
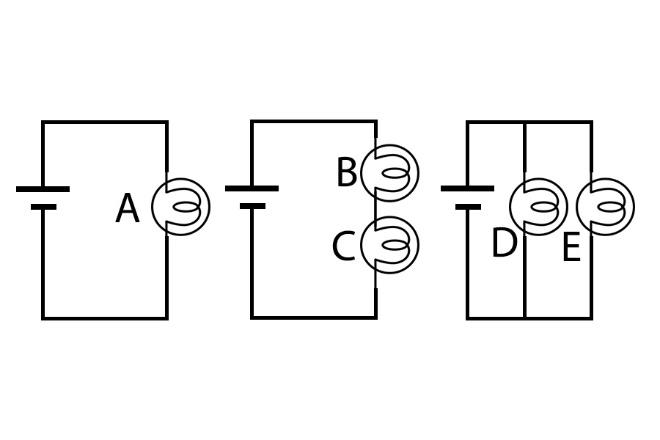
In these three circuits all the batteries are identical and have negligible internal resistance and all the light bulbs are identical. Rank all 5 light bulbs (A, B, C, D, E) in order of brightness from brightest to the dimmest
$\begin{array}{l}
1)\,{\rm{A = B = C > D = E}}\\
{\rm{2)A > B = C > D = E}}\\
{\rm{3)}}\,{\rm{A = D = E > B = C}}\\
{\rm{4)}}\,{\rm{A = D = E > B > C}}
\end{array}$

Answer
588.9k+ views
Hint: In this question we have to apply the concept of EMF, combination of resistors in a circuit in series and in parallel combination. And how the combination of resistors affects the amount of current in every branch of the circuit.
Complete step by step answer:
We have to find which bulb glows the brightest and which bulb glows the dimmest i.e. we have to find how much bright each of the bulbs will be. The brightness of a bulb is proportional to the amount of current flowing through it therefore if more current is flowing through a bulb the brighter it will glow.
The battery in all the circuits are the same therefore, let us assume the EMF of the battery to be V.
Since the bulbs are also identical in all of the circuits let us consider the resistance of each of the bulb to be R
For the first circuit we have a bulb directly connected to a battery. We have to find the amount of current passing through that bulb.
Therefore, by Ohm's law we can calculate the amount of current passing through it.
Ohm's law states that:
$V = IR$
Therefore, the making I the subject of the formula we get,
$I = \dfrac{V}{R}$
And the current in the first circuit i.e. in the bulb A will be:
${I_A} = \dfrac{V}{R}$
For the second circuit there are two bulbs connected in series to the battery therefore we have to calculate the equivalent resistance before calculating the current in them.
The equivalent resistance of the circuit is:
$\begin{array}{l}
{R_{eq}} = R + R\\
{R_{eq}} = 2R
\end{array}$
Since the bulbs B and C are in series circuit the amount of current passing through them will be equal.
Putting this value of R in the Ohm's law we can calculate the current passing through the resistors B and C,
${I_B} = {I_C} = \dfrac{V}{{2R}}$
Now in the third circuit the bulbs D and E are in parallel connection to each other. Therefore, the current coming from the battery will be divided into the two branches of the two bulbs. To be accurate the current will be divided equally therefore the current passing through the bulbs will be half of the current which is in the circuit.
Calculating the equivalent resistance of the combination of bulbs in parallel combination:
$
\dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{1}{R} + \dfrac{1}{R}\\
\implies \dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{2}{R}\\
\implies {R_{eq}} = \dfrac{R}{2}
$
If we put these values in the Ohm's law, we can calculate the current passing through the bulbs D and E.
$
I = \dfrac{V}{{\dfrac{R}{2}}}\\
\implies I = \dfrac{{2V}}{R}
$
This is the value of the current in the circuit but the current in the bulb will be half of this value.
$
{I_D} = {I_E} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{2V}}{R}}}{2}\\
\implies {I_D} = {I_E} = \dfrac{V}{R}
$
Now that we have calculated the current passing through each of the bulbs in the different circuits, we can say that the current in bulbs A D and E are equal and greater than the current in B and C.
Therefore, we can write the relation between the brightness of the bulbs in the descending order as follows:
${\rm{A = D = E > B = C}}$.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
These types of questions require understanding regarding the current passing through each of the components in a circuit. We have to keep in mind the formulas of the combination of resistors to solve this kind of analysis problem. Here the students should be smart enough to consider the bulb as resistors then only such kinds of problems can be solved.
Complete step by step answer:
We have to find which bulb glows the brightest and which bulb glows the dimmest i.e. we have to find how much bright each of the bulbs will be. The brightness of a bulb is proportional to the amount of current flowing through it therefore if more current is flowing through a bulb the brighter it will glow.
The battery in all the circuits are the same therefore, let us assume the EMF of the battery to be V.
Since the bulbs are also identical in all of the circuits let us consider the resistance of each of the bulb to be R
For the first circuit we have a bulb directly connected to a battery. We have to find the amount of current passing through that bulb.
Therefore, by Ohm's law we can calculate the amount of current passing through it.
Ohm's law states that:
$V = IR$
Therefore, the making I the subject of the formula we get,
$I = \dfrac{V}{R}$
And the current in the first circuit i.e. in the bulb A will be:
${I_A} = \dfrac{V}{R}$
For the second circuit there are two bulbs connected in series to the battery therefore we have to calculate the equivalent resistance before calculating the current in them.
The equivalent resistance of the circuit is:
$\begin{array}{l}
{R_{eq}} = R + R\\
{R_{eq}} = 2R
\end{array}$
Since the bulbs B and C are in series circuit the amount of current passing through them will be equal.
Putting this value of R in the Ohm's law we can calculate the current passing through the resistors B and C,
${I_B} = {I_C} = \dfrac{V}{{2R}}$
Now in the third circuit the bulbs D and E are in parallel connection to each other. Therefore, the current coming from the battery will be divided into the two branches of the two bulbs. To be accurate the current will be divided equally therefore the current passing through the bulbs will be half of the current which is in the circuit.
Calculating the equivalent resistance of the combination of bulbs in parallel combination:
$
\dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{1}{R} + \dfrac{1}{R}\\
\implies \dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{2}{R}\\
\implies {R_{eq}} = \dfrac{R}{2}
$
If we put these values in the Ohm's law, we can calculate the current passing through the bulbs D and E.
$
I = \dfrac{V}{{\dfrac{R}{2}}}\\
\implies I = \dfrac{{2V}}{R}
$
This is the value of the current in the circuit but the current in the bulb will be half of this value.
$
{I_D} = {I_E} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{2V}}{R}}}{2}\\
\implies {I_D} = {I_E} = \dfrac{V}{R}
$
Now that we have calculated the current passing through each of the bulbs in the different circuits, we can say that the current in bulbs A D and E are equal and greater than the current in B and C.
Therefore, we can write the relation between the brightness of the bulbs in the descending order as follows:
${\rm{A = D = E > B = C}}$.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
These types of questions require understanding regarding the current passing through each of the components in a circuit. We have to keep in mind the formulas of the combination of resistors to solve this kind of analysis problem. Here the students should be smart enough to consider the bulb as resistors then only such kinds of problems can be solved.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE




