
In \[\vartriangle ABC\], let \[R\]= circumradius, \[r\]=inradius. If \[r\] is the distance between the circumcenter and the in center, then ratio \[\dfrac{R}{r}\] is equal to
A) \[\sqrt 2 - 1\]
B) \[\sqrt 3 - 1\]
C) \[\sqrt 2 + 1\]
D) \[\sqrt 3 + 1\]
Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: Circumradius (R) of a triangle is the radius of the circumscribed circle having center as O of a triangle, whereas the inradius of a regular triangle is the radius of the incircle having center I, which is the largest circle that will fit inside the triangle.
Here, in the question, we need to determine the ratio of the circumradius and the inradius of the triangle ABC such that R is the circumradius, and r is the inradius. For this, we need to follow the defined generalized relation between the circumradius and the inradius of any triangle as \[r = \sqrt {{R^2} - 2rR} \] and solve the resulting quadratic equation to get the final result.
Complete step by step answer:
\[R\] = circumradius and \[r\] = inradius
Where \[r\] is the distance between the circumcenter and the incenter
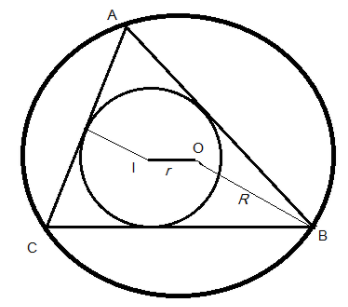
According to Euler’s theorem states that the distance between the circumcenter and the incenter is given by \[r = \sqrt {{R^2} - 2rR} \]
\[
OI = \sqrt {{R^2} - 2rR} = r \\
{R^2} - 2rR = {r^2} \\
{R^2} - 2rR - {r^2} = 0 - - - - (i) \\
\]
Now solve for the roots of the above quadratic equation (i) as:
\[
R = \dfrac{{2r \pm \sqrt {{{\left( { - 2r} \right)}^2} - 4(1)( - {r^2})} }}{{2(1)}} \\
= \dfrac{{2r \pm \sqrt {4{r^2} + 4{r^2}} }}{2} \\
= \dfrac{{2r \pm 2\sqrt 2 r}}{2} \\
= r \pm \sqrt 2 r - - - - (ii) \\
\]
Here, the minus (-) sign has been neglected (or dropped) as it will result in the negative value, which is not possible for the measurement purpose.
Hence, \[R = r\left( {1 + \sqrt 2 } \right) - - - - (iii)\]
Take r in the denominator of the equation (iii) as:
\[
R = \left( {\sqrt 2 + 1} \right)r \\
\dfrac{R}{r} = \left( {\sqrt 2 + 1} \right) \\
\]
Hence, the ratio of circumradius and inradius in the triangle ABC is given as: \[\dfrac{R}{r} = \left( {\sqrt 2 + 1} \right)\]
Hence option (C) is correct.
Note: Students must take precision while solving the question about R and r, as these two are different terms. R is the circumradius, which is the radius of the circumscribed circle, whereas r is the inradius, which is the radius of the incircle of the triangle ABC.
Here, in the question, we need to determine the ratio of the circumradius and the inradius of the triangle ABC such that R is the circumradius, and r is the inradius. For this, we need to follow the defined generalized relation between the circumradius and the inradius of any triangle as \[r = \sqrt {{R^2} - 2rR} \] and solve the resulting quadratic equation to get the final result.
Complete step by step answer:
\[R\] = circumradius and \[r\] = inradius
Where \[r\] is the distance between the circumcenter and the incenter

According to Euler’s theorem states that the distance between the circumcenter and the incenter is given by \[r = \sqrt {{R^2} - 2rR} \]
\[
OI = \sqrt {{R^2} - 2rR} = r \\
{R^2} - 2rR = {r^2} \\
{R^2} - 2rR - {r^2} = 0 - - - - (i) \\
\]
Now solve for the roots of the above quadratic equation (i) as:
\[
R = \dfrac{{2r \pm \sqrt {{{\left( { - 2r} \right)}^2} - 4(1)( - {r^2})} }}{{2(1)}} \\
= \dfrac{{2r \pm \sqrt {4{r^2} + 4{r^2}} }}{2} \\
= \dfrac{{2r \pm 2\sqrt 2 r}}{2} \\
= r \pm \sqrt 2 r - - - - (ii) \\
\]
Here, the minus (-) sign has been neglected (or dropped) as it will result in the negative value, which is not possible for the measurement purpose.
Hence, \[R = r\left( {1 + \sqrt 2 } \right) - - - - (iii)\]
Take r in the denominator of the equation (iii) as:
\[
R = \left( {\sqrt 2 + 1} \right)r \\
\dfrac{R}{r} = \left( {\sqrt 2 + 1} \right) \\
\]
Hence, the ratio of circumradius and inradius in the triangle ABC is given as: \[\dfrac{R}{r} = \left( {\sqrt 2 + 1} \right)\]
Hence option (C) is correct.
Note: Students must take precision while solving the question about R and r, as these two are different terms. R is the circumradius, which is the radius of the circumscribed circle, whereas r is the inradius, which is the radius of the incircle of the triangle ABC.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




