
In the three parts of a transistor, ‘Emitter’ is of
A. Moderate size and heavily doped.
B. Large size and lightly doped.
C. Thin size and heavily doped.
D. Large size and moderately doped.
Answer
588.9k+ views
Hint: Transistor is s device which transfers the signal or data from low resistance to high resistance. Transistor has mainly three parts: emitter, base and collector. Here we are asked about doping of the emitter. Doping means addition of impurity to the semiconductors to enhance the conductivity.
Complete answer:
Emitter is part of the transistor which supplies the charge carriers. There are basically two type of transistor p-n-p and n-p-n, in p-n-p transistor holes are the charge carriers and in n-p-n transistor electrons are the charge carriers. So in case of p-n-p, the emitter will supply holes to its junction with base and in case of n-p-n, the emitter will supply electrons to its junction with base. A simple diagram for p-n-p transistor and n-p-n transistor is shown below
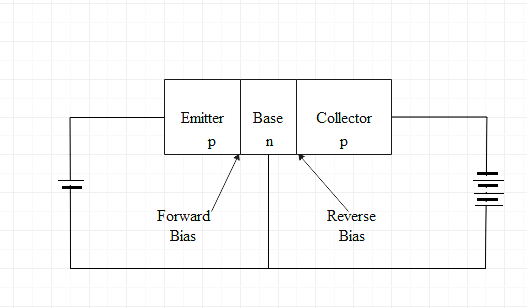
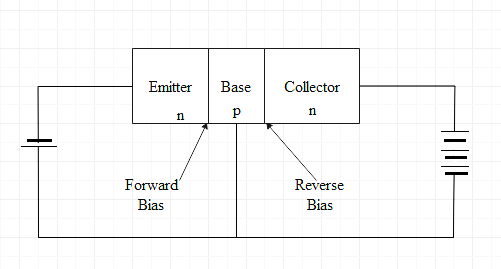
As it supplies the majority carrier therefore it is heavily doped so that it can inject large number of majority carrier into the base of the transistor and the size of emitter is moderate because if it was thin then it won’t be able to have more charge carriers and also because the collector should be larger than other two region.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Additional Information:
The emitter base junction is always forward base with respect to the base so that it can supply a large number of majority carriers.
Note:
The size of the emitter is moderate, it is larger than the base and slightly smaller than the collector, during operation the collector junction is heated and to dissipate heat the collector region is larger than the other two. Although the emitter is highly doped in comparison to the other two, whereas the base is lightly doped and collector is moderately doped.
Complete answer:
Emitter is part of the transistor which supplies the charge carriers. There are basically two type of transistor p-n-p and n-p-n, in p-n-p transistor holes are the charge carriers and in n-p-n transistor electrons are the charge carriers. So in case of p-n-p, the emitter will supply holes to its junction with base and in case of n-p-n, the emitter will supply electrons to its junction with base. A simple diagram for p-n-p transistor and n-p-n transistor is shown below


As it supplies the majority carrier therefore it is heavily doped so that it can inject large number of majority carrier into the base of the transistor and the size of emitter is moderate because if it was thin then it won’t be able to have more charge carriers and also because the collector should be larger than other two region.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Additional Information:
The emitter base junction is always forward base with respect to the base so that it can supply a large number of majority carriers.
Note:
The size of the emitter is moderate, it is larger than the base and slightly smaller than the collector, during operation the collector junction is heated and to dissipate heat the collector region is larger than the other two. Although the emitter is highly doped in comparison to the other two, whereas the base is lightly doped and collector is moderately doped.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




