
In the preparation of chlorine from $HCl$ , $Mn{{O}_{2}}$ acts as
(A) Oxidising agent
(B) Reducing agent
(C) Catalytic agent
(D) Dehydrating agent
Answer
373.5k+ views
Hint: In a redox reaction, the element that gains an electron is known as an oxidising agent, and the element that loses an electron is known as a reducing agent. A catalytic agent, also known as a catalyst, is a substance that does not itself take part in the chemical reaction; it just increases the rate of the chemical reaction. A dehydrating agent is a substance that removes water from a material.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
In the preparation of chlorine from $HCl$, $Mn{{O}_{2}}$, in which $Mn$ is in a +4 oxidation state gets converted to $MnC{{l}_{2}}$ , in which it is in a +2 oxidation state. This means the oxidation number is decreased and reduction is occurring. Thus, $Mn{{O}_{2}}$ acts as an oxidising agent.
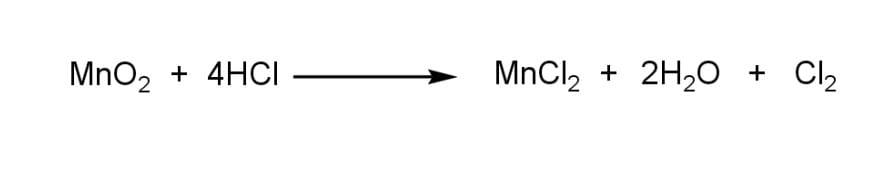
Here, manganese dioxide ($Mn{{O}_{2}}$) reacts with hydrochloric acid ($HCl$) to give manganese chloride ($MnC{{l}_{2}}$), water (${{H}_{2}}O$), and chlorine ($C{{l}_{2}}$).
Correct Option: (A) Oxidising agent.
Additional Information: Manganese dioxide ($Mn{{O}_{2}}$) is used in dry battery cells and to remove the green tint caused by iron impurities. Manganese reacts with oxygen in the atmosphere and forms manganese dioxide. This is the reason why manganese does not exist in its elemental form in nature. It is insoluble in water.
Note: Manganese dioxide ($Mn{{O}_{2}}$) can act as both an oxidising and a reducing agent. It can oxidise alcohols to aldehydes or ketones. It exists in a +4 oxidation state. $Mn{{O}_{2}}$ is black or brown in colour. It crystallises in a rutile crystal structure.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
In the preparation of chlorine from $HCl$, $Mn{{O}_{2}}$, in which $Mn$ is in a +4 oxidation state gets converted to $MnC{{l}_{2}}$ , in which it is in a +2 oxidation state. This means the oxidation number is decreased and reduction is occurring. Thus, $Mn{{O}_{2}}$ acts as an oxidising agent.

Here, manganese dioxide ($Mn{{O}_{2}}$) reacts with hydrochloric acid ($HCl$) to give manganese chloride ($MnC{{l}_{2}}$), water (${{H}_{2}}O$), and chlorine ($C{{l}_{2}}$).
Correct Option: (A) Oxidising agent.
Additional Information: Manganese dioxide ($Mn{{O}_{2}}$) is used in dry battery cells and to remove the green tint caused by iron impurities. Manganese reacts with oxygen in the atmosphere and forms manganese dioxide. This is the reason why manganese does not exist in its elemental form in nature. It is insoluble in water.
Note: Manganese dioxide ($Mn{{O}_{2}}$) can act as both an oxidising and a reducing agent. It can oxidise alcohols to aldehydes or ketones. It exists in a +4 oxidation state. $Mn{{O}_{2}}$ is black or brown in colour. It crystallises in a rutile crystal structure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell




