
In the reaction ${C_2}{H_5}OH \to X$ the molecular formula of X is,
A. ${C_4}{H_6}O$
B. ${C_4}{H_{10}}O$
C. ${C_2}{H_4}O$
D. ${C_2}{H_6}$
Answer
567k+ views
Hint: When alcohol is treated with copper catalyst at ${300^o}C$, then dehydrogenation will take place. There will be removal of hydrogen or oxidation will take place. This reagent is also used for the separation of the primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols.
Step by step answer: Let us see how Copper at ${300^o}C$ will react with different types of alcohol. In the primary alcohol, the carbon connecting to the hydroxyl group will be connected to only one carbon atom. While in case of secondary alcohol, the carbon connecting to the hydroxyl group will be further connected to two more carbon atoms. And in case of tertiary alcohols the carbon connecting to the hydroxyl group, will be further connected to three more carbon atoms.
Primary alcohol-The primary alcohols will react with copper vapours at ${300^o}C$ to form corresponding aldehyde.
Secondary alcohol-The secondary alcohol will react with copper vapours at ${300^o}C$ to form corresponding ketone.
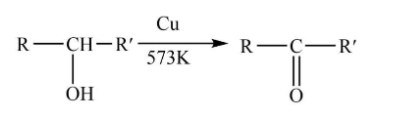
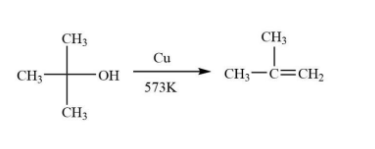
Tertiary alcohol-The tertiary alcohol will react with copper vapours at ${300^o}C$ to undergo dehydrogenation and corresponding alkene will be formed.
The given alcohol given is an example of primary alcohols named as Ethanol which reacts with vapours of copper to form corresponding aldehydes named Acetaldehyde.
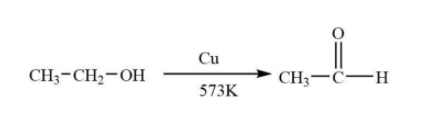
The molecular formula of Acetaldehyde is ${C_2}{H_4}O$.
Hence, option (C) ${C_2}{H_4}O$, is the correct option.
Note: There are various different reagents used for the oxidation of alcohols’ for example potassium dichromate, Collins reagent$Cr{O_3}$,Pyridinium chlorochromate, Dess Martin reagent, Dimethyl Sulphoxide (Swern Oxidation), Jones reagent aluminium isopropoxide/acetone (Oppenauer oxidation).
Step by step answer: Let us see how Copper at ${300^o}C$ will react with different types of alcohol. In the primary alcohol, the carbon connecting to the hydroxyl group will be connected to only one carbon atom. While in case of secondary alcohol, the carbon connecting to the hydroxyl group will be further connected to two more carbon atoms. And in case of tertiary alcohols the carbon connecting to the hydroxyl group, will be further connected to three more carbon atoms.
Primary alcohol-The primary alcohols will react with copper vapours at ${300^o}C$ to form corresponding aldehyde.
Secondary alcohol-The secondary alcohol will react with copper vapours at ${300^o}C$ to form corresponding ketone.

Tertiary alcohol-The tertiary alcohol will react with copper vapours at ${300^o}C$ to undergo dehydrogenation and corresponding alkene will be formed.

The given alcohol given is an example of primary alcohols named as Ethanol which reacts with vapours of copper to form corresponding aldehydes named Acetaldehyde.

The molecular formula of Acetaldehyde is ${C_2}{H_4}O$.
Hence, option (C) ${C_2}{H_4}O$, is the correct option.
Note: There are various different reagents used for the oxidation of alcohols’ for example potassium dichromate, Collins reagent$Cr{O_3}$,Pyridinium chlorochromate, Dess Martin reagent, Dimethyl Sulphoxide (Swern Oxidation), Jones reagent aluminium isopropoxide/acetone (Oppenauer oxidation).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




