
In the tetragonal crystal system, which of the following is true?
A. All axial lengths and all axial angles are equal
B. All three axial lengths are equal
C. All three axial angles are equal
D. Two axial angles are equal but the third is different
Answer
581.7k+ views
Hint: Here, we have to have the knowledge about crystal systems and their structures. Knowing the structures we can know whether the angles and lengths are equal or not. Crystallography is the study of crystals systems and lattice systems.
Complete step by step answer:
Here, it is important that we discuss the tetragonal crystal system in detail. Let’s first start with talking about crystallography and crystal systems.
In crystallography, the Crystal system, crystal family and lattice system refers to several classes of space groups, lattices, point groups and crystals. They are commonly confused with each other but are slightly different from each other. There are seven crystal systems which are Isometric. Tetragonal, Orthorhombic, Hexagonal, Triclinic, Monoclinic and Rhombohedral crystal systems.
Tetragonal crystal system is one of the seven crystal systems. Tetragonal Crystal lattices are formed as a result of stretching a cubic lattice along one of its lattice vectors. So, a cube becomes a rectangular prism with a square base. Examples of tetragonal crystal properties include apophyllite, zircon, rutile quartz and scheelite.
The structure of Tetragonal crystal system is as given below:
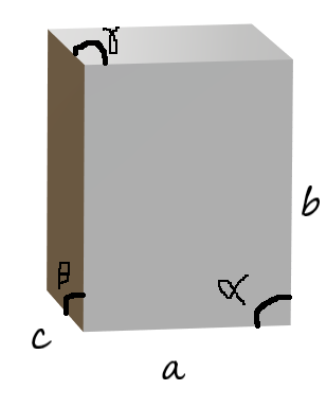
The sides a, b and c are called the axial lengths. The sides a and c are equal in length. But length b is different in length. That is
\[a = b \ne c\]
The angles alpha, beta and gamma are called the axial angles. The angle between sides a and b is called alpha ( \[\alpha \] ). The angle between sides b and c is called beta ( \[\beta \] ) and the angle between sides a and c is called gamma ( \[\gamma \] ). All the three angles are of the same degree. Therefore, as we see the options we can see that three options are true and one is incorrect. Option C is correct and the other three are incorrect.
Therefore, our answer is option C.
Note:
One should know the structures of every compound or crystal system to get the answers of every structural related question of any compound.
Complete step by step answer:
Here, it is important that we discuss the tetragonal crystal system in detail. Let’s first start with talking about crystallography and crystal systems.
In crystallography, the Crystal system, crystal family and lattice system refers to several classes of space groups, lattices, point groups and crystals. They are commonly confused with each other but are slightly different from each other. There are seven crystal systems which are Isometric. Tetragonal, Orthorhombic, Hexagonal, Triclinic, Monoclinic and Rhombohedral crystal systems.
Tetragonal crystal system is one of the seven crystal systems. Tetragonal Crystal lattices are formed as a result of stretching a cubic lattice along one of its lattice vectors. So, a cube becomes a rectangular prism with a square base. Examples of tetragonal crystal properties include apophyllite, zircon, rutile quartz and scheelite.
The structure of Tetragonal crystal system is as given below:

The sides a, b and c are called the axial lengths. The sides a and c are equal in length. But length b is different in length. That is
\[a = b \ne c\]
The angles alpha, beta and gamma are called the axial angles. The angle between sides a and b is called alpha ( \[\alpha \] ). The angle between sides b and c is called beta ( \[\beta \] ) and the angle between sides a and c is called gamma ( \[\gamma \] ). All the three angles are of the same degree. Therefore, as we see the options we can see that three options are true and one is incorrect. Option C is correct and the other three are incorrect.
Therefore, our answer is option C.
Note:
One should know the structures of every compound or crystal system to get the answers of every structural related question of any compound.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




