
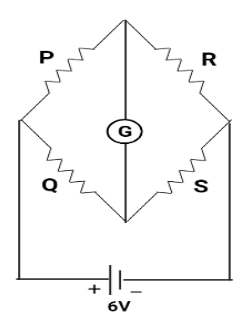
In the wheatstone’s network given, $P = 10\Omega ,Q = 20\Omega ,R = 15\Omega ,S = 30\Omega ,$ the current passing through the battery (of negligible internal resistance) is:
A. $0.36A$
B. $Zero$
C. $0.18A$
D0 $0.72A$

Answer
522.6k+ views
Hint:The Wheatstone bridge operates on the null deflection theorem, which states that their resistance ratios are identical and that no current passes through the circuit. In normal circumstances, the bridge is unbalanced, allowing current to pass through the galvanometer.
Complete step by step answer:
In the question it is given that,
$P = 10\Omega \\
\Rightarrow Q = 20\Omega \\
\Rightarrow R = 15\Omega \\
\Rightarrow S = 30\Omega \\ $
Now , we see that
$\dfrac{P}{Q} = \dfrac{{10}}{{20}} = \dfrac{1}{2}$
Similarly,
$\dfrac{R}{S} = \dfrac{{15}}{{30}} = \dfrac{1}{2}$
From the above two equations, We observe that $\dfrac{P}{Q} = \dfrac{R}{S}$ which states that their resistance ratios are identical. Hence, there is no current flowing through the galvanometer. Therefore, The Wheatstone bridge is satisfied.
Now, we see that $P$ and $R$ are in series. Hence, the net resistance will be,
${R_1} = P + R \\
\Rightarrow {R_1} = 10\Omega + 15\Omega \\
\Rightarrow {R_1} = 25\Omega \\ $
Similarly, $Q$ and $S$ are also in series. Hence, the net resistance will be,
${R_2} = Q + S \\
\Rightarrow {R_2} = 20\Omega + 30\Omega \\
\Rightarrow {R_2} = 50\Omega \\$
Now, ${R_1}$ and ${R_2}$ are in parallel combination,
$\dfrac{1}{R} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{R} = \dfrac{1}{{50}} + \dfrac{1}{{25}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{R} = \dfrac{{1 + 2}}{{50}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{R} = \dfrac{3}{{50}} \\
\Rightarrow R = \dfrac{{50}}{3} \\ $
Using ohm’s law, $I = \dfrac{V}{R}$
We know that,
$V = 6V \\
\Rightarrow R = \dfrac{{50}}{3}\Omega \\ $
Substituting these values we get,
$I = \dfrac{V}{R} \\
\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{6 \times 3}}{{50}} \\
\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{18}}{{50}} \\
\therefore I = 0.36A \\ $
Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Note:A Wheatstone bridge is an electrical circuit that balances two legs of a bridge circuit, one of which contains the unknown part, to test an unknown electrical resistance. The circuit's main advantage is its ability to produce highly precise measurements.
Complete step by step answer:
In the question it is given that,
$P = 10\Omega \\
\Rightarrow Q = 20\Omega \\
\Rightarrow R = 15\Omega \\
\Rightarrow S = 30\Omega \\ $
Now , we see that
$\dfrac{P}{Q} = \dfrac{{10}}{{20}} = \dfrac{1}{2}$
Similarly,
$\dfrac{R}{S} = \dfrac{{15}}{{30}} = \dfrac{1}{2}$
From the above two equations, We observe that $\dfrac{P}{Q} = \dfrac{R}{S}$ which states that their resistance ratios are identical. Hence, there is no current flowing through the galvanometer. Therefore, The Wheatstone bridge is satisfied.
Now, we see that $P$ and $R$ are in series. Hence, the net resistance will be,
${R_1} = P + R \\
\Rightarrow {R_1} = 10\Omega + 15\Omega \\
\Rightarrow {R_1} = 25\Omega \\ $
Similarly, $Q$ and $S$ are also in series. Hence, the net resistance will be,
${R_2} = Q + S \\
\Rightarrow {R_2} = 20\Omega + 30\Omega \\
\Rightarrow {R_2} = 50\Omega \\$
Now, ${R_1}$ and ${R_2}$ are in parallel combination,
$\dfrac{1}{R} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{R} = \dfrac{1}{{50}} + \dfrac{1}{{25}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{R} = \dfrac{{1 + 2}}{{50}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{R} = \dfrac{3}{{50}} \\
\Rightarrow R = \dfrac{{50}}{3} \\ $
Using ohm’s law, $I = \dfrac{V}{R}$
We know that,
$V = 6V \\
\Rightarrow R = \dfrac{{50}}{3}\Omega \\ $
Substituting these values we get,
$I = \dfrac{V}{R} \\
\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{6 \times 3}}{{50}} \\
\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{18}}{{50}} \\
\therefore I = 0.36A \\ $
Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Note:A Wheatstone bridge is an electrical circuit that balances two legs of a bridge circuit, one of which contains the unknown part, to test an unknown electrical resistance. The circuit's main advantage is its ability to produce highly precise measurements.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




