - 6) = - 4\]
\[x = - 4 + 6\]
\[x = + 2\]
So, chromium is in +2 oxidation state.
The atomic number of Cr is 24.
The electronic configuration of Cr is \[[Ar]3{d^5}4{s^1}\] .
So \[C{r^{2 + }}\] is \[[Ar]3{d^4}\] .
This complex is \[{d^2}s{p^3}\] hybridised.
Cyanide is a strong field ligand and hence the pairing energy is lesser than the energy required to add an electron in the higher energy orbital.
The splitting of \[C{r^{2 + }}\] will be as follows;

Hence the electrons are paired and occupied only in the lower energy level.
Hence with all this evidence shows that the \[{K_4}[Cr{(CN)_6}]\] complex is a low spin complex.
Note:
\[C{r^{2 + }}\] acts as a reducing agent. It is unstable with 4 electrons in the complex hence it tends to donate 1 electron and become a half filled orbital which is more stable.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




