
Increasing rate of ${S_N}1$ reaction in the following compound is:
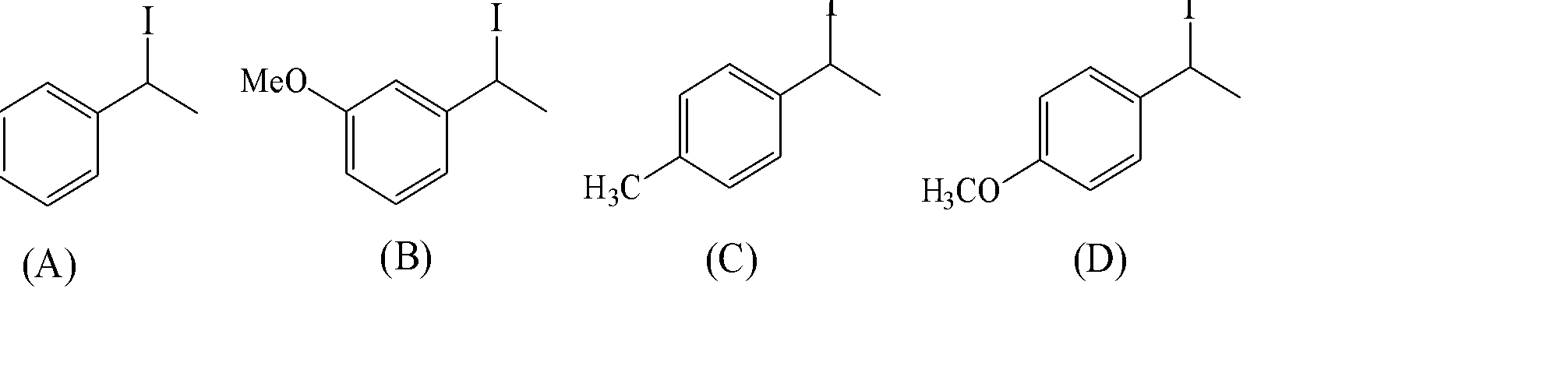
A) (A) < (B) < (C) < (D)
B) (B) < (A) < (D) < (C)
C) (B) < (A) < (C) < (D)
D) (A) < (B) < (D) < (C)

Answer
581.1k+ views
Hint: The ${S_N}1$ reaction forms the carbocation in an intermediate step. One can analyse which formed carbocation is stable based on the attached electron withdrawing group and the electron donating group.
Complete step by step answer:
1) First of all let's learn about the ${S_N}1$ reaction where it is the nucleophilic substitution reaction. The number ${\text{1}}$ indicates that the reaction is a unimolecular reaction. This reaction is a two-step reaction and there is the formation of carbocation as an intermediate.
2) The intermediate carbocation which is to be formed always tries to be stable. Stable carbocation always forms the major product. The stability of a carbocation depends upon the electron-withdrawing or electron-donating groups present in the structure.
3) The iodine atom leaves and there is the formation of carbocation which is at the carbon where the iodine atom is attached. Now let’s analyze each structure and decide the order of the stability of carbocation.
4) structure A doesn’t possess any extra electron-withdrawing or donating groups. The structure B has the ${\text{OMe}}$ group which is an electron-donating group present to nearer position to carbocation which will stabilize the carbocation formed. Hence this is the most stable structure.
5) structure C has $C{H_3}$ a group that shows the hyperconjugation effect to the carbocation. The structure D shows the presence of an electron-donating group ${\text{OMe}}$ which is present far to the carbocation than in structure B. Hence, it will be the least stable structure.
Therefore, the order of carbocation stability will be (B) < (A) < (C) < (D) which shows the option C as a correct choice.
Note:
The position of the electron-withdrawing group or the electron-donating group from the carbocation is important as electron donation or withdrawal happens through the bonds. Hyperconjugation is a stability effect that happens due to the interaction of hydrogen atoms through $\sigma - $ bond or a $\pi - $ bond.
Complete step by step answer:
1) First of all let's learn about the ${S_N}1$ reaction where it is the nucleophilic substitution reaction. The number ${\text{1}}$ indicates that the reaction is a unimolecular reaction. This reaction is a two-step reaction and there is the formation of carbocation as an intermediate.
2) The intermediate carbocation which is to be formed always tries to be stable. Stable carbocation always forms the major product. The stability of a carbocation depends upon the electron-withdrawing or electron-donating groups present in the structure.
3) The iodine atom leaves and there is the formation of carbocation which is at the carbon where the iodine atom is attached. Now let’s analyze each structure and decide the order of the stability of carbocation.
4) structure A doesn’t possess any extra electron-withdrawing or donating groups. The structure B has the ${\text{OMe}}$ group which is an electron-donating group present to nearer position to carbocation which will stabilize the carbocation formed. Hence this is the most stable structure.
5) structure C has $C{H_3}$ a group that shows the hyperconjugation effect to the carbocation. The structure D shows the presence of an electron-donating group ${\text{OMe}}$ which is present far to the carbocation than in structure B. Hence, it will be the least stable structure.
Therefore, the order of carbocation stability will be (B) < (A) < (C) < (D) which shows the option C as a correct choice.
Note:
The position of the electron-withdrawing group or the electron-donating group from the carbocation is important as electron donation or withdrawal happens through the bonds. Hyperconjugation is a stability effect that happens due to the interaction of hydrogen atoms through $\sigma - $ bond or a $\pi - $ bond.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




