
In this reaction$Me - C \equiv C - Et\xrightarrow{{Na/liq.N{H_3}}}P\xrightarrow[{CC{l_4}}]{{B{r_2}}}Q$; then Q is:
A. a pure compound which is optically inactive due to internal compensation
B. a binary mixture which is optically inactive due to external compensation
C. a binary mixture which is optically active
D. a pure compound which is optically inactive due to absence of chiral center
Answer
582.3k+ views
Hint:To solve this question, first we need to understand the meaning of optically inactive. A racemic mixture is optically inactive. A racemic mixture is one which contains two enantiomers in d and l-forms in equal proportions. Thus, the rotation due to one isomer gets cancelled by the rotation due to another. Therefore, it has zero optical rotation. So, the mixture is called optically inactive.
Complete step by step answer:
To find the value of Q, we will solve the first part of the equation given in the question.
$Me - C \equiv C - Et\xrightarrow{{Na/liq.N{H_3}}}P$
When Na or liq. $N{H_3}$ is added then trans-reduction takes place. When we add sodium or ammonia to the reaction, it is known as dissolving metal reduction reaction. In this reaction, the electrons from Na metal sequentially add to the alkyne that further results in an anion that is protonated by the $N{H_3}$ solvent.
So, the compound formed in the first part i.e. P is,
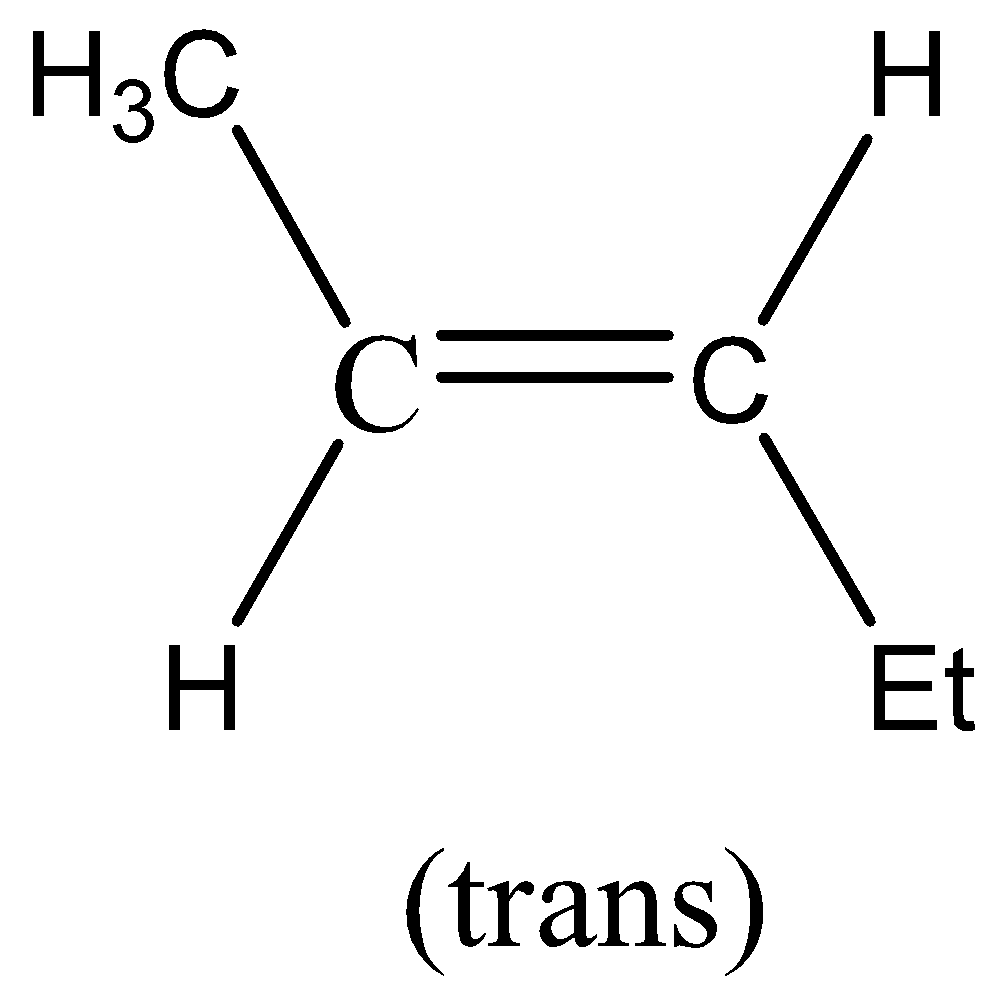
Now, with the help of this we will find the other find of the reaction i.e. Q.
$P\xrightarrow[{CC{l_4}}]{{B{r_2}}}Q$
Here, we can see 2 Br atoms are taken so the compound P is divided into two different parts. Then, anti-reduction takes place due to which mirror images are formed in the compound Q. Now, we rotate the first and second part of compound Q move in clockwise and anticlockwise direction. Due to this movement, these compounds are optically inactive due to external compensation.
So, the racemic mixture in this reaction Q is:
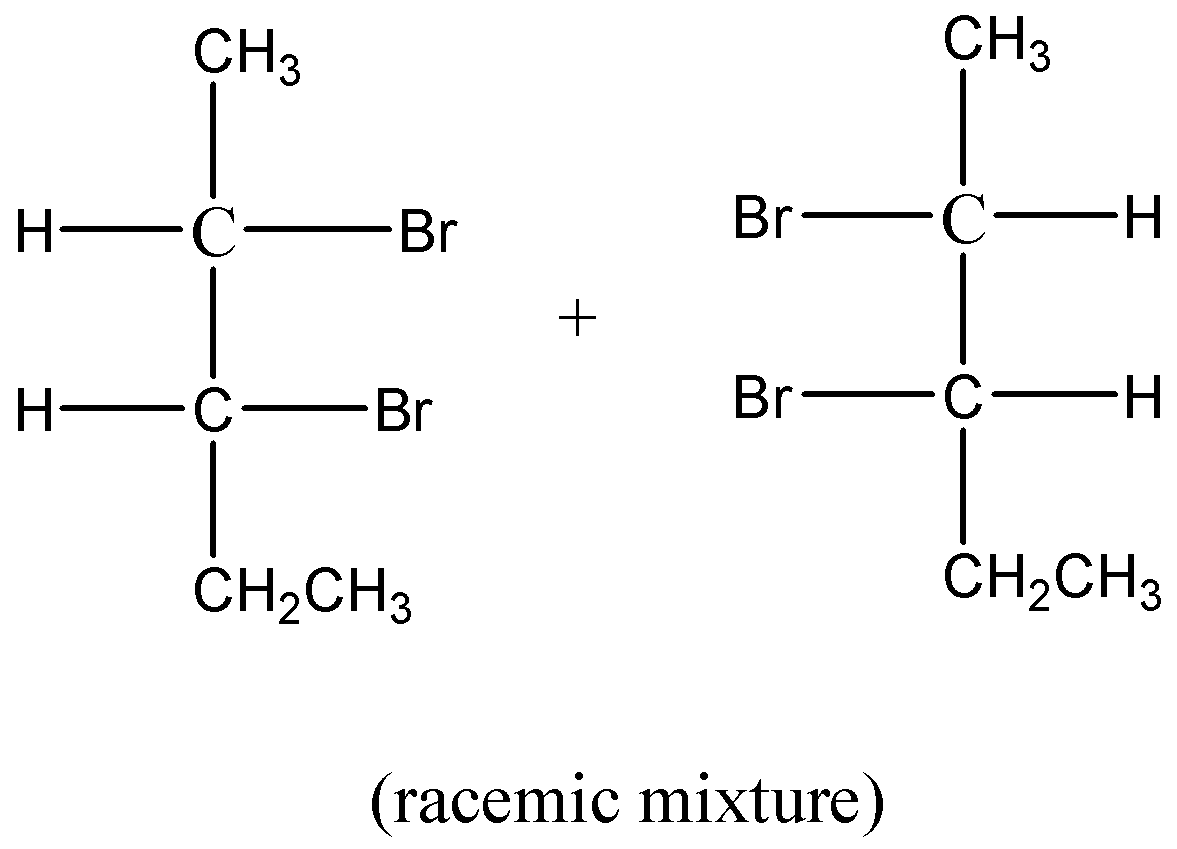
Therefore, we can say that the binary mixture which is optically inactive due to external compensation. Hence option B is correct.
Note: After solving, this question we need to keep in mind, when $B{r_2}$ and $CC{l_4}$ are involved in this reaction then an induced dipole interaction between the molecules and bromine gives $B{r^ + }$ and $B{r^ - }$, $B{r^ + }$ attacks as an electrophile on alkene then undergoes electrophilic addition reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
To find the value of Q, we will solve the first part of the equation given in the question.
$Me - C \equiv C - Et\xrightarrow{{Na/liq.N{H_3}}}P$
When Na or liq. $N{H_3}$ is added then trans-reduction takes place. When we add sodium or ammonia to the reaction, it is known as dissolving metal reduction reaction. In this reaction, the electrons from Na metal sequentially add to the alkyne that further results in an anion that is protonated by the $N{H_3}$ solvent.
So, the compound formed in the first part i.e. P is,

Now, with the help of this we will find the other find of the reaction i.e. Q.
$P\xrightarrow[{CC{l_4}}]{{B{r_2}}}Q$
Here, we can see 2 Br atoms are taken so the compound P is divided into two different parts. Then, anti-reduction takes place due to which mirror images are formed in the compound Q. Now, we rotate the first and second part of compound Q move in clockwise and anticlockwise direction. Due to this movement, these compounds are optically inactive due to external compensation.
So, the racemic mixture in this reaction Q is:

Therefore, we can say that the binary mixture which is optically inactive due to external compensation. Hence option B is correct.
Note: After solving, this question we need to keep in mind, when $B{r_2}$ and $CC{l_4}$ are involved in this reaction then an induced dipole interaction between the molecules and bromine gives $B{r^ + }$ and $B{r^ - }$, $B{r^ + }$ attacks as an electrophile on alkene then undergoes electrophilic addition reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




