
In the reaction
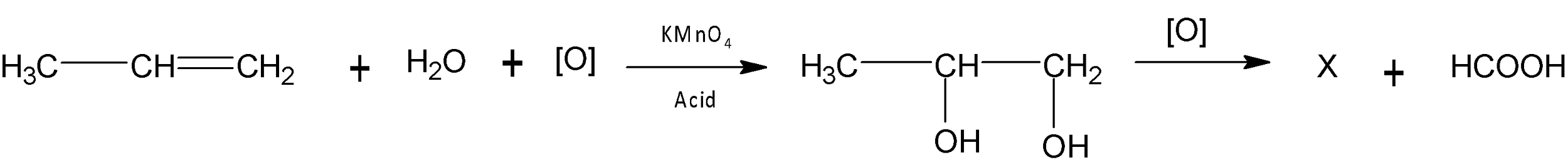
X is
A. $C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}COOH$
B. $C{{H}_{3}}COOH$
C. $C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}CHO$
D. $C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}OH$

Answer
357.3k+ views
Hint: Alkene undergoes oxidation in presence of acidic potassium permanganate ($KMn{{O}_{4}}$) formed vicinal diol or $1,2-diol$. Further oxidation of vicinal diol produces two acids X and formic acid. Here X is formed by oxidative cleavage $1,2-diol$.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Potassium permanganate is a stronger oxidising agent in an acidic medium. In an acidic medium $Mn(VII)$in $MnO_{4}^{-}$is reduced to $Mn(II)$. The half-cell reactions are shown below:
$MnO_{4}^{-}+8{{H}^{+}}+5{{e}^{-}}\to M{{n}^{2+}}+4{{H}_{2}}O$
This oxidative reagent, potassium permanganate, involves oxidative cleavage of vicinal diol and forming aldehyde and ketones depending on the structure of the alcohol. The produced carbonyl compounds undergo further oxidation to give a carboxylic acid derivative.
During oxidative cleavage two things are happening;
a.the hydroxyl group ($-OH$) oxidised to a carbonyl compound.
b.the cleavage of carbon-carbon bonds with oxygen.
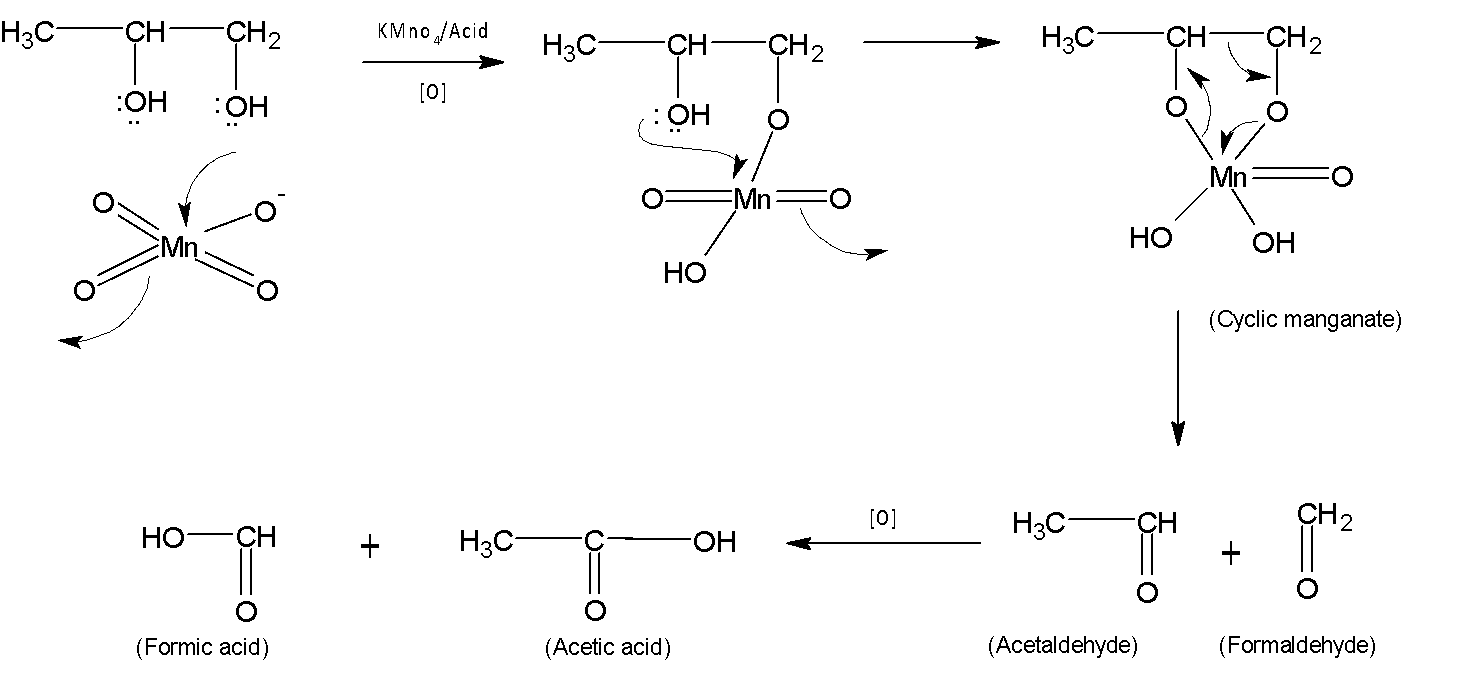
The main pattern of the product is a primary OH group forms formaldehyde, and a secondary and tertiary OH group forms a ketone. Nucleophilic addition of OH groups to the manganese forms cyclic manganate which eventually after protonation steps is broken down into two carbonyl groups and forms carboxylic acid followed by further oxidation.
The mechanism is shown below:
Therefore X is acetic acid, $C{{H}_{3}}COOH$.
Thus, option (B) is correct.
Note: The same mechanism is followed when we use sodium periodate, $NaI{{O}_{4}}$ forming carbonyl compounds. In that case, cyclic iodate is formed and further cleaved in the protonation step and produces carbonyls. The main difference is that for sodium periodate the final product is carbonyl compounds but $KMn{{O}_{4}}$ carbonyls are further oxidised to carboxylic acid.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Potassium permanganate is a stronger oxidising agent in an acidic medium. In an acidic medium $Mn(VII)$in $MnO_{4}^{-}$is reduced to $Mn(II)$. The half-cell reactions are shown below:
$MnO_{4}^{-}+8{{H}^{+}}+5{{e}^{-}}\to M{{n}^{2+}}+4{{H}_{2}}O$
This oxidative reagent, potassium permanganate, involves oxidative cleavage of vicinal diol and forming aldehyde and ketones depending on the structure of the alcohol. The produced carbonyl compounds undergo further oxidation to give a carboxylic acid derivative.
During oxidative cleavage two things are happening;
a.the hydroxyl group ($-OH$) oxidised to a carbonyl compound.
b.the cleavage of carbon-carbon bonds with oxygen.
The main pattern of the product is a primary OH group forms formaldehyde, and a secondary and tertiary OH group forms a ketone. Nucleophilic addition of OH groups to the manganese forms cyclic manganate which eventually after protonation steps is broken down into two carbonyl groups and forms carboxylic acid followed by further oxidation.
The mechanism is shown below:

Therefore X is acetic acid, $C{{H}_{3}}COOH$.
Thus, option (B) is correct.
Note: The same mechanism is followed when we use sodium periodate, $NaI{{O}_{4}}$ forming carbonyl compounds. In that case, cyclic iodate is formed and further cleaved in the protonation step and produces carbonyls. The main difference is that for sodium periodate the final product is carbonyl compounds but $KMn{{O}_{4}}$ carbonyls are further oxidised to carboxylic acid.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell




