
In the reaction between phenol and bromine water, the equivalent weight of phenol is obtained by dividing the molecular weight of phenol by:
(A). $3$
(B). $4$
(C). $5$
(D). $6$
Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint:
Equivalent weight is defined as the molecular mass of substance divided by its Acidity / Basicity / valency / No. of gram equivalents. The equivalent weight of an element is the mass which combines with or displaces $1.008$ gram of hydrogen or $8.0$ grams of oxygen or $35.5$ grams of chlorine.
Complete step by step answer:
First of all we have to understand the equivalent weight of an element. The weight of an element is the mass which displaces or reacts with $1$ gram of hydrogen, $8$ grams of oxygen and $35.5$ grams of chlorine. Equivalent weight and molecular weight both are different things. Molecular weight both are different things. Molecular mass of a substance is the average relative mass of its molecule as compared with an atom of carbon$ - 12$ isotope. Molecular mass can be calculated by adding the atomic masses of all the atoms present in one molecule of the substance.
For e.g. molecular mass of ${H_2}S{O_4} = 2 \times $ Atomic mass of $S$
OR = $2 \times 1 + 32 + 4 \times 16 = 98.0\mu $
Whereas equivalent weights are calculated in various methods. Equivalent weight of acid can be calculated as molecular mass of acid divided by basicity. Here basicity is the number of replaceable ${H^ + }$ ions present in an acid.
Mathematically we can write equivalent weight of acid or $\dfrac{{MolecularWeight}}{{Basicity.}}$
Equivalent Weight of base can be calculated as Molecular Mass of base divided by acidity of base. Here acidity is the number of replaceable $O{H^ - }$ ions present in a base.
Mathematically we can write it as
$ = \dfrac{{Molecular{\text{ }}weight}}{{Acidity.}}$
Equivalent weight of salt can be calculated as Molecular Mass of salt divided by valency or charge on the salt
Or mathematically it is $\dfrac{{Molecular{\text{ weight }}}}{{valency}}$
Now we have to calculate the equivalent weight of phenol.
The Reaction of phenol with bromine water takes place as follow:-
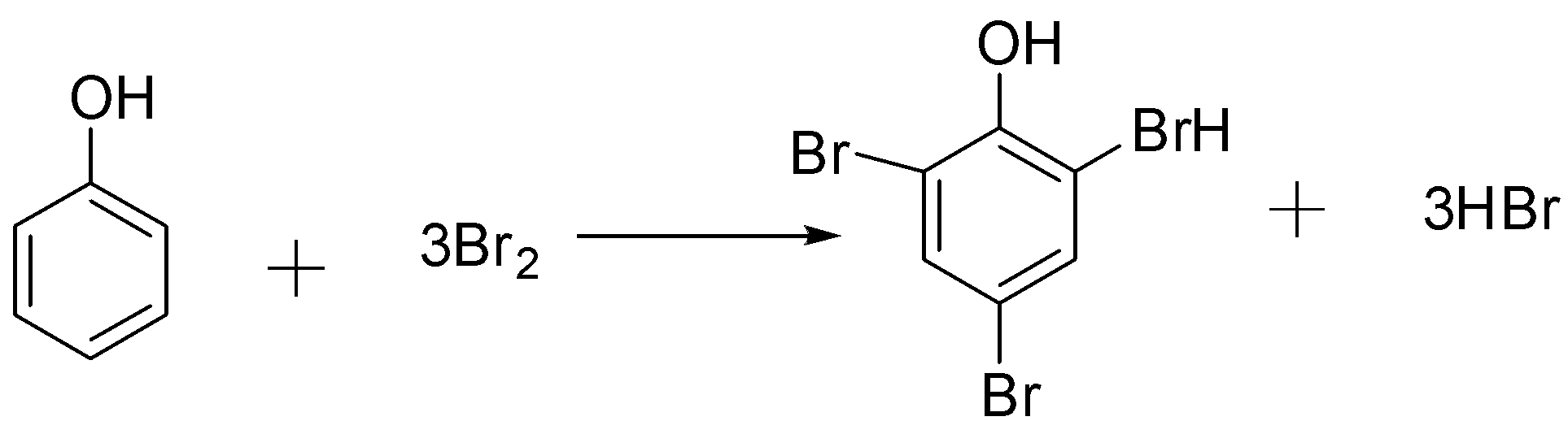
From the above equation, we got to know that one mole of phenol reacts with $3$ molecules of Bromine. This means that one mole of phenol reacts with $3 \times 2 = 6$ equivalents of mass of Bromine.
This in order to phenol, its molecular option (D) is the correct answer.
Note: The phenol contains one $O{H^ - }$ group but we didn’t divide molecular mass of phenol with $1$ because $B{r_2}$ did not replace $OH$ in this reaction. Only $6$ hydrogen atoms are replaceable. Hence we divide its molecular mass with $6$.
Equivalent weight is defined as the molecular mass of substance divided by its Acidity / Basicity / valency / No. of gram equivalents. The equivalent weight of an element is the mass which combines with or displaces $1.008$ gram of hydrogen or $8.0$ grams of oxygen or $35.5$ grams of chlorine.
Complete step by step answer:
First of all we have to understand the equivalent weight of an element. The weight of an element is the mass which displaces or reacts with $1$ gram of hydrogen, $8$ grams of oxygen and $35.5$ grams of chlorine. Equivalent weight and molecular weight both are different things. Molecular weight both are different things. Molecular mass of a substance is the average relative mass of its molecule as compared with an atom of carbon$ - 12$ isotope. Molecular mass can be calculated by adding the atomic masses of all the atoms present in one molecule of the substance.
For e.g. molecular mass of ${H_2}S{O_4} = 2 \times $ Atomic mass of $S$
OR = $2 \times 1 + 32 + 4 \times 16 = 98.0\mu $
Whereas equivalent weights are calculated in various methods. Equivalent weight of acid can be calculated as molecular mass of acid divided by basicity. Here basicity is the number of replaceable ${H^ + }$ ions present in an acid.
Mathematically we can write equivalent weight of acid or $\dfrac{{MolecularWeight}}{{Basicity.}}$
Equivalent Weight of base can be calculated as Molecular Mass of base divided by acidity of base. Here acidity is the number of replaceable $O{H^ - }$ ions present in a base.
Mathematically we can write it as
$ = \dfrac{{Molecular{\text{ }}weight}}{{Acidity.}}$
Equivalent weight of salt can be calculated as Molecular Mass of salt divided by valency or charge on the salt
Or mathematically it is $\dfrac{{Molecular{\text{ weight }}}}{{valency}}$
Now we have to calculate the equivalent weight of phenol.
The Reaction of phenol with bromine water takes place as follow:-

From the above equation, we got to know that one mole of phenol reacts with $3$ molecules of Bromine. This means that one mole of phenol reacts with $3 \times 2 = 6$ equivalents of mass of Bromine.
This in order to phenol, its molecular option (D) is the correct answer.
Note: The phenol contains one $O{H^ - }$ group but we didn’t divide molecular mass of phenol with $1$ because $B{r_2}$ did not replace $OH$ in this reaction. Only $6$ hydrogen atoms are replaceable. Hence we divide its molecular mass with $6$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




