
In the saturation region the collector-base junction is _____ biased and the base-emitter junction is _____ biased for a transistor.
A. Reverse, forward
B. Forward, reverse
C. Reverse, reverse
D. Forward, forward
Answer
546.3k+ views
Hint: Let us consider a common-emitter configuration of a p-n-p transistor.
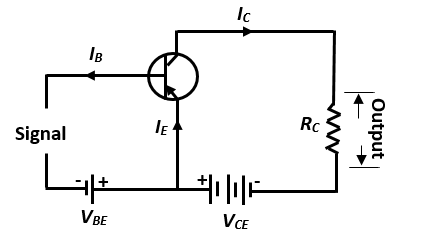
Keeping the emitter grounded, the base is kept forward biased, as n type base of the transistor is connected with a negative pole of source $V_{BE}$. Keeping the emitter grounded, the collector is kept at reverse bias, so the p type collector is connected to the negative pole of $V_{CE}$.
In the figure,
The source voltage of input= $V_{BE}$
The voltage of output= $V_{CE}$
Base current= Input current= $I_B$
Collector current= Output current= $I_C$
Clearly,\[{I_E} = {\text{ }}{I_B} + {\text{ }}{I_C}\]
Among input and output currents and voltages only the input current ($I_B$) and output voltage ($V_{CE}$) can be changed easily according to the need. In CE circuits $I_B$ and $V_{CE}$ should be taken as independent variables and $V_{BE}$ as well as $I_C$ are two dependent functions of them. Out of these$V_{BE}$ has less importance in the analysis of the circuit.
So,${I_C} = f({I_B},{V_{CE}})$.
Complete step by step answer:
The output characteristic is determined keeping $I_B$ at different values and the graphs of $I_C$ with respect to $V_{CE}$. For different values of $I_B$ a series of different output characteristics is obtained and divided into three clear regions as mentioned in the following diagram:
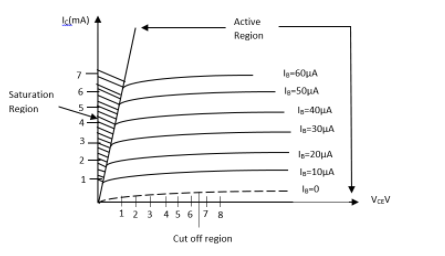
In the active region the base-emitter is forward biased and collector-emitter junction is reversed biased.
In the cut-off region both junctions are reversed biased and in saturation region both base-emitter and base-collector junctions are forward biased as in this region high currents flows as both junctions of the transistor are forward biased and bulk resistance offered is very much less.
So, the correct answer is (D) forward, forward
Note:Transistor in the saturation region is considered as on state in digital logic. Same characteristics can be obtained for the n-p-n transistor of common emitter configuration.

Keeping the emitter grounded, the base is kept forward biased, as n type base of the transistor is connected with a negative pole of source $V_{BE}$. Keeping the emitter grounded, the collector is kept at reverse bias, so the p type collector is connected to the negative pole of $V_{CE}$.
In the figure,
The source voltage of input= $V_{BE}$
The voltage of output= $V_{CE}$
Base current= Input current= $I_B$
Collector current= Output current= $I_C$
Clearly,\[{I_E} = {\text{ }}{I_B} + {\text{ }}{I_C}\]
Among input and output currents and voltages only the input current ($I_B$) and output voltage ($V_{CE}$) can be changed easily according to the need. In CE circuits $I_B$ and $V_{CE}$ should be taken as independent variables and $V_{BE}$ as well as $I_C$ are two dependent functions of them. Out of these$V_{BE}$ has less importance in the analysis of the circuit.
So,${I_C} = f({I_B},{V_{CE}})$.
Complete step by step answer:
The output characteristic is determined keeping $I_B$ at different values and the graphs of $I_C$ with respect to $V_{CE}$. For different values of $I_B$ a series of different output characteristics is obtained and divided into three clear regions as mentioned in the following diagram:

In the active region the base-emitter is forward biased and collector-emitter junction is reversed biased.
In the cut-off region both junctions are reversed biased and in saturation region both base-emitter and base-collector junctions are forward biased as in this region high currents flows as both junctions of the transistor are forward biased and bulk resistance offered is very much less.
So, the correct answer is (D) forward, forward
Note:Transistor in the saturation region is considered as on state in digital logic. Same characteristics can be obtained for the n-p-n transistor of common emitter configuration.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




