
In urotropine, the number of $-N-N-$ bonds is:
(a)- 6
(b)- 4
(c)- 2
(d)- 0
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: Urotropine is also known as hexamethylenetetramine. The molecular formula of urotropine is${{(C{{H}_{2}})}_{6}}{{N}_{4}}$. It has a cage-like structure with 6 $N-C{{H}_{2}}-N$ bonds.
Complete answer:
The urotropine or hexamine is also known as Hexamethylenetetramine or methenamine. It is a heterocyclic organic compound. It has a formula of${{(C{{H}_{2}})}_{6}}{{N}_{4}}$.
Urotropine is a white crystalline compound. It is highly soluble in water and polar organic solvents.
It has a cage-like structure. It is used in the synthesis of chemical compounds like rubber additives, plastics, pharmaceuticals, etc.
It is prepared by reacting formaldehyde with ammonia. This reaction can be conducted in the gas phase as well as in the solution.
The reaction is given below:
$4N{{H}_{3}}+6HCHO\to {{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{N}_{4}}+6{{H}_{2}}O$
It has a symmetric tetrahedral cage-like structure.
The structure is given below:
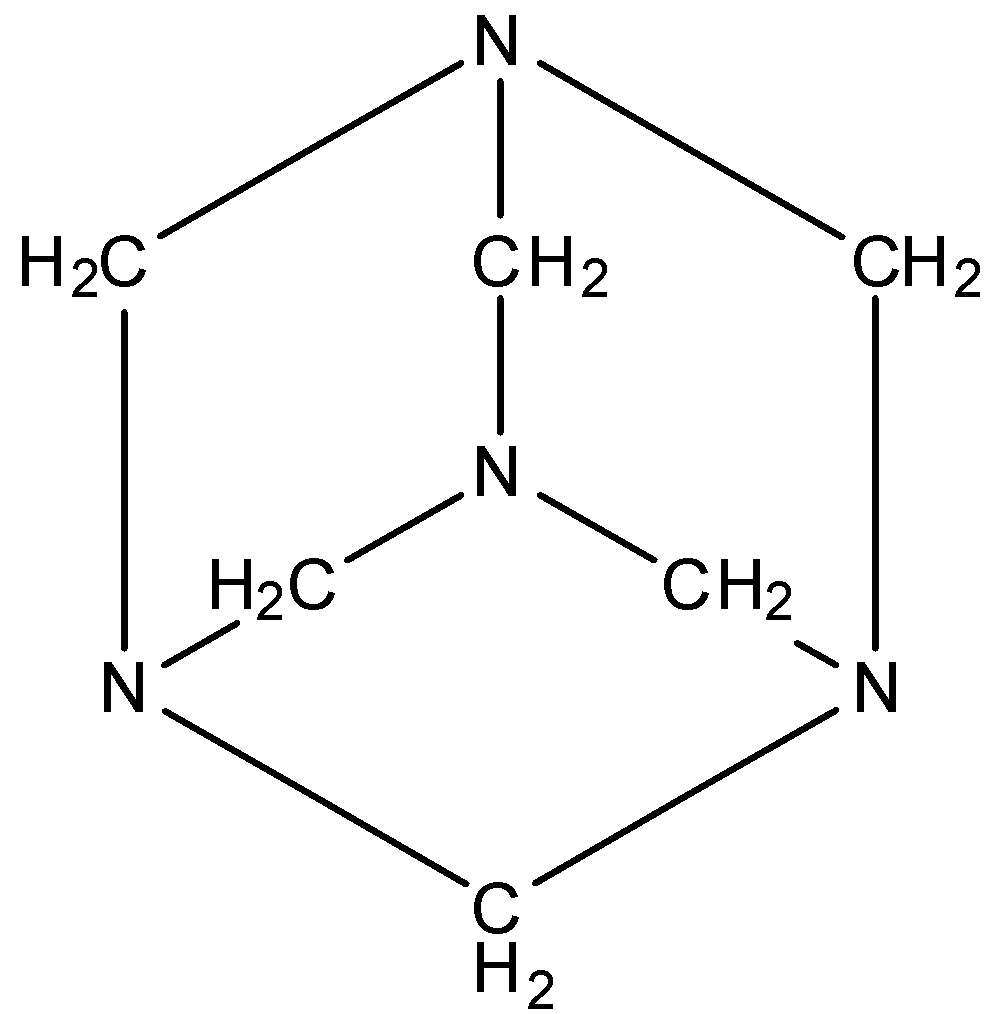
It doesn’t have any space or void in between for other molecules to bind.
It undergoes protonation and behaves like an amine base.
So, in the structure, you can see that there are 6 bonds and each bond is $N-C{{H}_{2}}-N$.
The urotropine is used for medical purposes as mandelic acid salt used for the treatment of urinary tract infection. It is also used as a preservative for food.
So, the molecule of urotropine doesn't have a $-N-N-$ bond.
Hence, the correct answer is an option (d)- 0.
Note:
Urotropine is a versatile reagent used in much organic synthesis. It is used in reactions like the Duff reaction (formylation of arenes), in Sommelet reaction (converting benzyl halides to aldehydes), and in Delepine reaction (synthesis of amines from alkyl halides).
Complete answer:
The urotropine or hexamine is also known as Hexamethylenetetramine or methenamine. It is a heterocyclic organic compound. It has a formula of${{(C{{H}_{2}})}_{6}}{{N}_{4}}$.
Urotropine is a white crystalline compound. It is highly soluble in water and polar organic solvents.
It has a cage-like structure. It is used in the synthesis of chemical compounds like rubber additives, plastics, pharmaceuticals, etc.
It is prepared by reacting formaldehyde with ammonia. This reaction can be conducted in the gas phase as well as in the solution.
The reaction is given below:
$4N{{H}_{3}}+6HCHO\to {{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{N}_{4}}+6{{H}_{2}}O$
It has a symmetric tetrahedral cage-like structure.
The structure is given below:

It doesn’t have any space or void in between for other molecules to bind.
It undergoes protonation and behaves like an amine base.
So, in the structure, you can see that there are 6 bonds and each bond is $N-C{{H}_{2}}-N$.
The urotropine is used for medical purposes as mandelic acid salt used for the treatment of urinary tract infection. It is also used as a preservative for food.
So, the molecule of urotropine doesn't have a $-N-N-$ bond.
Hence, the correct answer is an option (d)- 0.
Note:
Urotropine is a versatile reagent used in much organic synthesis. It is used in reactions like the Duff reaction (formylation of arenes), in Sommelet reaction (converting benzyl halides to aldehydes), and in Delepine reaction (synthesis of amines from alkyl halides).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




