
In Victor Meyer’s test, the colour given by ${1^0}$ , ${2^0}$ and ${3^0}$ alcohols are respectively
A) red, colourless, blue
B) red, blue, colourless
C) colourless, red, blue
D) red, blue, violet
Answer
582.9k+ views
Hint: Victor Maeyer’s test is used to differentiate primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols. In Victor Maeyer’s test, alcohols are treated with the reagents $P + {I_2}$ , $AgN{O_2}$, $HONO$ and $NaOH$ in the steps one by one. The colours obtained with the alkali helps us to distinguish the alcohols.
Complete step by step solution:
${1^0}$ , ${2^0}$ and ${3^0}$ alcohols can be distinguished using the Victor Maeyer’s test. Victor Maeyer’s test is done in four steps with the reagents $P + {I_2}$ , $AgN{O_2}$, $HONO$ and $NaOH$ respectively.
In Victor Maeyer’s test, the alcohols are treated in the following steps.
Step 1: Firstly, the sample alcohol is treated with the reagent $P + {I_2}$ to get the iodoalkane as a product.
Step 2: The iodoalkane obtained is then treated with $AgN{O_2}$ solution to get the nitroalkane.
Step 3: The nitroalkane obtained is then treated with $HONO$ (nitrous acid).
Step 4: The resulting solution in step 3 is then treated with the alkali like $NaOH$ and the colour is obtained.
Let us now do Victor Maeyer’s test of primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols.
- Victor Maeyer’s test of ${1^o}$ alcohols:
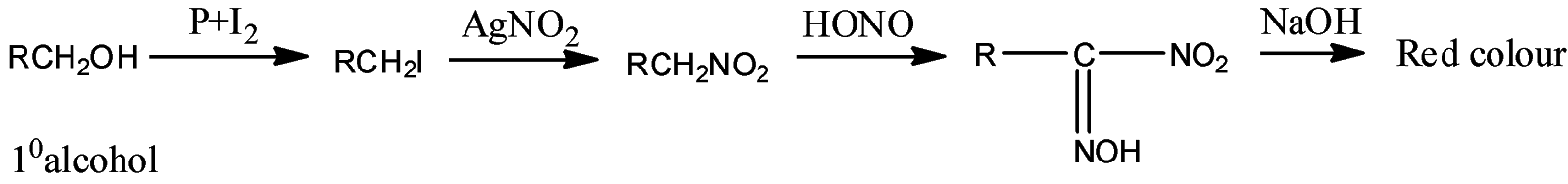
- Victor Maeyer’s test for ${2^o}$ alcohols:
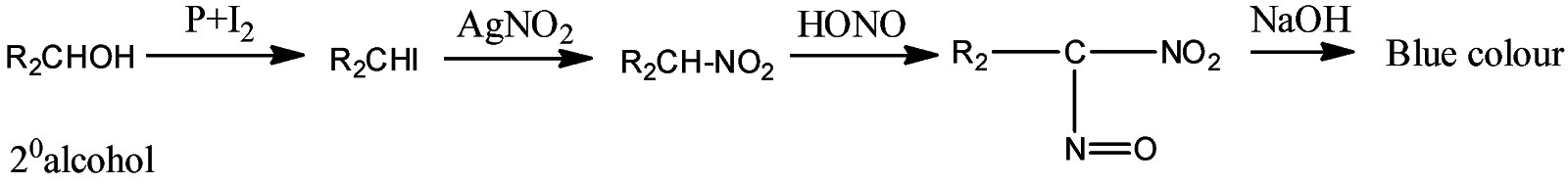
- Victor Maeyer’s test for ${3^o}$ alcohols:
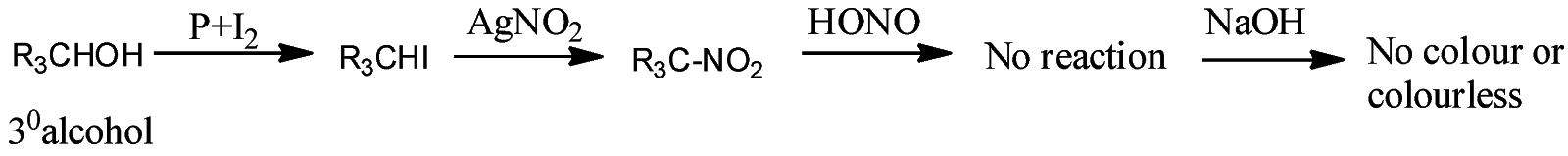
Thus, we can conclude from the above reactions of Victor Maeyer’s test of ${1^0}$, ${2^0}$ and ${3^0}$ alcohols that, primary alcohols (${1^o}$) gives the red colour solution with alkali, secondary alcohols (${2^o}$) gives the blue colour solution with alkali, and tertiary alcohols (${3^o}$) gives the colourless solution.
Thus, option (B) is the correct answer.
Note: Nitrous acid (HONO) is the combination of two reagents $NaN{O_3}$ and ${H_2}S{O_4}$. A key point to note is that Victor Maeyer’s test is not given by phenols because the procedure involves the breaking of OH bonds with carbon but in case of phenol, a carbon-oxygen bond is much stronger, having a partial bond character.
Complete step by step solution:
${1^0}$ , ${2^0}$ and ${3^0}$ alcohols can be distinguished using the Victor Maeyer’s test. Victor Maeyer’s test is done in four steps with the reagents $P + {I_2}$ , $AgN{O_2}$, $HONO$ and $NaOH$ respectively.
In Victor Maeyer’s test, the alcohols are treated in the following steps.
Step 1: Firstly, the sample alcohol is treated with the reagent $P + {I_2}$ to get the iodoalkane as a product.
Step 2: The iodoalkane obtained is then treated with $AgN{O_2}$ solution to get the nitroalkane.
Step 3: The nitroalkane obtained is then treated with $HONO$ (nitrous acid).
Step 4: The resulting solution in step 3 is then treated with the alkali like $NaOH$ and the colour is obtained.
Let us now do Victor Maeyer’s test of primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols.
- Victor Maeyer’s test of ${1^o}$ alcohols:
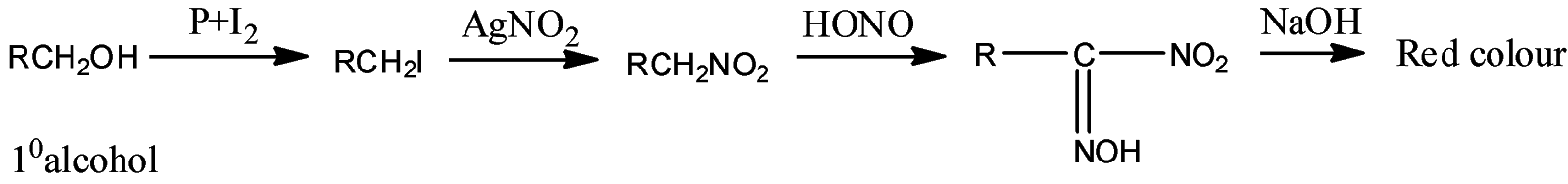
- Victor Maeyer’s test for ${2^o}$ alcohols:

- Victor Maeyer’s test for ${3^o}$ alcohols:
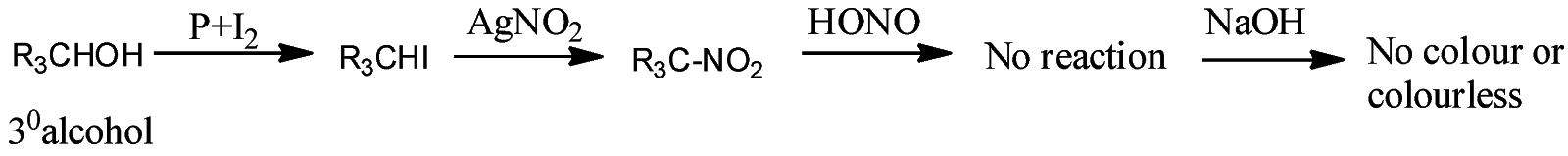
Thus, we can conclude from the above reactions of Victor Maeyer’s test of ${1^0}$, ${2^0}$ and ${3^0}$ alcohols that, primary alcohols (${1^o}$) gives the red colour solution with alkali, secondary alcohols (${2^o}$) gives the blue colour solution with alkali, and tertiary alcohols (${3^o}$) gives the colourless solution.
Thus, option (B) is the correct answer.
Note: Nitrous acid (HONO) is the combination of two reagents $NaN{O_3}$ and ${H_2}S{O_4}$. A key point to note is that Victor Maeyer’s test is not given by phenols because the procedure involves the breaking of OH bonds with carbon but in case of phenol, a carbon-oxygen bond is much stronger, having a partial bond character.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




