
In which part of the plant water stored
A. Roots
B. Stem
C. Leaves
D. Bark
Answer
573k+ views
Hint:-Plants are fundamentally multicellular life forms, overwhelmingly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the realm Plantae. They have particular organs that assist them with enduring and imitating an extraordinary variety of living spaces. Significant organs of most plants incorporate roots, stems, and leaves.
Complete Answer:- Leaves are the keys not exclusively to vegetation yet to all earthbound life. The essential function of leaves is to gather daylight and make food by photosynthesis. Despite the major significance of the work they do, there is an incredible variety in the leaves of plants. Nonetheless, given the variety of environments wherein plants live, it's not amazing that there is no single most ideal approach to gather sunlight-based energy for photosynthesis. Leaves may change in size, shape, and plan on stems. Nonflowering vascular plants have three fundamental sorts of leaves: microphylls ("small leaves"), fronds, and needles. Blooming vascular plants additionally have various leaves. Nonetheless, the leaves of all blooming plants share two essential parts practically speaking: the sharp edge and petiole. The edge of the leaf is the moderately wide, level aspect of the leaf that assembles daylight and goes through photosynthesis. The petiole is the part that joins the leaf to a stem of the plant. This occurs at a node.
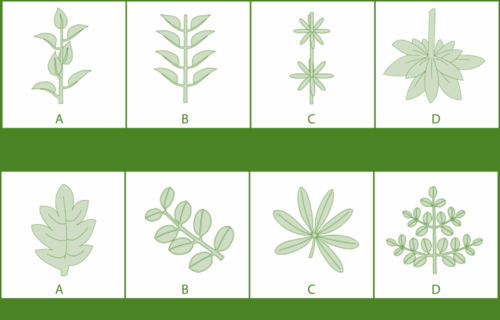
- By and large, the structure and course of action of leaves boost light introduction while preserving water, decreasing breeze obstruction, or profiting the plant in some other path in its specific territory.
- Leaves masterminded in whorls enclose upstanding stems at spans. They gather daylight from all headings.
- Leaves masterminded in basal rosettes exploit warm temperatures close to the ground.
- Leaves masterminded in substitute or restricting sets gather light from above. They are normally found on plants with a solitary, upstanding stem.
- The sharp edges of straightforward leaves are not partitioned. This gives the most extreme surface zone to gathering daylight.
- The sharp edges of compound leaves are separated into numerous littler flyers. This decreases wind opposition and water misfortune.
Note:- The essential capacity of leaves is to gather daylight and make food by photosynthesis. Specific tissues go home together to play out this capacity. In a deciduous plant, leaves occasionally turn tone and tumble off the plant. They are supplanted with new leaves later in the year. An evergreen plant keeps its green leaves all year. It might have needle-like leaves to lessen water misfortune.
Complete Answer:- Leaves are the keys not exclusively to vegetation yet to all earthbound life. The essential function of leaves is to gather daylight and make food by photosynthesis. Despite the major significance of the work they do, there is an incredible variety in the leaves of plants. Nonetheless, given the variety of environments wherein plants live, it's not amazing that there is no single most ideal approach to gather sunlight-based energy for photosynthesis. Leaves may change in size, shape, and plan on stems. Nonflowering vascular plants have three fundamental sorts of leaves: microphylls ("small leaves"), fronds, and needles. Blooming vascular plants additionally have various leaves. Nonetheless, the leaves of all blooming plants share two essential parts practically speaking: the sharp edge and petiole. The edge of the leaf is the moderately wide, level aspect of the leaf that assembles daylight and goes through photosynthesis. The petiole is the part that joins the leaf to a stem of the plant. This occurs at a node.

- By and large, the structure and course of action of leaves boost light introduction while preserving water, decreasing breeze obstruction, or profiting the plant in some other path in its specific territory.
- Leaves masterminded in whorls enclose upstanding stems at spans. They gather daylight from all headings.
- Leaves masterminded in basal rosettes exploit warm temperatures close to the ground.
- Leaves masterminded in substitute or restricting sets gather light from above. They are normally found on plants with a solitary, upstanding stem.
- The sharp edges of straightforward leaves are not partitioned. This gives the most extreme surface zone to gathering daylight.
- The sharp edges of compound leaves are separated into numerous littler flyers. This decreases wind opposition and water misfortune.
Note:- The essential capacity of leaves is to gather daylight and make food by photosynthesis. Specific tissues go home together to play out this capacity. In a deciduous plant, leaves occasionally turn tone and tumble off the plant. They are supplanted with new leaves later in the year. An evergreen plant keeps its green leaves all year. It might have needle-like leaves to lessen water misfortune.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




