
In the reaction
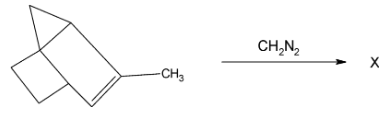
The product X is
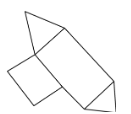
A.
B.
C.
D.





Answer
545.7k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, you must recall the attacking species formed by different reagents and the reaction that they carry out with a given reactant. Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons with $\pi - $ bonds that are susceptible to electrophilic attack.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The reagent given in the following question is $C{H_2} - {N_2}$. The structure of this reagent is as follows:
$N \equiv \mathop N\limits^ + - \mathop {\text{C}}\limits^ - {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$.
The less electronegative carbon atom carries a negative charge while more electronegative nitrogen atom is carrying a positive charge. As a result, the compound is highly unstable and nitrogen tends to withdraw the pair of electrons and depart as a nitrogen molecule.
This leaves behind $\mathop C\limits_{}^{..} {H_2}$. This carbon species carrying a lone pair of electrons as well as a vacant orbital is known as carbene. It can act both as a nucleophile as well as an electrophile.
The electrons in $\pi - $bonds are present above and below the plane of the molecule and thus are like an electron cloud surrounding the bond. This electron cloud attracts electrophiles, thus making alkenes susceptible to electrophilic attack.
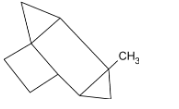
Thus, in this case, the alkene acts as the nucleophile and carbene attacks it as an electrophile. It adds onto the double bond and forms a closed three- membered ring with the methyl group already present.
The product formed as a result of this addition is
The correct answer is A.
Note:A carbene is a neutral carbon atom with a valency of two and two extra valence electrons accompanied by an empty orbital. The two bonds can be formed with any species. In this question, the two bonds were formed by hydrogen atoms and this carbene is known as methylene. Another very commonly used carbene is di- chloro carbene in which the two bonds are formed with chlorine atoms. It is even more reactive due to increased electrophilic character.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The reagent given in the following question is $C{H_2} - {N_2}$. The structure of this reagent is as follows:
$N \equiv \mathop N\limits^ + - \mathop {\text{C}}\limits^ - {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$.
The less electronegative carbon atom carries a negative charge while more electronegative nitrogen atom is carrying a positive charge. As a result, the compound is highly unstable and nitrogen tends to withdraw the pair of electrons and depart as a nitrogen molecule.
This leaves behind $\mathop C\limits_{}^{..} {H_2}$. This carbon species carrying a lone pair of electrons as well as a vacant orbital is known as carbene. It can act both as a nucleophile as well as an electrophile.
The electrons in $\pi - $bonds are present above and below the plane of the molecule and thus are like an electron cloud surrounding the bond. This electron cloud attracts electrophiles, thus making alkenes susceptible to electrophilic attack.
Thus, in this case, the alkene acts as the nucleophile and carbene attacks it as an electrophile. It adds onto the double bond and forms a closed three- membered ring with the methyl group already present.
The product formed as a result of this addition is

The correct answer is A.
Note:A carbene is a neutral carbon atom with a valency of two and two extra valence electrons accompanied by an empty orbital. The two bonds can be formed with any species. In this question, the two bonds were formed by hydrogen atoms and this carbene is known as methylene. Another very commonly used carbene is di- chloro carbene in which the two bonds are formed with chlorine atoms. It is even more reactive due to increased electrophilic character.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




